一、文本
1.文本颜色:color
颜色属性被用来设置文字的颜色。
颜色是通过CSS最经常的指定:
- 十六进制值 - 如: #FF0000
- 一个RGB值 - 如: RGB(255,0,0)
- 颜色的名称 - 如: red
2.水平对齐方式
text-align 属性规定元素中的文本的水平对齐方式。
- left 把文本排列到左边。默认值:由浏览器决定。
- right 把文本排列到右边。
- center 把文本排列到中间。
- justify 实现两端对齐文本效果。
二、文本其他操作
text-align:cnter 文本居中
line heigth 垂直居中 :行高,和高度对应
vertical-align:设置图片与文本的距离
text-decoration:none 去掉超链接下划线
font-style:oblique 或者italic....(设置字体的样式为斜体)font-size: 10px; line-height: 200px; 文本行高 通俗的讲,文字高度加上文字上下的空白区域的高度 50%:基于字体大小的百分比 vertical-align:-4px 设置元素内容的垂直对齐方式 ,只对行内元素有效,对块级元素无效 text-decoration:none text-decoration 属性用来设置或删除文本的装饰。主要是用来删除链接的下划线 font-family: 'Lucida Bright' font-weight: lighter/bold/border/ font-style: oblique text-indent: 150px; 首行缩进150px letter-spacing: 10px; 字母间距 word-spacing: 20px; 单词间距 text-transform: capitalize/uppercase/lowercase ; 文本转换,用于所有字句变成大写或小写字母,或每个单词的首字母大写 */
三、背景属性
background-color:背景颜色
background-image:url('11.jpg'); 背景图片链接
background-repeat:repeat-x; x轴平铺
background-repeat:no-repeat; 不重复
background-position:400px 200px 调整背景的位置(距左。距右)
background-position: center:center; 背景居中
简写:background:#ffffff url('1.png') no-repeat right top;

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>背景处理</title>
<style>
.c1{
100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid red;
background: url("xhr.jpg") -206px -29px;
/*可在那个网页上右击点击检查,调试*/
/*background-position: center; */
/*定位*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c1">
</div>
</body>
</html>
四、边框属性
常用属性
简写:border :1px soild red;
deshed:虚线
只加有一个方向的:border-right :1px soild red;
五、列表属性
去掉列表前面的标志:ul li{list-style:none;}
去掉列表前面的空格:ul{padding:0}
上面两行也可写成下面一行
去掉盒子上面的间隙:*{margin:0; padding :0;}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
ul li{
font-family: 华文中宋;
list-style: none; //去掉点
/*list-style: circle;//空心圆*/
/*list-style: disc;//实心圆(默认也是实心圆)*/
}
ul{
padding: 0; //把字体移到前面
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
<li>第一章</li>
<li>第二章</li>
<li>第三章</li>
<li>第四章</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
六、display属性
display属性
1.将块级标签设置成内联标签:disply:inline;
2.将内联标签设置成块级标签:disply:block;
3.内联块级标签:像块级一样可设长宽,也可像内联一样在一行显示:display:inline-block;
4.display:none; 吧不想让用户看到的给隐藏了(很重要的一个属性)
5.visibility :hiddon; 也是隐藏
注意与visibility:hidden的区别:
visibility:hidden:可以隐藏某个元素,但隐藏的元素仍需占用与未隐藏之前一样的空间。也就是说,该元素虽然被隐藏了,但仍然会影响布局。
display:none:可以隐藏某个元素,且隐藏的元素不会占用任何空间。也就是说,该元素不但被隐藏了,而且该元素原本占用的空间也会从页面布局中消失。

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.c1{
100px;
height:100px;
background-color: rebeccapurple;
}
.c2{
100px;
height:100px;
background-color: burlywood;
}
.c3{
100px;
height:100px;
background-color: crimson;
display: inline;
}
.c4{
100px;
height:100px;
background-color: gray;
}
.s1{
display: block;
200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: royalblue;
/*visibility: hidden;*/ //隐藏了其他的不会顶上去
display:none; //隐藏了其他的会顶上去
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c4">div</div>
<span class="s1">span</span>
<div class="c1">年后</div>
<div class="c2">年后</div>
<div class="c3">年后</div>
</body>
</html>
七、外边距(margin)和内边距(padding)
1.盒子模型
- margin: 用于控制元素与元素之间的距离;margin的最基本用途就是控制元素周围空间的间隔,从视觉角度上达到相互隔开的目的。
- padding: 用于控制内容与边框之间的距离;
- Border(边框): 围绕在内边距和内容外的边框。
- Content(内容): 盒子的内容,显示文本和图像。
2.margin(外边距)
单边外边距属性:
margin-top:100px;
margin-bottom:100px;
margin-right:50px;
margin-left:50px;
简写属性:
margin:10px 20px 20px 10px;
上边距为10px
右边距为20px
下边距为20px
左边距为10px
margin:10px 20px 10px;
上边距为10px
左右边距为20px
下边距为10px
margin:10px 20px;
上下边距为10px
左右边距为20px
margin:25px;
所有的4个边距都是25px
居中应用
margin: 0 auto;
3.padding(内边距)
单独使用填充属性可以改变上下左右的填充。缩写填充属性也可以使用,一旦改变一切都改变。
设置同margine;
思考1:body的外边距
边框在默认情况下会定位于浏览器窗口的左上角,但是并没有紧贴着浏览器的窗口的边框,这是因为body本身也是一个盒子(外层还有html),在默认情况下, body距离html会有若干像素的margin,具体数值因各个浏览器不尽相同,所以body中的盒子不会紧贴浏览器窗口的边框了,为了验证这一点,加上:
body{
border: 1px solid;
background-color: cadetblue;
}
>>>>解决方法:
body{
margin: 0;
}
八、边距的塌陷问题
1、兄弟div:
上面div的margin-bottom和下面div的margin-top会塌陷,也就是会取上下两者margin里最大值作为显示值
2、父子div:
if 父级div中没有border,padding,inlinecontent,子级div的margin会一直向上找,直到找到某个标签包括border,padding,inline content中的其中一个,然后按此div 进行margin;

解决方法
解决方法
这两种会改变结构
1.加上padding
2.加上border
不改变结构
3.overflow:hidden

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
margin: 0;
}
.outer{
background-color: gold;
300px;
height: 300px;
/*第一种解决方法:但是改变了结构padding: 10px;*/
/*第二种方法:加个border*/ /*border: 1px solid;*/
/*第三种方法*/
overflow: hidden;
}
.box1{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
/*如果父级标签什么都没有,那么就会找叔叔的*/
margin-top:10px;
}
.box2{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: darksalmon;
/*如果这样的话就合适呢,对着就下去了*/
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="background-color: burlywood; 300px; height
:300px"></div>
<div class="outer">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
处理后的结果如图:
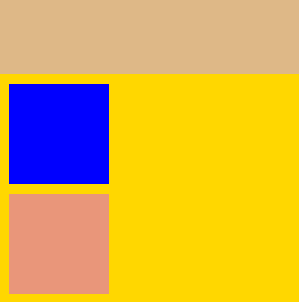
溢出问题

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>css属性操作</title>
<style>
.c1{
border: 1px solid;
background-color: blueviolet;
100%;
height:200px;
/*text-align: center;*/
/*设置两端对齐*/
text-align: justify;
line-height: 200px;
/*如果你写的多了,会溢出来*/
/*第一种方法:overflow: hidden;*/
overflow: scroll;
}
.btn{
45px;
height: 70px;
background-color: gray;
/*设置透明度*/
opacity: 0.4;
text-align: center;
line-height: 70px;
/*行高和高度对应*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c1">啦啦啦啦啦绿绿绿
绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿绿
啦啦啦啦啦 绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿
绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿
绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿
绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿lllllllllllllllllllllll
绿绿绿绿绿</div>
<div class="btn"> < </div>
</body>
</html>

解决溢出的方法
解决溢出的方法 overflow:auto;
overflow: hidden;
overflow:scoll; #加上滚动条

九、清除浮动
clear语法:
clear:none | left | right | both
1.clear:left 清除的是左边的浮动
2.clear:both :保证左右两边都没有浮动
注意:
排序的时候是一个标签一个标签的排
如果上一个是浮动的,就紧贴个上一个
如果上一个不是浮动的,就和上一个保持垂直不变
十、float属性
布局关键点:如何能够让可以调节长度的元素(标签)在一行显示
如果上一个是浮动的,那么就紧贴这
如果上一个不是浮动的,那么就保持垂直距离不变
基本浮动规则
先来了解一下block元素和inline元素在文档流中的排列方式。
block元素通常被现实为独立的一块,独占一行,多个block元素会各自新起一行,默认block元素宽度自动填满其父元素宽度。block元素可以设置width、height、margin、padding属性;
inline元素不会独占一行,多个相邻的行内元素会排列在同一行里,直到一行排列不下,才会新换一行,其宽度随元素的内容而变化。inline元素设置width、height属性无效
- 常见的块级元素有 div、form、table、p、pre、h1~h5、dl、ol、ul 等。
- 常见的内联元素有span、a、strong、em、label、input、select、textarea、img、br等
所谓的文档流,指的是元素排版布局过程中,元素会自动从左往右,从上往下的流式排列。
脱离文档流,也就是将元素从普通的布局排版中拿走,其他盒子在定位的时候,会当做脱离文档流的元素不存在而进行定位。
假如某个div元素A是浮动的,如果A元素上一个元素也是浮动的,那么A元素会跟随在上一个元素的后边(如果一行放不下这两个元素,那么A元素会被挤到下一行);如果A元素上一个元素是标准流中的元素,那么A的相对垂直位置不会改变,也就是说A的顶部总是和上一个元素的底部对齐。此外,浮动的框之后的block元素元素会认为这个框不存在,但其中的文本依然会为这个元素让出位置。 浮动的框之后的inline元素,会为这个框空出位置,然后按顺序排列。

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
}
.r1{
300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #7A77C8;
float: left;
}
.r2{
200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: wheat;
/*float: left;*/
}
.r3{
100px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkgreen;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="r1"></div>
<div class="r2"></div>
<div class="r3"></div>
非完全脱离文档流
左右结构div盒子重叠现象,一般是由于相邻两个DIV一个使用浮动一个没有使用浮动。一个使用浮动一个没有导致DIV不是在同个“平面”上,但内容不会造成覆盖现象,只有DIV形成覆盖现象。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
}
.r1{
100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #7A77C8;
float: left;
}
.r2{
200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: wheat;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="r1"></div>
<div class="r2">region2</div>
>>>>解决方法:要么都不使用浮动;要么都使用float浮动;要么对没有使用float浮动的DIV设置margin样式。
十一、float父级的塌陷问题
float它不是完全脱离,它是半脱离的。像是文字环绕的就是用float实现的。float是不覆盖文字的
半脱离的,吧文字给挤过去了。

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.c1{
100px;
height: 60px;
background-color: blue;
float: left;
}
.c2{
200px;
height: 30px;
background-color: aqua;
float: left;
}
.c3{
200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: crimson;
float: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c1"></div>
<div class="c2"></div>
<div class="c3"></div>
<div class="content">
content
</div>
</body>
</html>

解决方案
解决方案
1.<div style='clear:both'></div>
也可以不加div
2.用after
.header:after{
content:""; #内容为空
display:block; #块级标签
clear:both; #清楚浮动的功能
}
约定的名字:clearfix
.clearfix:after{
content:""; #内容为空
display:block; #块级标签
clear:both; #清楚浮动的功能(可以做到一个自动切换的功能)
}
解决问题以后的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.header{
/*height: 30px;*/
}
.box1{
200px;
height: 80px;
background-color: wheat;
float: left;
}
.box2{
200px;
height: 30px;
background-color: rebeccapurple;
float: left;
}
.box3{
100px;
height: 50px;
background-color: rosybrown;
float: left;
}
.content{
100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: royalblue;
}
.clearfix:after{
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header clearfix">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
<div class="content">
Content
</div>
</body>
</html>
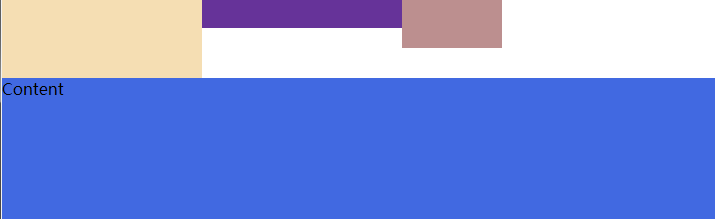
十二、position(定位)属性
position的四种属性
1.static:默认位置
2.fixed:完全脱离文档流,固定定位(以可视窗口为参照物)
3.relative:相对定位(参照的是自己本身的位置),没有脱离文档流,没有顶上去,会保持自己的位置不动。可以使用top left 进行定位
4.absolute:绝对定位:脱离了文档流(参照的是按已定位的父级标签定位,如果找不到会按body的去找)
注意:将定位标签设置为absolute,将他的父级标签设置为定位标签 (relative)
field举例(做一个返回顶部的样式。不管你拉不拉滚动条,他都会固定位置不变给它加一个)

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>固定位置</title>
<style>
.c1{
background-color: limegreen;
100%;
height: 1000px;
}
.returntop{
100px;
height: 40px;
background-color: gray;
/*透明度*/
/*opacity: 0.4;*/
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
position: fixed;
bottom:50px;
right: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="c1"></div>
<div class="returntop">返回顶部>></div>
</body>
</html>
相对位置,绝对位置例子

===============
一开始父级没有定位、
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
}
.box1 ,.box2,.box3{
200px;
height: 200px;
}
.box1{
background-color: blueviolet; position: relative;
}
.box2{
background-color: darksalmon;
position: relative;
/*position: absolute;*/
left: 200px;
/*right: 200px;*/
top: 200px;
}
.box3{
background-color: lime;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>

<!--父级有了定位-->
<!--================-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
.father{
position: relative;
}
*{
margin: 0;
}
.box1 ,.box2,.box3{
200px;
height: 200px;
}
.box1{
background-color: blueviolet; position: relative;
}
.box2{
background-color: darksalmon;
/*position: relative;*/
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
/*right: 200px;*/
top: 200px;
}
.box3{
background-color: lime;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="father">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
十三、float和position的区别
float:半脱离文档流
position:全脱离文档流
