剑指 Offer 17. 打印从1到最大的n位数
解法一:
缺点:未考虑到大数的情况,当数字较大时,int不够用
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printNumbers(int n) {
//1.先判断n为几位数
n = pow(10,n);
vector<int>v;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
v.push_back(i);
}
return v;
}
};
解法二:考虑大数的情况
大数加法的模板
string Add(string a,string b) {
string ans;
int numA[MAX_SIZE]={0},numB[MAX_SIZE]={0};//用来保存数字
int lenA = a.size();
int lenB = b.size();
for(int i=0;i<lenA;i++){
//字符串转数字
numA[lenA-1-i] = a[i] - '0';//从个位开始转换
}
for(int i=0;i<lenB;i++){
numB[lenB-1-i] = b[i] - '0';
}
int lenMax = lenA>lenB ? lenA:lenB;
// 从个位开始计算
for(int i=0;i<lenMax;i++){
numA[i]+=numB[i];
numA[i+1]+=numA[i]/10;//判断是否有进位
numA[i]%=10;
}
//去除前置0
if(!numA[lenMax]) lenMax--;
for(int i= lenMax;i>=0;i--){
ans+=numA[i]+'0'; //保存到结果中
}
return ans;
}
用字符串模拟数字加法:流程为,先判断是否有溢出,没有溢出就加1并保存该值
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> output;
vector<int> printNumbers(int n) {
// 以下注释的前提:假设 n = 3
if(n <= 0) return vector<int>(0);
string s(n, '0'); // s最大会等于999,即s的长度为n
while(!overflow(s)) inputNumbers(s);// 当没有溢出999时
return output;
}
bool overflow(string& s) //判断溢出情况
{
// 本函数用于模拟数字的累加过程,并判断是否越界(即 999 + 1 = 1000,就是越界情况)
bool isOverFlow = false;
int carry = 0; // carry表示进位
for(int i=s.length()-1; i>=0; --i) //从高到低
{
int current = s[i] - '0' + carry; // current表示当前这次的操作
if(i == s.length() - 1) current ++; // 如果i此时在个位,current执行 +1 操作
if(current >= 10) //有进位了
{
// 假如i已经在最大的那一位了,而current++之后>=10,说明循环到头了,即999 + 1 = 1000
if(i == 0) isOverFlow = true;
else
{
// 只是普通进位,比如current从9变成10
carry = 1;
s[i] = current - 10 + '0';
}
}
else
{
// 如果没有进位,更新s[i]的值,然后直接跳出循环,这样就可以回去执行inputNumbers函数了,即往output里添加元素
s[i] = current + '0';
break;
}
}
return isOverFlow;
}
void inputNumbers(string s)
{
// 本函数用于循环往output中添加符合传统阅读习惯的元素。比如001,我们会添加1而不是001。
bool isZero = true; // 判断是否是0,比如001前面的两个0
string temp = "";
for(int i=0; i<s.length(); ++i)
{
if(isZero && s[i] != '0') isZero = false;
if(!isZero) temp += s[i]; //去除0后,将该值保存
}
output.push_back(stoi(temp));//stoi string to integer
}
};
剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点

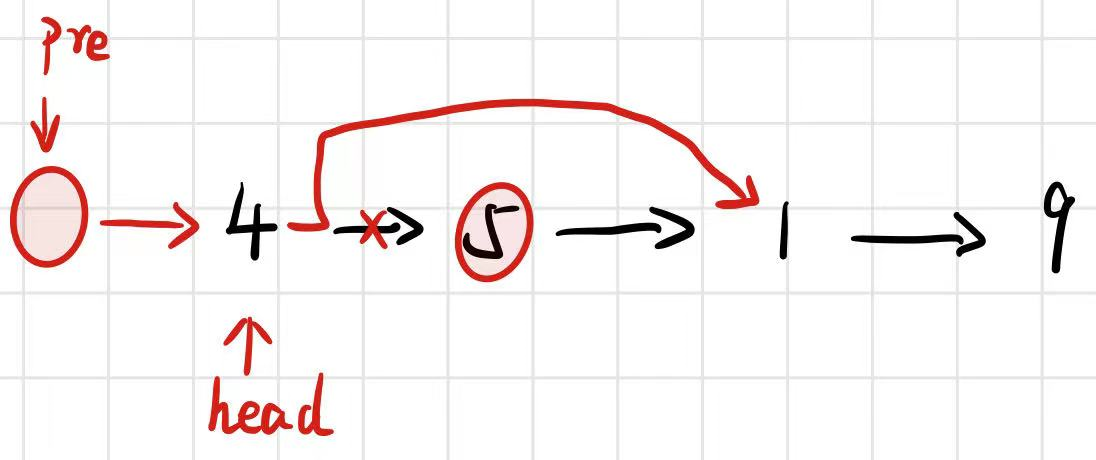
//主要是要考虑到头结点也有可能要被删除这种情况,所有再开辟一个新结点指向头结点,这样循环向后一个判断即可可以方便不少
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode *pre = new ListNode(0);
pre->next = head;
head = pre;
while(pre->next!=NULL){
if(pre->next->val==val){
pre->next = pre->next->next;
return head->next;
}
pre = pre->next;
}
return head->next;
}
};
剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
第一时间我想到的是快速排序中的类似partition函数这样做分割,但关键地方有点卡住了,就先暴力过了一边
法一:暴力法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int>res;
for(auto it=nums.begin();it!=nums.end();++it){
if( (*it)%2!=0 ){
res.push_back((*it));
}
}
for(auto it=nums.begin();it!=nums.end();++it){
if( (*it)%2==0 ){
res.push_back((*it));
}
}
return res;
}
};
法二:双指针法
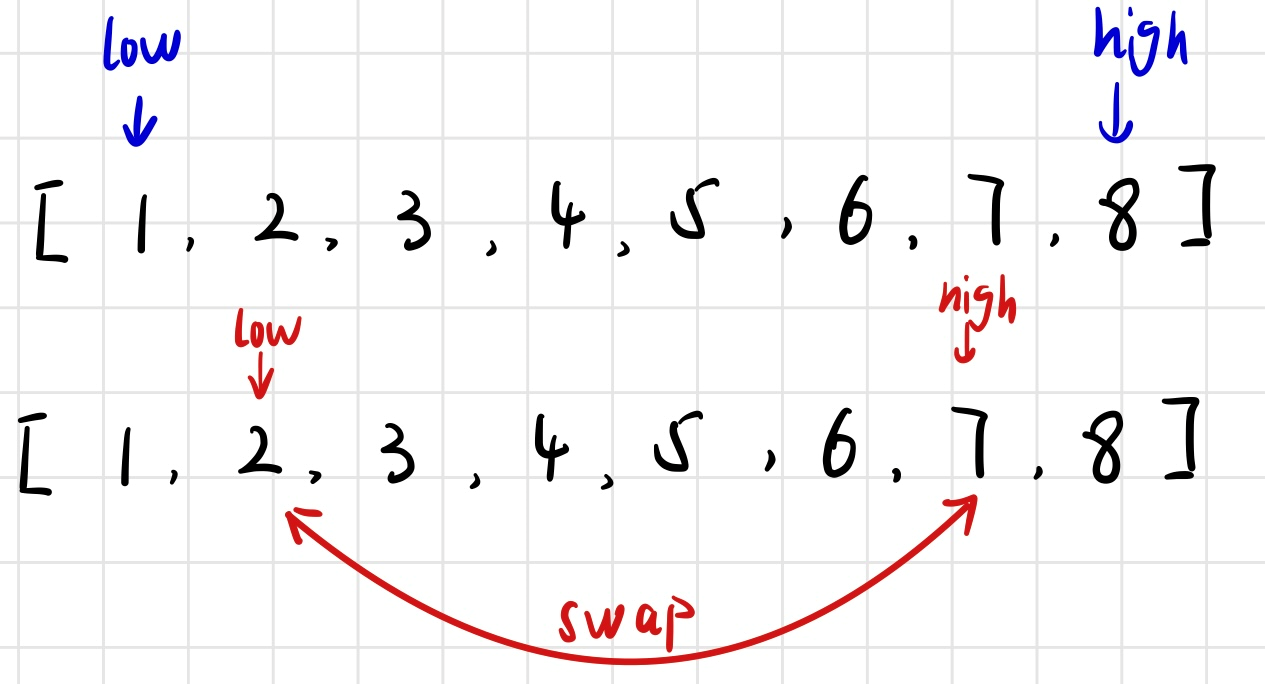
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
int i=0;
int j=nums.size()-1;
while(i < j){
while(i<j && (nums[i] & 1) == 1) i++; //奇数
while(i<j && (nums[j] & 1) == 0) j--; //偶数
swap(nums[i],nums[j]);
}
return nums;
}
};
法三.快慢指针
思路是让一个先走,而每当快指针指向的是奇数时,将其与low交换(即向左边靠)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> exchange(vector<int>& nums) {
int low = 0, fast = 0;
while (fast < nums.size()) {
if (nums[fast] & 1) { //当快指针指向的是奇数时
swap(nums[low], nums[fast]);
low ++;
}
fast ++;
}
return nums;
}
};
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
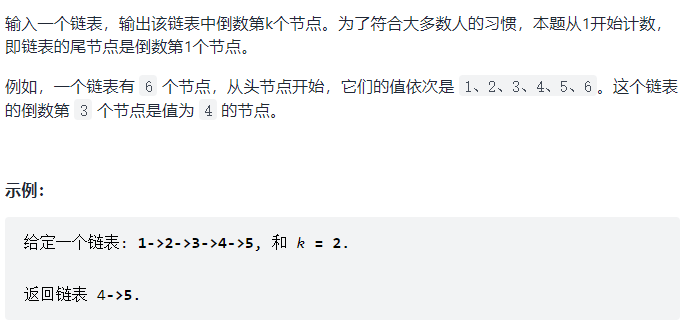
没什么难度,直接双指针就出来了,倒数第K个,就让一个先走K步,再两个指针一起走,当先走的到达链尾时,后走的正好到达倒数第K个
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* getKthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode *rear = head;
for(int i = 0;i<k;++i){
rear = rear->next;
if(rear==NULL){//代表K超出范围
return head;
}
}
while(rear){
rear = rear->next;
head = head->next;
}
return head;
}
};
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表

相当简单,就是画个图,分析一下断链的情况和指针的情况就行了。
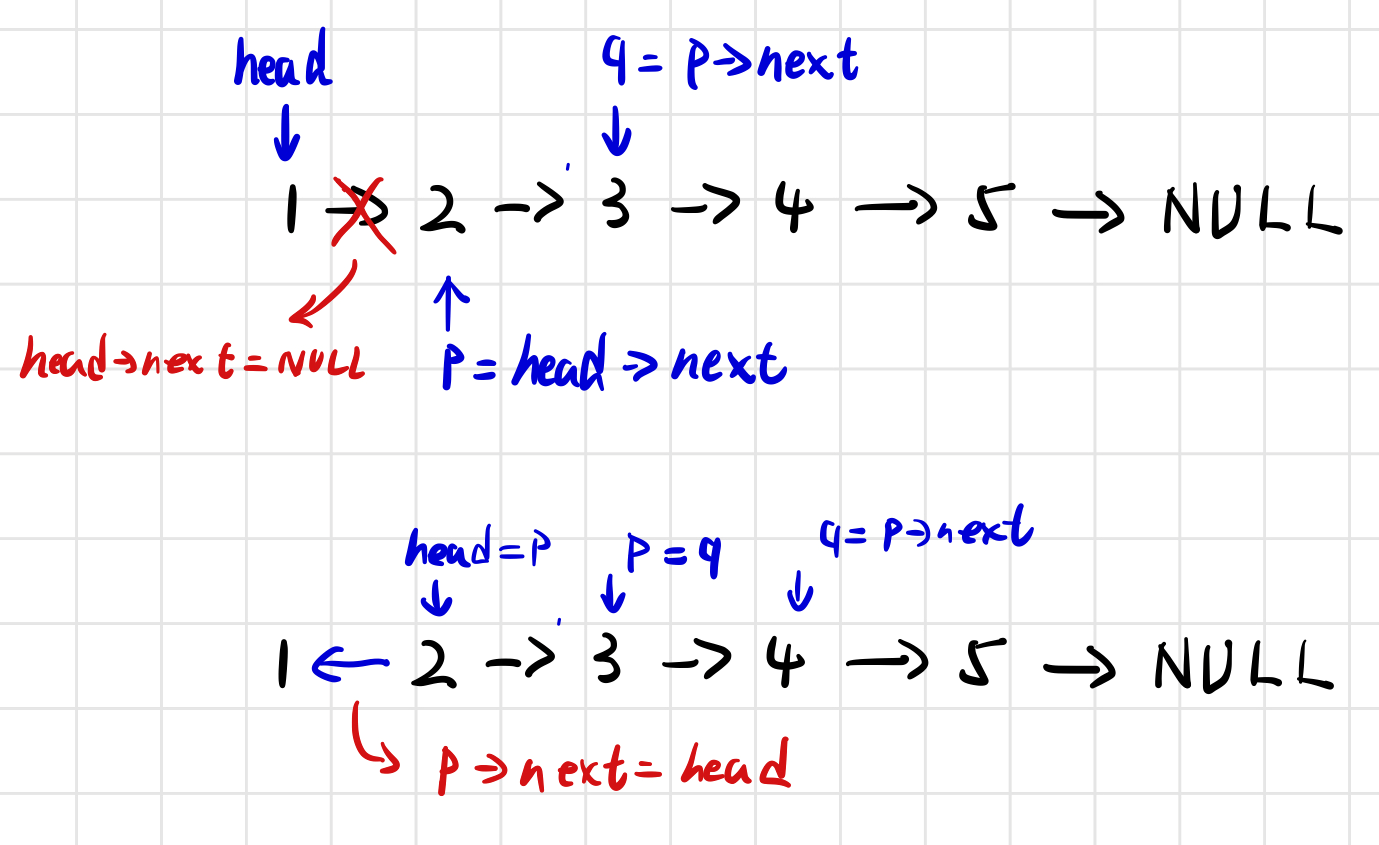
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(head==NULL) return head;
ListNode *p,*q;
p = head->next;
head->next = NULL;
while(p!=NULL){
q = p->next;
p->next = head;
head = p;
p = q;
}
return head;
}
};
方案二:递归实现
链表的逆序可以自然想到递归,桟
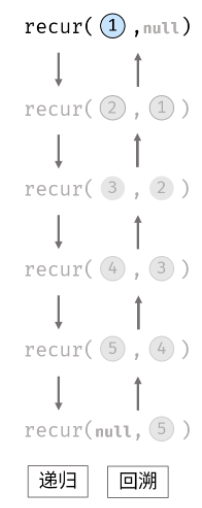
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
return recur(head, nullptr); // 调用递归并返回
}
private:
ListNode* recur(ListNode* cur, ListNode* pre) {
if (cur == nullptr) return pre; // 终止条件,开始回溯
//该语句会一直向下指到5
ListNode* res = recur(cur->next, cur); // 递归后继节点
//开始回溯时修改指针指向 5->next = 4 4->next = 3....
cur->next = pre; // 修改节点引用指向
return res; // 返回反转链表的头节点
}
};
剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
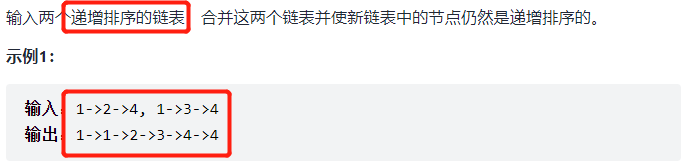
解法一
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list_1, ListNode* list_2) {
ListNode * list = new ListNode(0),*cur =list;
while(list_1 && list_2){
//按递增排序
if(list_1->val<list_2->val){
cur->next = list_1;
list_1 = list_1->next;
}else{
cur->next = list_2;
list_2 = list_2->next;
}
cur = cur ->next;
}
cur->next = list_1 ? list_1 : list_2 ;//处理剩余的结点,因为前一个while循环一定会让一个链表到尾
return list->next;//为什么要return list->next呢?因为一开始申请的时候申请了一个0当头结点
}
};
解法二
递归写法,貌似有关链表的题目,都可以用递归来写,但是有一点难理解
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2) {
if(l1 == NULL) return l2; //l1到头了
if(l2 == NULL) return l1; //l2到头了
if(l1->val <= l2->val) {
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2); //l1向后
return l1;
} else {
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next); //l2向后
return l2;
}
}
};
剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像
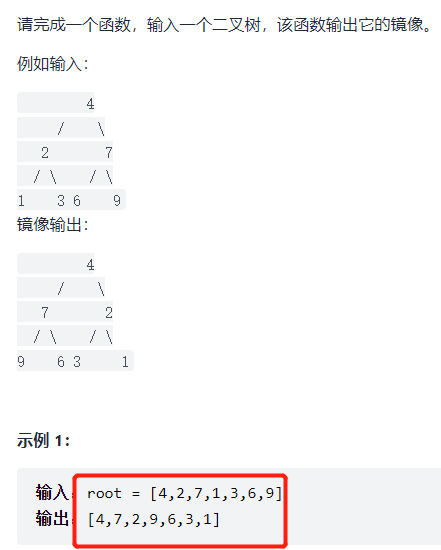
解法一法:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr; //这里是边界条件
TreeNode * temp = root->left;
root->left=
mirrorTree(root->right);//根节点的左结点应该向右递归
root->right=
mirrorTree(temp); //右结点向左递归
return root;
}
};
解法二:
用栈来处理
//桟的写法
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return nullptr;//一个特殊情况的判断
stack<TreeNode *>s;
s.push(root);
while(!s.empty()){//非空
TreeNode *node = s.top();//根结点出栈 处理顺序为4,7,9,6,2,3,1
s.pop();
if(node->left!=NULL) s.push(node->left);//左进桟
if(node->right!=NULL) s.push(node->right);
//实现左右指针的一个交换
TreeNode *temp = node->left;
node->left = node ->right;
node->right = temp;
}
return root;
}
};
总结:这几天写了下这种有类似反转啊,逆置啊,感觉一般首先可以想递归,然后想桟,这种FILO的结构来处理
剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树
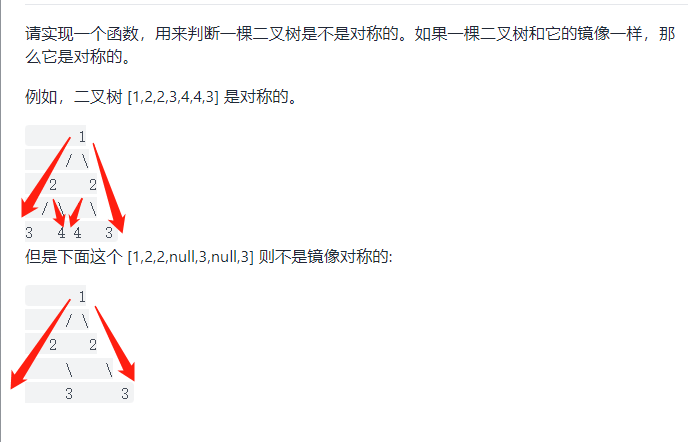
大佬的写法
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
// 如果是空树
if(!root)
return true;
else
return isSymmetric(root->left, root->right); //判断左子树和右子树是否对称
}
// 此函数比较二叉树中位置对称的两个节点
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right){
// 结束条件1:如果对称两个节点都为空,则返回true
if(!left && !right){
return true;
}
// 结束条件2:如果单独一个节点为空,另一个节点不为空,又或者是对称节点间的val值不等,则返回false
if(!left || !right || left->val != right->val)
return false;
// 该层符合对称二叉树的要求,开始比较下一层
//左结点的左结点,右结点的右结点
return isSymmetric(left->left, right->right) && isSymmetric(left->right, right->left);
}
};
补一下递归:
递归,一定有1.递推关系2.递推出口
-
递归计算数组的前你项和

-
实现一个字符串的逆序输出
void reverse_print(int index,string str){ if(str[index]==NULL){ return; //1 } else{ reverse_print(index+1,str); //2 cout<<str[index]; //3 } } 执行流程是: 2 2 2 2 2..... 1 3 3 3 3 3..... -
杨辉三角
最核心的也是找出递推关系:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows) {
vector<vector<int>> ret(numRows);
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; ++i) {
ret[i].resize(i + 1); //空间的初始化
ret[i][0] = ret[i][i] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j) {
ret[i][j] = ret[i - 1][j] + ret[i - 1][j - 1]; //最核心的递推关系
}
}
return ret;
}
};
217. 存在重复元素
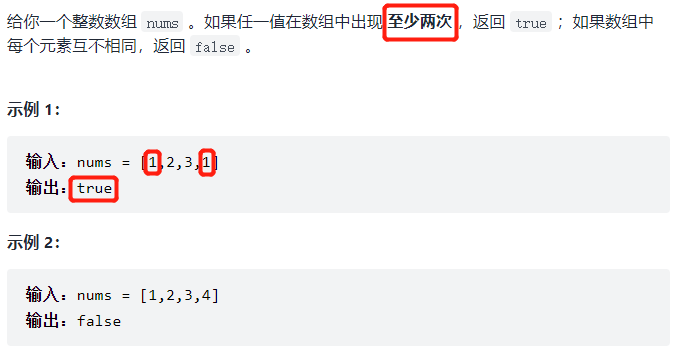
这是用集合的特性来做的,集合本身就具有排同性O(nlog2n),还有一种解法就是先排序,之后再判断相邻元素是否相等来判断O(n)
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int>s;
for(int x:nums){
if(s.find(x)!=s.end()){
return true;
}
s.insert(x);
}
return false;
}
};
类似的287. 寻找重复数
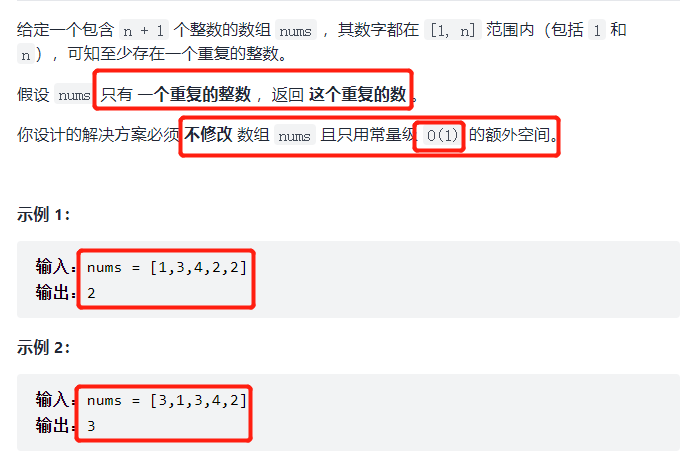
和上篇文章剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字的解题思路一样,详情见上篇文章
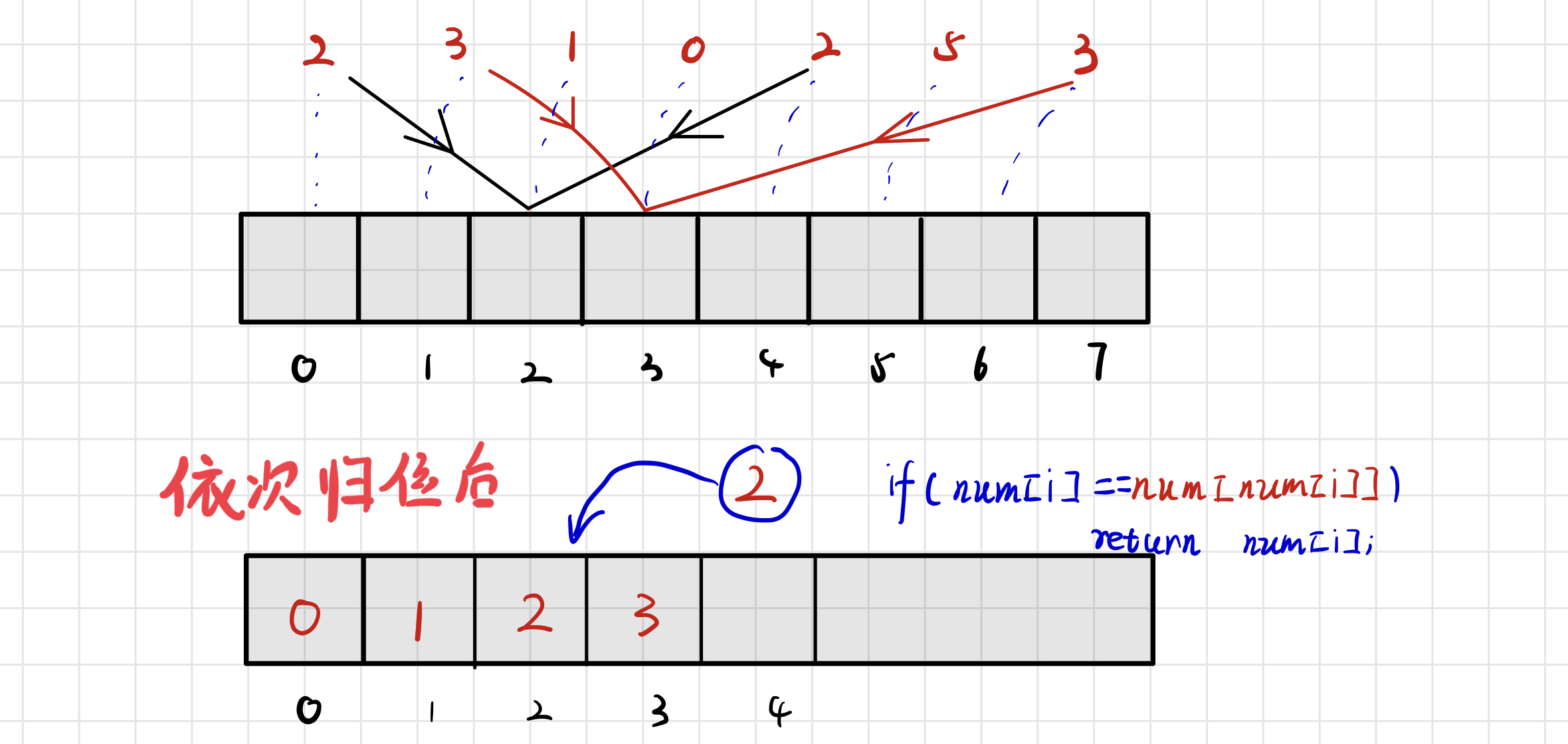
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
int res;
int i=0;
while(i<nums.size()){
if(nums[i]==i){ //已经归位
i++;
continue;
}
else if(nums[i]==nums[nums[i]])
return nums[i];
swap(nums[i],nums[nums[i]]);
}
return res;
}
};
剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵


模拟这个顺时针的过程,一开始向右走到右边界,走完上边界++,向下走到下边界,走完右边界--,向左走到左边界,走完下边界--,向上走上边界,走完左边界++
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix)
{
if (matrix.empty()) return {};
vector<int> res;
int l = 0; //左边界
int r = matrix[0].size() - 1; //右边界
int t = 0; //上边界
int b = matrix.size() - 1; //下边界
while (true)
{
//left -> right
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) res.push_back(matrix[t][i]);
if (++t > b) break;
//top -> bottom
for (int i = t; i <= b; i++) res.push_back(matrix[i][r]);
if (--r < l) break;
//right -> left
for (int i = r; i >= l; i--) res.push_back(matrix[b][i]);
if (--b < t) break;
//bottom -> top
for (int i = b; i >= t; i--) res.push_back(matrix[i][l]);
if (++l > r) break;
}
return res;
}
};