- 公共部分
struct hp{ int len; int s[LEN+1]; hp(){ len=1; int i; for(i=1;i<=LEN;i++){ s[i]=0; } } hp(char* ch){ int i; len=strlen(ch); for(i=1;i<=len;i++) s[i]=ch[len-i]-48; for(;i<=LEN;i++) s[i]=0; } void print(){ int i; for(i=len;i>=1;i--) printf("%d",s[i]); } };
定义了高精度数据结构“hp”,并且定义了输入(构造函数),输出(print),以及初始化(默认构造函数),隐藏了部分细节。
并且hp内部存储的数据是真实数据的逆序,但是在输入和输出的时候自动换序
- 高精度乘高精度
代码:
void multiplyh(const hp& a,const hp& b,hp& c){ int i,j,len; c=hp(); for(i=1;i<=a.len;i++){ for(j=1;j<=b.len;j++){ c.s[i+j-1]+=a.s[i]*b.s[j]; c.s[i+j]+=c.s[i+j-1]/10; c.s[i+j-1]%=10; } } len=a.len+b.len+1; while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0)len--; c.len=len; }
代码理解:
这是一段相当精简的代码,非常有利于程序员记忆。我昨天还在学习一个很复杂的模板,今天看到这个代码直接弃了。复杂代码:

void mult(char a[],char b[],char s[]){//a 被乘数,b 乘数,t 结果 int i,j,k=0,alen,blen,sum=0,res[65][65]={0},flag=0; char result[65]; alen=strlen(a); blen=strlen(b); for(i=0;i<alen;i++) for(j=0;j<blen;j++) res[i][j]=(a[i]-48)*(b[j]-48); for(i=alen-1;i>=0;i--){ //i: a的下标逆序循环 for(j=blen-1;j>=0;j--) //j: b的下标逆序循环 sum+=res[i+blen-j-1][j]; result[k]=sum%10; k++; sum/=10; } for(i=blen-2;i>=0;i--){ for(j=0;j<=i;j++) sum+=res[i-j][j]; result[k]=sum%10; k++; sum/=10; } if(sum!=0){ result[k]=sum; k++; } for(i=0;i<k;i++) result[i]+=48; for(i=k-1;i>=0;i--) s[i]=result[k-1-i]; s[k]=0; while(1){ if(strlen(s)!=strlen(a) && s[0]==48) strcpy(s,s+1); else break; } }
下面来谈对代码的理解。以123 x 456 = 56088 为例,我们来看手算过程:
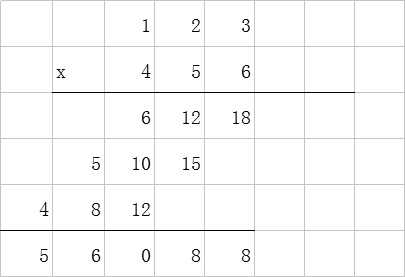
那么,我们来看算法是怎样简化计算的:
首先进行逆序: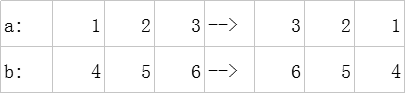
然后,我们来看相乘的过程:循环变量 i 和 j 分别对 a 和 b 进行遍历:
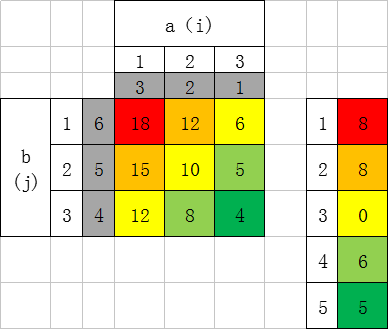
计算结果c的当前下标: i + j - 1,下一位下标: i + j ,
然后通过代码:
c.s[i+j-1]+=a.s[i]*b.s[j]; c.s[i+j]+=c.s[i+j-1]/10; c.s[i+j-1]%=10;
来对下一位进行进位,典型的加法知识。
然后删除高位0,计算计算结果 c 的 len :
len=a.len+b.len+1; while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0)len--;
- 高精度乘低精度
1 void multiply(const hp &a, int b,hp &c){ 2 int i,len=a.len; 3 c=hp(); 4 for(i=1;i<=len;i++){ 5 c.s[i]+=a.s[i]*b; 6 c.s[i+1]+=c.s[i]/10; 7 c.s[i]%=10; 8 } 9 len++; 10 while(c.s[len]>=10){ //处理末尾 11 c.s[len+1]+=c.s[len]/10; 12 c.s[len]%=10; 13 len++; 14 } 15 while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0) len--;//删除末尾0 16 c.len=len; 17 }
- 高精度除低精度
void divide(const hp& a,int b ,hp & c,int &d){ int i,len=a.len; c=hp(); d=0; for(i=len;i>=1;i--){ //在数据结构内部使用逆序,相当于使用正序 d=d*10+a.s[i]; c.s[i]=d/b; d%=b; } while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0) len--; c.len=len; }
- 高精度比较
int compare(const hp& a,const hp& b){ int len; if(a.len>b.len) len=a.len; else len=b.len; while(len>0 && a.s[len]==b.s[len]) len--; if(len==0) return 0; else return a.s[len]-b.s[len]; }
- 高精度乘10
void multiply10(hp &a){ int i; for(i=a.len;i>=1;i--) a.s[i+1]=a.s[i]; a.s[1]=0; a.len++; while(a.len>1 && a.s[a.len]==0) a.len--; }
- 高精度减法
void subtract(const hp& a,const hp &b,hp &c){//大数-小数,不支持负数 int i,len=max(a.len,b.len); c=hp(); for(i=1;i<=len;i++){ c.s[i]+=a.s[i]-b.s[i]; if(c.s[i]<0){ c.s[i]+=10; c.s[i+1]--; } } while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0) len--; c.len=len; }
- 高精度除高精度
void divideh(const hp &a,const hp &b,hp &c,hp &d){ hp e; int i,len; c=hp(),d=hp(); len=a.len; for(i=len;i>=1;i--){ multiply10(d); d.s[1]=a.s[i]; while(compare(d,b)>=0){ //余数d不断变小,直到等于除数b subtract(d,b,e); //e=d-b d=e; //两部合起来,d-=b c.s[i]++; } } while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0) len--; c.len=len; }
- 高精度加高精度
void plush(const hp&a,const hp&b,hp &c){ int i,len; c=hp(); len=max(a.len,b.len); for(i=1;i<=len;i++){ c.s[i]+=a.s[i]+b.s[i]; if(c.s[i]>=10){ c.s[i]-=10; c.s[i+1]++; } } if(c.s[len+1]>0) len++; c.len=len; }
- 整套代码及测试正确语句

#include <stdio.h> #include <memory.h> #include <math.h> #include <string.h> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #define I scanf #define OL puts #define O printf #define F(a,b,c) for(a=b;a<c;a++) #define FF(a,b) for(a=0;a<b;a++) #define FG(a,b) for(a=b-1;a>=0;a--) #define LEN 100 #define MAX 0x06FFFFFF #define V vector<int> using namespace std; struct hp{ int len; int s[LEN+1]; hp(){ len=1; int i; for(i=1;i<=LEN;i++){ s[i]=0; } } hp(char* ch){ int i; len=strlen(ch); for(i=1;i<=len;i++) s[i]=ch[len-i]-48; for(;i<=LEN;i++) s[i]=0; } void print(){ int i; for(i=len;i>=1;i--) printf("%d",s[i]); } string output(){ int i; string ans; for(i=len;i>=1;i--){ char buf[100]; sprintf(buf,"%d",s[i]); ans+=buf; } return ans; } }; void multiply(const hp &a, int b,hp &c){ int i,len=a.len; c=hp(); for(i=1;i<=len;i++){ c.s[i]+=a.s[i]*b; c.s[i+1]+=c.s[i]/10; c.s[i]%=10; } len++; while(c.s[len]>=10){ //处理末尾 c.s[len+1]+=c.s[len]/10; c.s[len]%=10; len++; } while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0) len--;//删除末尾0 c.len=len; } void multiplyh(const hp& a,const hp& b,hp& c){ int i,j,len; c=hp(); for(i=1;i<=a.len;i++){ for(j=1;j<=b.len;j++){ c.s[i+j-1]+=a.s[i]*b.s[j]; c.s[i+j]+=c.s[i+j-1]/10; c.s[i+j-1]%=10; } } len=a.len+b.len+1; while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0)len--; c.len=len; } void divide(const hp& a,int b ,hp & c,int &d){ int i,len=a.len; c=hp(); d=0; for(i=len;i>=1;i--){ //在数据结构内部使用逆序,相当于使用正序 d=d*10+a.s[i]; c.s[i]=d/b; d%=b; } while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0) len--; c.len=len; } int compare(const hp& a,const hp& b){ int len=max(a.len,b.len); while(len>0 && a.s[len]==b.s[len]) len--; if(len==0) return 0; else return a.s[len]-b.s[len]; } void multiply10(hp &a){ int i; for(i=a.len;i>=1;i--) a.s[i+1]=a.s[i]; a.s[1]=0; a.len++; while(a.len>1 && a.s[a.len]==0) a.len--; } void subtract(const hp& a,const hp &b,hp &c){//大数-小数,不支持负数 int i,len=max(a.len,b.len); c=hp(); for(i=1;i<=len;i++){ c.s[i]+=a.s[i]-b.s[i]; if(c.s[i]<0){ c.s[i]+=10; c.s[i+1]--; } } while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0) len--; c.len=len; } void divideh(const hp &a,const hp &b,hp &c,hp &d){ hp e; int i,len; c=hp(),d=hp(); len=a.len; for(i=len;i>=1;i--){ multiply10(d); d.s[1]=a.s[i]; while(compare(d,b)>=0){ //余数d不断变小,直到等于除数b subtract(d,b,e); //e=d-b d=e; //两部合起来,d-=b c.s[i]++; } } while(len>1 && c.s[len]==0) len--; c.len=len; } void plush(const hp&a,const hp&b,hp &c){ int i,len; c=hp(); len=max(a.len,b.len); for(i=1;i<=len;i++){ c.s[i]+=a.s[i]+b.s[i]; if(c.s[i]>=10){ c.s[i]-=10; c.s[i+1]++; } } if(c.s[len+1]>0) len++; c.len=len; } int main(){ int d; hp c,D; // 加法测试 plush("999","999",c); if(c.output()=="1998") puts("加法编写正确"); else puts("加法编写错误"); // 减法测试 subtract("2001","999",c); if(c.output()=="1002") puts("减法编写正确"); else puts("减法编写错误"); // 乘低精度测试 multiply("999",1009,c); if(c.output()=="1007991") puts("乘低精度编写正确"); else puts("乘低精度编写错误"); // 乘高精度测试 multiplyh("999","1009",c); if(c.output()=="1007991") puts("乘高精度编写正确"); else puts("乘高精度编写错误"); // 除低精度测试 divide("56090",123,c,d); if(c.output()=="456" && d==2) puts("除低精度编写正确"); else puts("除低精度编写错误"); // 除高精度测试 divideh("56090","123",c,D); if(c.output()=="456" && D.output()=="2") puts("除高精度编写正确"); else puts("除高精度编写错误"); return 0; }
void plush(const hp&a,const hp&b,hp &c){
int i,len;
c=hp();
len=max(a.len,b.len);
for(i=1;i<=len;i++){
c.s[i]+=a.s[i]+b.s[i];
if(c.s[i]>=10){
c.s[i]-=10;
c.s[i+1]++;
}
}
if(c.s[len+1]>0) len++;
c.len=len;
}
