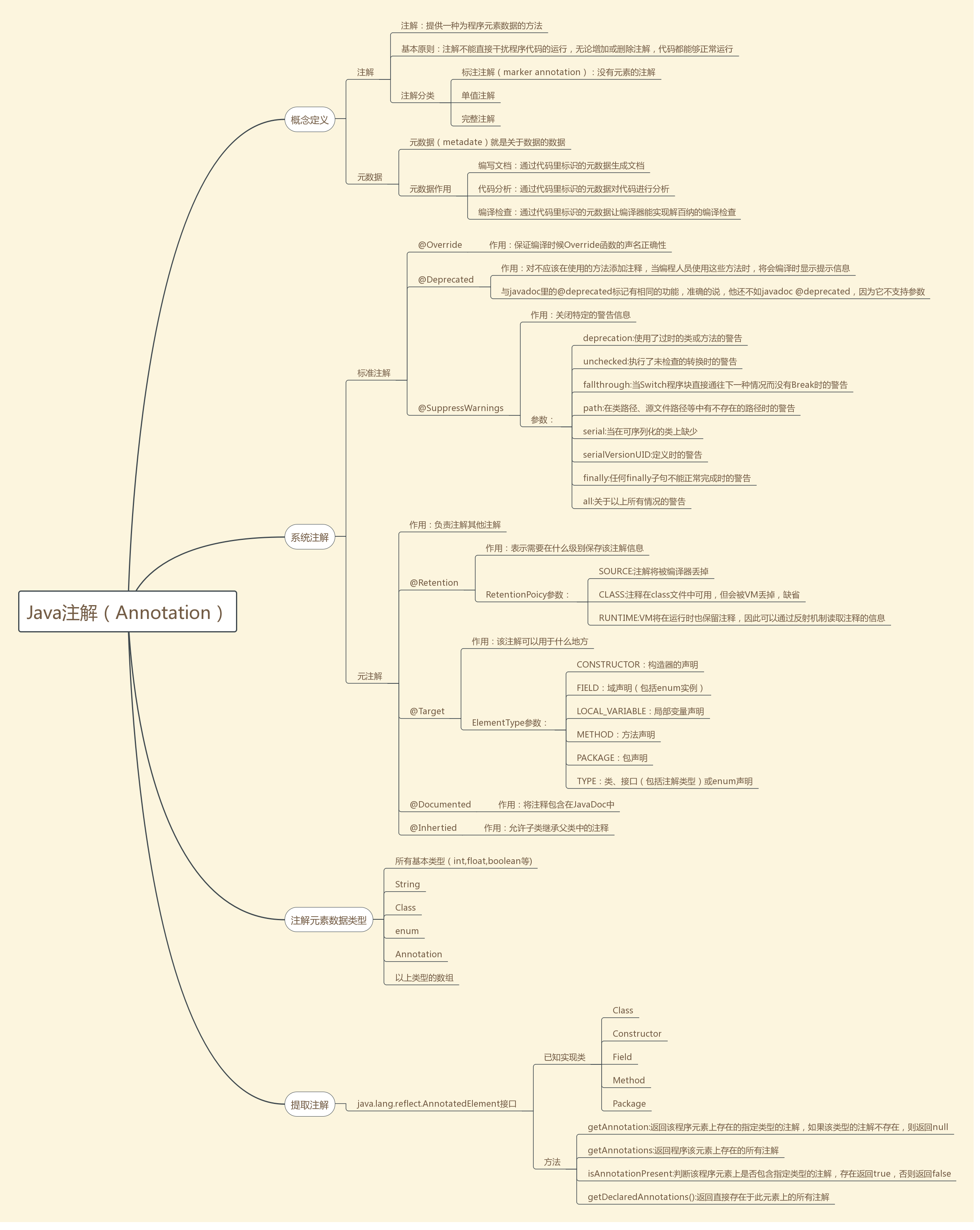
注解
概念及作用
- 概念
- 注解即元数据,就是源代码的元数据
- 注解在代码中添加信息提供了一种形式化的方法,可以在后续中更方便的 使用这些数据
- Annotation是一种应用于类、方法、参数、变量、构造器及包声明中的特殊修饰符。它是一种由JSR-175标准选择用来描述元数据的一种工具。
- 作用
- 生成文档
- 跟踪代码依赖性,实现替代配置文件功能,减少配置。如Spring中的一些注解
- 在编译时进行格式检查,如@Override等
- 每当你创建描述符性质的类或者接口时,一旦其中包含重复性的工作,就可以考虑使用注解来简化与自动化该过程。
什么是java注解?
在java语法中,使用@符号作为开头,并在@后面紧跟注解名。被运用于类,接口,方法和字段之上,例如:
@Override
void myMethod() {
......
}
这其中@Override就是注解。这个注解的作用也就是告诉编译器,myMethod()方法覆写了父类中的myMethod()方法。
java中内置的注解
java中有三个内置的注解:
-
@Override:表示当前的方法定义将覆盖超类中的方法,如果出现错误,编译器就会报错。
-
@Deprecated:如果使用此注解,编译器会出现警告信息。
-
@SuppressWarnings:忽略编译器的警告信息。
本文不在阐述三种内置注解的使用情节和方法,感兴趣的请看这里
元注解
自定义注解的时候用到的,也就是自定义注解的注解;(这句话我自己说的,不知道对不对)
元注解的作用就是负责注解其他注解。Java5.0定义了4个标准的meta-annotation类型,它们被用来提供对其它 annotation类型作说明。
Java5.0定义的4个元注解:
- @Target
- @Retention
- @Documented
- @Inherited
java8加了两个新注解,后续我会讲到。
这些类型和它们所支持的类在java.lang.annotation包中可以找到。
@Target
@Target说明了Annotation所修饰的对象范围:Annotation可被用于 packages、types(类、接口、枚举、Annotation类型)、类型成员(方法、构造方法、成员变量、枚举值)、方法参数和本地变量(如循环变量、catch参数)。在Annotation类型的声明中使用了target可更加明晰其修饰的目标。
作用:用于描述注解的使用范围(即:被描述的注解可以用在什么地方)
取值(ElementType)有:
| 类型 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| CONSTRUCTOR | 用于描述构造器 |
| FIELD | 用于描述域 |
| LOCAL_VARIABLE | 用于描述局部变量 |
| METHOD | 用于描述方法 |
| PACKAGE | 用于描述包 |
| PARAMETER | 用于描述参数 |
| TYPE | 用于描述类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum声明 |
比如说这个注解表示只能在方法中使用:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface MyCustomAnnotation {
}
//使用
public class MyClass {
@MyCustomAnnotation
public void myMethod()
{
......
}
}
@Retention
@Retention定义了该Annotation被保留的时间长短:某些Annotation仅出现在源代码中,而被编译器丢弃;而另一些却被编译在class文件中;编译在class文件中的Annotation可能会被虚拟机忽略,而另一些在class被装载时将被读取(请注意并不影响class的执行,因为Annotation与class在使用上是被分离的)。使用这个meta-Annotation可以对 Annotation的“生命周期”限制。
作用:表示需要在什么级别保存该注释信息,用于描述注解的生命周期(即:被描述的注解在什么范围内有效)
取值(RetentionPoicy)有:
| 类型 | 用途 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| SOURCE | 在源文件中有效(即源文件保留) | 仅出现在源代码中,而被编译器丢弃 |
| CLASS | 在class文件中有效(即class保留) | 被编译在class文件中 |
| RUNTIME | 在运行时有效(即运行时保留) | 编译在class文件中 |
使用示例:
/***
* 字段注解接口
*/
@Target(value = {ElementType.FIELD})//注解可以被添加在属性上
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//注解保存在JVM运行时刻,能够在运行时刻通过反射API来获取到注解的信息
public @interface Column {
String name();//注解的name属性
}
@Documented
@Documented用于描述其它类型的annotation应该被作为被标注的程序成员的公共API,因此可以被例如javadoc此类的工具文档化。Documented是一个标记注解,没有成员。
作用:将注解包含在javadoc中
示例:
java.lang.annotation.Documented
@Documented
public @interface MyCustomAnnotation { //Annotation body}
@Inherited
-
是一个标记注解
-
阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的
-
使用了@Inherited修饰的annotation类型被用于一个class,则这个annotation将被用于该class的子类
@Inherited annotation类型是被标注过的class的子类所继承。类并不从实现的接口继承annotation,方法不从它所重载的方法继承annotation -
当@Inherited annotation类型标注的annotation的Retention是RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME,则反射API增强了这种继承性。如果我们使用java.lang.reflect去查询一个@Inherited annotation类型的annotation时,反射代码检查将展开工作:检查class和其父类,直到发现指定的annotation类型被发现,或者到达类继承结构的顶层。
作用:允许子类继承父类中的注解
示例,这里的MyParentClass 使用的注解标注了@Inherited,所以子类可以继承这个注解信息:
java.lang.annotation.Inherited
@Inherited
public @interface MyCustomAnnotation {
}
@MyCustomAnnotation
public class MyParentClass {
...
}
public class MyChildClass extends MyParentClass {
...
}
自定义注解
格式
public @interface 注解名{
定义体
}
注解参数的可支持数据类型:
- 所有基本数据类型(int,float,double,boolean,byte,char,long,short)
- String 类型
- Class类型
- enum类型
- Annotation类型
- 以上所有类型的数组
规则
- 修饰符只能是public 或默认(default)
- 参数成员只能用基本类型byte,short,int,long,float,double,boolean八种基本类型和String,Enum,Class,annotations及这些类型的数组
- 如果只有一个参数成员,最好将名称设为”value”
- 注解元素必须有确定的值,可以在注解中定义默认值,也可以使用注解时指定,非基本类型的值不可为null,常使用空字符串或0作默认值
- 在表现一个元素存在或缺失的状态时,定义一下特殊值来表示,如空字符串或负值
示例:
/**
* test注解
* @author ddk
*
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface TestAnnotation {
/**
* id
* @return
*/
public int id() default -1;
/**
* name
* @return
*/
public String name() default "";
}
注解处理器类库
java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement
Java使用Annotation接口来代表程序元素前面的注解,该接口是所有Annotation类型的父接口。除此之外,Java在java.lang.reflect 包下新增了AnnotatedElement接口,该接口代表程序中可以接受注解的程序元素,该接口主要有如下几个实现类:
- Class:类定义
- Constructor:构造器定义
- Field:累的成员变量定义
- Method:类的方法定义
- Package:类的包定义
java.lang.reflect 包下主要包含一些实现反射功能的工具类,实际上,java.lang.reflect 包所有提供的反射API扩充了读取运行时Annotation信息的能力。当一个Annotation类型被定义为运行时的Annotation后,该注解才能是运行时可见,当class文件被装载时被保存在class文件中的Annotation才会被虚拟机读取。
AnnotatedElement 接口是所有程序元素(Class、Method和Constructor)的父接口,所以程序通过反射获取了某个类的AnnotatedElement对象之后,程序就可以调用该对象的如下四个个方法来访问Annotation信息:
- 方法1: T getAnnotation(Class annotationClass): 返回改程序元素上存在的、指定类型的注解,如果该类型注解不存在,则返回null。
- 方法2:Annotation[] getAnnotations():返回该程序元素上存在的所有注解。
- 方法3:boolean is AnnotationPresent(Class<?extends Annotation> annotationClass):判断该程序元素上是否包含指定类型的注解,存在则返回true,否则返回false.
- 方法4:Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations():返回直接存在于此元素上的所有注释。与此接口中的其他方法不同,该方法将忽略继承的注释。(如果没有注释直接存在于此元素上,则返回长度为零的一个数组。)该方法的调用者可以随意修改返回的数组;这不会对其他调用者返回的数组产生任何影响。
注解处理器示例:
/***********注解声明***************/
/**
* 水果名称注解
* @author peida
*
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FruitName {
String value() default "";
}
/**
* 水果颜色注解
* @author peida
*
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FruitColor {
/**
* 颜色枚举
* @author peida
*
*/
public enum Color{ BULE,RED,GREEN};
/**
* 颜色属性
* @return
*/
Color fruitColor() default Color.GREEN;
}
/**
* 水果供应者注解
* @author peida
*
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface FruitProvider {
/**
* 供应商编号
* @return
*/
public int id() default -1;
/**
* 供应商名称
* @return
*/
public String name() default "";
/**
* 供应商地址
* @return
*/
public String address() default "";
}
/***********注解使用***************/
public class Apple {
@FruitName("Apple")
private String appleName;
@FruitColor(fruitColor=Color.RED)
private String appleColor;
@FruitProvider(id=1,name="陕西红富士集团",address="陕西省西安市延安路89号红富士大厦")
private String appleProvider;
public void setAppleColor(String appleColor) {
this.appleColor = appleColor;
}
public String getAppleColor() {
return appleColor;
}
public void setAppleName(String appleName) {
this.appleName = appleName;
}
public String getAppleName() {
return appleName;
}
public void setAppleProvider(String appleProvider) {
this.appleProvider = appleProvider;
}
public String getAppleProvider() {
return appleProvider;
}
public void displayName(){
System.out.println("水果的名字是:苹果");
}
}
/***********注解处理器***************/
//其实是用的反射
public class FruitInfoUtil {
public static void getFruitInfo(Class<?> clazz){
String strFruitName=" 水果名称:";
String strFruitColor=" 水果颜色:";
String strFruitProvicer="供应商信息:";
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field :fields){
if(field.isAnnotationPresent(FruitName.class)){
FruitName fruitName = (FruitName) field.getAnnotation(FruitName.class);
strFruitName=strFruitName+fruitName.value();
System.out.println(strFruitName);
}
else if(field.isAnnotationPresent(FruitColor.class)){
FruitColor fruitColor= (FruitColor) field.getAnnotation(FruitColor.class);
strFruitColor=strFruitColor+fruitColor.fruitColor().toString();
System.out.println(strFruitColor);
}
else if(field.isAnnotationPresent(FruitProvider.class)){
FruitProvider fruitProvider= (FruitProvider) field.getAnnotation(FruitProvider.class);
strFruitProvicer=" 供应商编号:"+fruitProvider.id()+" 供应商名称:"+fruitProvider.name()+" 供应商地址:"+fruitProvider.address();
System.out.println(strFruitProvicer);
}
}
}
}
/***********输出结果***************/
public class FruitRun {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
FruitInfoUtil.getFruitInfo(Apple.class);
}
}
====================================
水果名称:Apple
水果颜色:RED
供应商编号:1 供应商名称:陕西红富士集团 供应商地址:陕西省西安市延安路89号红富士大厦
Java 8 中注解新特性
-
@Repeatable 元注解,表示被修饰的注解可以用在同一个声明式或者类型加上多个相同的注解(包含不同的属性值)
-
@Native 元注解,本地方法
-
java8 中Annotation 可以被用在任何使用 Type 的地方
//初始化对象时
String myString = new @NotNull String();
//对象类型转化时
myString = (@NonNull String) str;
//使用 implements 表达式时
class MyList<T> implements @ReadOnly List<@ReadOnly T>{
...
}
//使用 throws 表达式时
public void validateValues() throws @Critical ValidationFailedException{
...
}
思维导图
扩展阅读
http://www.cnblogs.com/ITtangtang/p/3974531.html
www.jianshu.com/p/948549b92e0a