一、缓存总览
Mybatis在设计上处处都有用到的缓存,而且Mybatis的缓存体系设计上遵循单一职责、开闭原则、高度解耦。及其精巧,充分的将缓存分层,其独到之处可以套用到很多类似的业务上。这里将主要的缓存体系做一下简单的分析笔记。以及借助Mybatis缓存体系的学习,进一步窥探责任链派发模式企业级实践,以及对象循环依赖场景下如何避免装载死循环的企业级解决方案。
先来一张之前的执行体系图:

对照这张执行图,不难看出,其实对于一次Mybatis查询调用,即SqlSession -> SimpleExecutor/ReuseExecutor/BatchExecutor -> JDBC,其实缓存就是在SqlSession到Executor*之间做一层截获请求的逻辑。从宏观上很好理解。CachingExecutor作为BaseExecutor的一个前置增强装饰器,其增强的功能就是,判断是否命中了缓存,如果命中缓存,则不进行BaseExecutor的执行派发。
1 public class CachingExecutor implements Executor { 2 // BaseExecutor 3 private final Executor delegate; 4 public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) { 5 this.delegate = delegate; 6 delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this); 7 } 8 @Override 9 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) 10 throws SQLException { 11 Cache cache = ms.getCache(); 12 if (cache != null) { 13 flushCacheIfRequired(ms); 14 if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) { 15 ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql); 16 List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key); 17 if (list == null) { 18 list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); 19 tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116 20 } 21 return list; 22 } 23 } 24 // 如果未命中缓存则向BaseExecutor派发 25 return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); 26 } 27 }
所以由此来看,mybatis的缓存是先尝试命中CachingExecutor的二级缓存,如果未命中,则派发个BaseExecutor,下来才会去尝试命中一级缓存。由于一级缓存比较简单,我们先来看一级缓存。
二、一级缓存概览
之前执行器的那一节讲过,Mybatis的执行器和SqlSession都是一对一的关系
1 public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession { 2 // ... 3 private final Executor executor; 4 // ... 5 }
而每个执行器里边用一个成员变量来做缓存容器
1 public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor { 2 // ... 3 protected PerpetualCache localCache; 4 // ... 5 }
那么也就是说,一旦SqlSession关闭,即对象销毁,必然BaseExecutor对象销毁,所以一级缓存容器跟着销毁。由此可以推到出:一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存。也就是要命中一级缓存,必须是同一个SqlSession,而且未关闭。
再来看一下一级缓存是如何设置缓存的:
1 public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor { 2 protected PerpetualCache localCache; 3 @Override 4 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { 5 BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter); 6 CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql); 7 return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); 8 } 9 @Override 10 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { 11 ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); 12 if (closed) { 13 throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); 14 } 15 if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { 16 clearLocalCache(); 17 } 18 List<E> list; 19 try { 20 queryStack++; 21 list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; 22 if (list != null) { 23 handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); 24 } else { 25 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); 26 } 27 } finally { 28 queryStack--; 29 } 30 if (queryStack == 0) { 31 for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { 32 deferredLoad.load(); 33 } 34 // issue #601 35 deferredLoads.clear(); 36 if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { 37 // issue #482 38 clearLocalCache(); 39 } 40 } 41 return list; 42 } 43 }
通过这一段源码,可以看到,是在第6行去构建缓存key,在第21行尝试获取缓存。构建缓存key,取决于四个维度:MappedStatement(同一个statementId)、parameter(同样的查询参数)、RowBounds(同样的行数)、BoundsSql(同样的SQL),加上上边SqlSession的条件,一级缓存的命中条件为:相同的SqlSession、statementId、parameter、行数、Sql,才能命中一级缓存。
这里在说一句题外话,就是当mybatis与Spring集成时,SqlSession的管理就交给Spring框架了,每次Mybatis的查询都会由Spring框架新建一个Sqlsession供mybatis用,看起来一级缓存永远失效。解决办法就是给查询加上事务,当加上事务的时候,Spring框架会保证在一个事务里边只提供给mybatis同一个SqlSession对象。
再看下一级缓存何时会被刷新掉,来上源码:
1 public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor { 2 protected PerpetualCache localCache; 3 @Override 4 public void close(boolean forceRollback) { 5 try { 6 try { 7 rollback(forceRollback); 8 } finally { 9 if (transaction != null) { 10 transaction.close(); 11 } 12 } 13 } catch (SQLException e) { 14 log.warn("Unexpected exception on closing transaction. Cause: " + e); 15 } finally { 16 transaction = null; 17 deferredLoads = null; 18 localCache = null; 19 localOutputParameterCache = null; 20 closed = true; 21 } 22 } 23 @Override 24 public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { 25 ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId()); 26 if (closed) { 27 throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); 28 } 29 clearLocalCache(); 30 return doUpdate(ms, parameter); 31 } 32 @Override 33 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { 34 if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { 35 clearLocalCache(); 36 } 37 if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { 38 clearLocalCache(); 39 } 40 } 41 @Override 42 public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException { 43 clearLocalCache(); 44 } 45 46 @Override 47 public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException { 48 if (!closed) { 49 try { 50 clearLocalCache(); 51 flushStatements(true); 52 } finally { 53 if (required) { 54 transaction.rollback(); 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 60 @Override 61 public void clearLocalCache() { 62 if (!closed) { 63 localCache.clear(); 64 localOutputParameterCache.clear(); 65 } 66 }
对于这段源码,清除缓存的场景,着重关注一下clearLocalCache的调用的地方:
即触发更新操作(第29行)、配置flushCache=true(第35行)、配置缓存作用于为STATEMENT(第38行)、commit时候(第42行)、rollback时候(第50行)、执行器关闭时候(第7行)都会清除一级缓存。
三、一级缓存对于嵌套子查询循环依赖场景的解决方案
循环依赖的情况处处可见,比如:一个班主任,下边有多个学生,每个学生又有一个对应的班主任。
对于班主任和学生这种场景,在mybatis层面属于典型的嵌套子查询。mybatis在处理嵌套查询的时候,都会查询,然后在设置属性的时候,如果发现有子查询,则发起子查询。那么,如果不加特殊干预,这种场景将会陷入设置属性触发查询的死循环中。
1 <select id="selectHeadmasterById" resultMap="teacherMap"> 2 select * from teacher where id = #{id} 3 </select> 4 <resultMap id="teacherMap" type="Teacher" autoMapping="true"> 5 <result column="name" property="name"/> 6 <collection property="students" column="id" select="selectStudentsByTeacherId" fetchType="eager"/> 7 </resultMap> 8 <select id="selectStudentsByTeacherId" resultMap="studentMap"> 9 select * from student where teacher_id = #{teacherId} 10 </select> 11 <resultMap id="studentMap" type="comment"> 12 <association property="teacher" column="teacher_id" select="selectHeadmasterById" fetchType="eager"/> 13 </resultMap>
mybatis在处理这种情况的时候,巧妙的用了一个临时一级缓存占位符与延迟装载(不同于懒加载),解决了查询死循环的问题。这里我们直接上源码:
每次查询,如果没有命中有效缓存(即非占位符缓存)mybatis都会事先给一级缓存写入一个占位符,待数据库查询完毕后,再将真正的数据覆盖掉占位符缓存。
1 public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor { 2 protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad> deferredLoads; 3 protected PerpetualCache localCache; 4 protected int queryStack; 5 @Override 6 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { 7 ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); 8 if (closed) { 9 throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); 10 } 11 if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { 12 clearLocalCache(); 13 } 14 List<E> list; 15 try { 16 queryStack++; 17 list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; 18 if (list != null) { 19 handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); 20 } else { 21 // 如果未获取到缓存则查库 22 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); 23 } 24 } finally { 25 queryStack--; 26 } 27 if (queryStack == 0) { 28 for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { 29 deferredLoad.load(); 30 } 31 deferredLoads.clear(); 32 if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { 33 clearLocalCache(); 34 } 35 } 36 return list; 37 } 38 }
如上Query方法的第22行进去:
1 private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { 2 List<E> list; 3 // 查库之前先设置占位符缓存 4 localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); 5 try { 6 list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); 7 } finally { 8 localCache.removeObject(key); 9 } 10 localCache.putObject(key, list); 11 if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { 12 localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); 13 } 14 return list; 15 }
BaseExecutor.queryFromDataBase方法的第6行,会触发数据库查询,紧接着会进入结果值设定的逻辑。那么首先会探测有无嵌套的子查询,如果有,则前一步主查询暂时等待,立即发起子查询。
1 private Object getNestedQueryMappingValue(ResultSet rs, MetaObject metaResultObject, ResultMapping propertyMapping, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix) 2 throws SQLException { 3 final String nestedQueryId = propertyMapping.getNestedQueryId(); 4 final String property = propertyMapping.getProperty(); 5 final MappedStatement nestedQuery = configuration.getMappedStatement(nestedQueryId); 6 final Class<?> nestedQueryParameterType = nestedQuery.getParameterMap().getType(); 7 final Object nestedQueryParameterObject = prepareParameterForNestedQuery(rs, propertyMapping, nestedQueryParameterType, columnPrefix); 8 Object value = null; 9 if (nestedQueryParameterObject != null) { 10 final BoundSql nestedBoundSql = nestedQuery.getBoundSql(nestedQueryParameterObject); 11 final CacheKey key = executor.createCacheKey(nestedQuery, nestedQueryParameterObject, RowBounds.DEFAULT, nestedBoundSql); 12 final Class<?> targetType = propertyMapping.getJavaType(); 13 // 判断当前的子查询是否和之前的某一步主查询相同 14 if (executor.isCached(nestedQuery, key)) { 15 executor.deferLoad(nestedQuery, metaResultObject, property, key, targetType); 16 value = DEFERRED; 17 } else { 18 final ResultLoader resultLoader = new ResultLoader(configuration, executor, nestedQuery, nestedQueryParameterObject, targetType, key, nestedBoundSql); 19 if (propertyMapping.isLazy()) { 20 lazyLoader.addLoader(property, metaResultObject, resultLoader); 21 value = DEFERRED; 22 } else { 23 // 立即发起子查询 24 value = resultLoader.loadResult(); 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 return value; 29 }
这块重点关注第13行和第23行。其中第23行又会递归到上边BaseExecutor.query代码片段的第22行。如果getNestedQueryMappingValue代码段走的是滴15行逻辑,那么,会对应BaseExecutor.query代码片段的第28行。这块递归比较绕。下来做下通俗的解释:
首先查询班主任的主查询给一级缓存写入一个占位符缓存,然后去查库,然后设定属性,如果没有嵌套子查询,那么到这里就把设置好属性的值写入覆盖刚才一级占位符缓存。流畅完毕。
但是恰好有嵌套子查询,所以查询班主任的主查询就停在设置属性这一步,然后又发起一次查询,查询学生,然后又进入查询学生设定属性的方法。
设定学生属性方法又发现又有嵌套子查询,所以有发起一次学生查询班主任的查询操作,又进入到设定属性这块,但是发现一级缓存里边有前边住查询的站位缓存。所以没有在查库,而是将本次子查询放入延迟装载的容器里边。本次子查询结束。紧接着前一步子查询(老师查学生)结束。
紧接着查询老师的住查询设定属性完毕,并将自己的结果覆盖之前写入的站位缓存。同时启动了延时装载的逻辑,延时装载就是从一级缓存取出刚才查询老师的一级缓存数据(老师),给第二步子查询(学生)做一下MetaObject属性设置。
说的通俗一点:主查询(查班主任)执行时先写入站位缓存,紧接着挂起,发起第一个嵌套子查询(用老师查学生),紧接着该子查询再挂起,发起学生查老师,但是发现第一步主查询有一级缓存(站位缓存),那么本次子查询自动加入延迟装载队列,然后终结改子查询,等待主查询真正查完,然后延迟装载器再从缓存取出数据给第一个子查询(老师查学生)进行属性设定。
说了这么多,肯定晕车了,这里给出一个时序图:
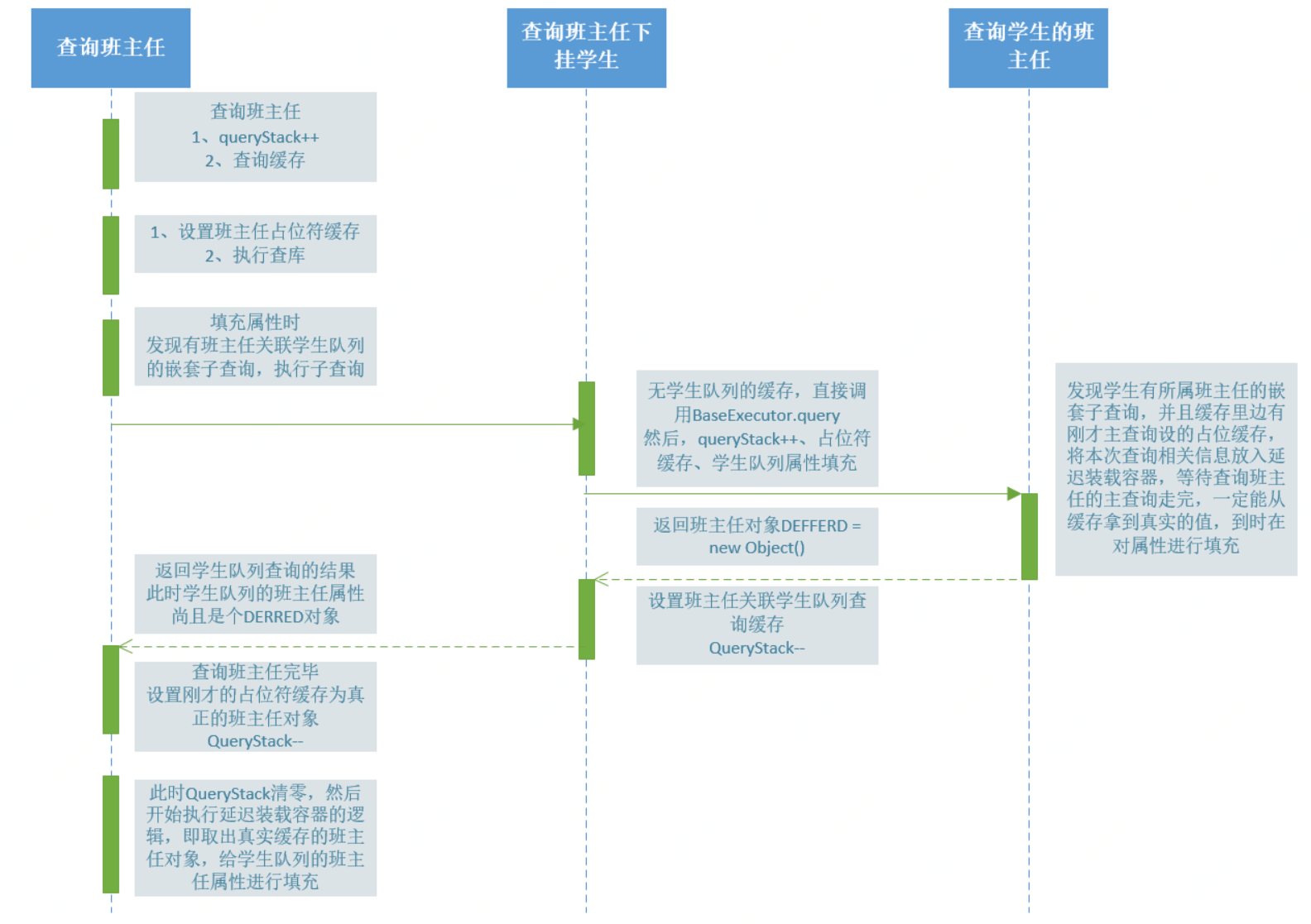
总结一下:
1、占位符缓存作用在于标识与当前查询相同的前边的嵌套查询。比如:查询学生所属班主任,发现前边的主查询就是查询班主任,所以就不在执行班主任查询。等待真正的班主任查询完毕,我们只需去缓存里边取即可。所以我们不执行查询,只是将本次属性设置放入延迟装载队列即可。
2、queryStack用来记录当前查询处于嵌套的第几层。当queryStack == 0时,证明整个查询已经回归到最初的主查询上,此时,所有过程中需要延迟装载的对象,都能启动真实装载了。
3、一级缓存在解决嵌套子查询属性设置循环依赖上启至关作用。所以以及缓存是不能完全关闭的。但是我们可以设置:LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT,来让一级缓存及时清空。参见源码
1 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { 2 // ... 3 try { 4 queryStack++; 5 list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; 6 if (list != null) { 7 handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); 8 } else { 9 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); 10 } 11 } finally { 12 queryStack--; 13 } 14 if (queryStack == 0) { 15 for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { 16 deferredLoad.load(); 17 } 18 deferredLoads.clear(); 19 // 设置LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT来及时清空缓存 20 if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { 21 clearLocalCache(); 22 } 23 } 24 return list; 25 }
四、二级缓存
来先上一个二级缓存的执行流程:

二级缓存是BaseExecutor的前置增强包装类CachingExecutor里边实现的,即如果从CachingExecutor里边命中缓存,则不进行BaseExecutor的派发(如下第14行)。
1 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) 2 throws SQLException { 3 Cache cache = ms.getCache(); 4 if (cache != null) { 5 flushCacheIfRequired(ms); 6 if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) { 7 ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql); 8 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 9 List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key); 10 if (list == null) { 11 list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); 12 tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116 13 } 14 return list; 15 } 16 } 17 return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); 18 }
11行与17行的区别在于,是否启动二级缓存,如果启动了,则将派发给BaseExecutor的查询结果写入暂存区(第12行,TransactionCacheManager),等事务提交在真正刷入二级缓存。下来我们重点来关注一下缓存的读写(第9行、第12行),这里边真正的执行对象是一系列Cache接口的实现,按职责有:线程安全、日志记录、过期清理、溢出淘汰、序列化、执行存储等等环节。而二级缓存的设计精巧之处就在于此处,完美的按职责进行责任派发,完全解耦。
接下来我们来看下,默认情况下,缓存责任链的初始化过程:
1 public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass, 2 Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass, 3 Long flushInterval, 4 Integer size, 5 boolean readWrite, 6 boolean blocking, 7 Properties props) { 8 Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace) 9 // 这里设置默认的存储为内存 10 .implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class)) 11 // 这里设置默认的溢出淘汰为LRU 12 .addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class)) 13 .clearInterval(flushInterval) 14 .size(size) 15 .readWrite(readWrite) 16 .blocking(blocking) 17 .properties(props) 18 .build(); 19 configuration.addCache(cache); 20 currentCache = cache; 21 return cache; 22 }
然后是初始化过程:
1 public Cache build() { 2 setDefaultImplementations(); 3 Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id); 4 setCacheProperties(cache); 5 // issue #352, do not apply decorators to custom caches 6 if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) { 7 for (Class<? extends Cache> decorator : decorators) { 8 cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache); 9 setCacheProperties(cache); 10 } 11 cache = setStandardDecorators(cache); 12 } else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) { 13 cache = new LoggingCache(cache); 14 } 15 return cache; 16 } 17 private Cache setStandardDecorators(Cache cache) { 18 try { 19 MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache); 20 if (size != null && metaCache.hasSetter("size")) { 21 metaCache.setValue("size", size); 22 } 23 if (clearInterval != null) { 24 cache = new ScheduledCache(cache); 25 ((ScheduledCache) cache).setClearInterval(clearInterval); 26 } 27 if (readWrite) { 28 cache = new SerializedCache(cache); 29 } 30 cache = new LoggingCache(cache); 31 cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache); 32 if (blocking) { 33 cache = new BlockingCache(cache); 34 } 35 return cache; 36 } catch (Exception e) { 37 throw new CacheException("Error building standard cache decorators. Cause: " + e, e); 38 } 39 }
这里从第3、8、24、28、30、31、33行分别进行了责任装饰初始化。这种依据职责分别拆分然后嵌套的解耦方式,其实是一种很成熟的企业级责任派发设计模式。而且形如第8行的循环装饰嵌套,在很多开源框架中都能见到,比如Dubbo的AOP机制就是这样初始化的。
下边直接列一下Mybatis的二级缓存在设计上所覆盖的功能,以及各功能责任链派发的结构图:
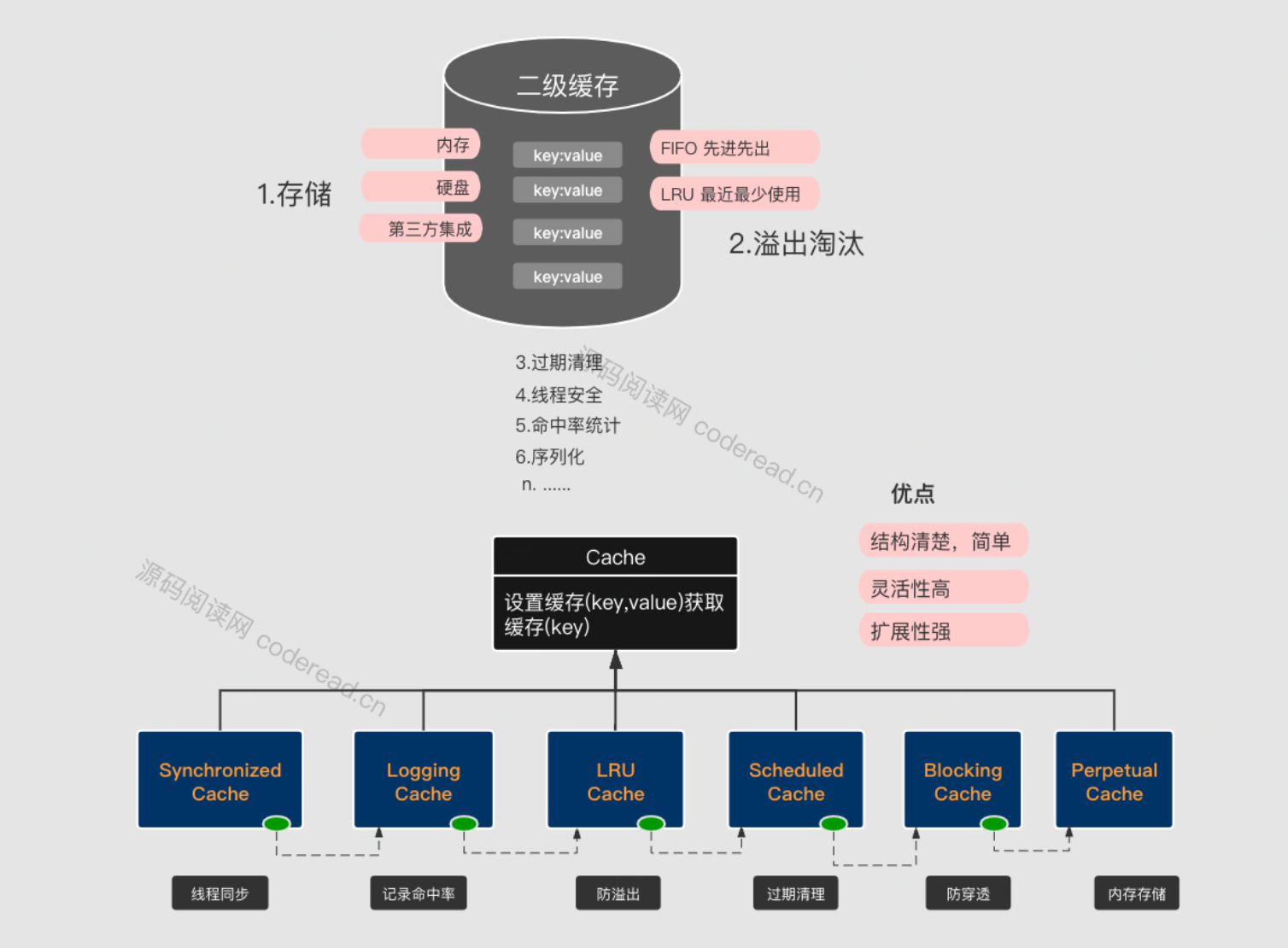
从上边的代码可以看出,如果设置了blocking的话,那么最外层将会包裹BlockingCache、下来是SynchronizedCache,这两个均是进行线程安全,防止缓存穿透的处理。
1 public class BlockingCache implements Cache { 2 private final Cache delegate; 3 private final ConcurrentHashMap<Object, ReentrantLock> locks; 4 public BlockingCache(Cache delegate) { 5 this.delegate = delegate; 6 this.locks = new ConcurrentHashMap<Object, ReentrantLock>(); 7 } 8 @Override 9 public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { 10 try { 11 delegate.putObject(key, value); 12 } finally { 13 releaseLock(key); 14 } 15 } 16 @Override 17 public Object getObject(Object key) { 18 acquireLock(key); 19 Object value = delegate.getObject(key); 20 if (value != null) { 21 releaseLock(key); 22 } 23 return value; 24 } 25 }
1 public class SynchronizedCache implements Cache { 2 private Cache delegate; 3 @Override 4 public synchronized void putObject(Object key, Object object) { 5 delegate.putObject(key, object); 6 } 7 @Override 8 public synchronized Object getObject(Object key) { 9 return delegate.getObject(key); 10 } 11 }
再看一下负责溢出淘汰的LruCache:
1 public class LruCache implements Cache { 2 private final Cache delegate; 3 private Map<Object, Object> keyMap; 4 // 记录当溢出时,需要淘汰的Key 5 private Object eldestKey; 6 public void setSize(final int size) { 7 // LinkedHashMap.accessOrder设置为true,即,每个被访问的元素会一次放到队列末尾。当溢出的时候就能从首部来移除了 8 keyMap = new LinkedHashMap<Object, Object>(size, .75F, true) { 9 @Override 10 protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Object, Object> eldest) { 11 boolean tooBig = size() > size; 12 if (tooBig) { 13 eldestKey = eldest.getKey(); 14 } 15 return tooBig; 16 } 17 }; 18 } 19 @Override 20 public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { 21 delegate.putObject(key, value); 22 cycleKeyList(key); 23 } 24 private void cycleKeyList(Object key) { 25 keyMap.put(key, key); 26 if (eldestKey != null) { 27 delegate.removeObject(eldestKey); 28 eldestKey = null; 29 } 30 } 31 }
二级缓存就讲到这里,总结一下二级缓存件:
1、默认开启,cachEnable开关。作用于提交后。
2、相同的StatementId。
3、相同的SQL、参数、行数。
4、跨Mapper调用。
五、总结
虽然在目前各种分布式应用的场景下,一级缓存和二级缓存都有很大概率的脏读现象,而被禁止,但是Mybatis对这种局部场景的设计是及其精巧的。比如,解决对象循环嵌套查询的场景设计,其实这种成熟的解决方案也被Spring(也存在对象循环注入的情景)所应用。以及责任装饰的设计,Dubbo同样在使用。其实我们能从得到很多启发,比如,对于既定的业务场景,要加入现成安全的考量,那在不侵入业务代码的前提下,我们是否也能增加一层责任装饰,进行派发来完成呢?