Set接口:
Set接口存储一组唯一,无序的对象 HashSet是Set接口常用的实现类
HashSet的创建及方法调用:
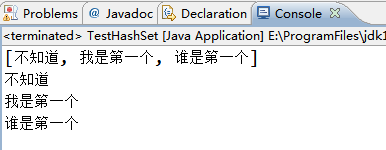
1 public class TestHashSet { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 HashSet<String> hs=new HashSet<String>(); 4 hs.add("谁是第一个"); 5 hs.add("不知道"); 6 hs.add("我是第一个"); 7 System.out.println(hs); 8 //Tterator迭代器 9 Iterator<String> it=hs.iterator(); 10 //判断是否有下一个元素,若有打印出来 11 while(it.hasNext()){ 12 System.out.println(it.next()); 13 } 14 } 15 }
输出结果:由结果可以看出Set集合的无序特性
Map接口:
Map接口专门处理键值映射数据的存储,可以根据键实现对值的操作,最常用的实现类是HashMap
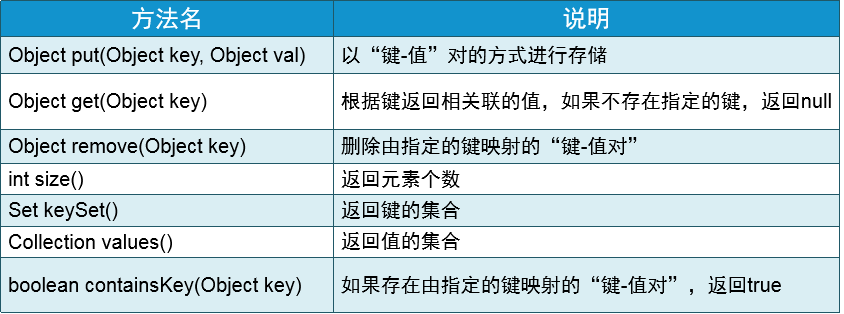
Map接口常用方法:
HashMap集合的创建,添加数据和遍历:
1 public class NationalEnglish { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Map<String, String> m = new HashMap<String, String>(); 4 m.put("CN", "中国"); 5 m.put("USA", "美国"); 6 m.put("GY", "德国"); 7 System.out.println(m); 8 // 使用Set集合获取key值 9 Set<String> set = m.keySet(); 10 // 使用Iterator遍历key来获取values值 11 Iterator<String> it = set.iterator(); 12 while (it.hasNext()) { 13 // 打印获取的values值 14 System.out.println(m.get(it.next())); 15 } 16 // 直接遍历values 17 for (String s : m.values()) { 18 System.out.println(s); 19 } 20 // 同时遍历key和value 21 Set<Entry<String, String>> set1 = m.entrySet(); 22 for (Entry<String, String> ent : set1) { 23 System.out.println("键值是:" + ent.getKey() + ",values是:" 24 + ent.getValue()); 25 } 26 } 27 }
通过重写一些方法,来实现一些功能:
1 public class Student implements Comparator<Student>{ 2 private String name; 3 private char sex; 4 private int age; 5 6 public Student(){} 7 public Student(String name,int age){ 8 this.name=name; 9 this.age=age; 10 } 11 //重写equals方法 12 public boolean equals(Object obj){ 13 if(obj instanceof Student){ 14 Student stu=(Student) obj; 15 if(this.age==stu.getAge()){ 16 return true; 17 }else{ 18 return false; 19 } 20 } 21 return false; 22 } 23 //重写hashCode方法 24 public int hashCode(){ 25 return this.age; 26 } 27 public String getName() { 28 return name; 29 } 30 public void setName(String name) { 31 this.name = name; 32 } 33 public char getSex() { 34 return sex; 35 } 36 public void setSex(char sex) { 37 this.sex = sex; 38 } 39 public int getAge() { 40 return age; 41 } 42 public void setAge(int age) { 43 this.age = age; 44 } 45 //按名字排序,名字相同比较年龄 46 public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) { 47 if(s1.getName().equals(s2.getName())){ 48 return s1.getAge()-s2.getAge();//通过比较年龄排序 49 }else{ 50 return s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()); 51 } 52 } 53 }
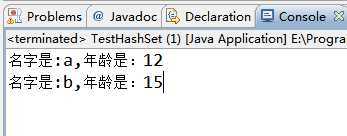
重写equals()和hashCode()方法,来实现去除年龄重复的测试类:
1 public class TestHashSet { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 //重写equals方法,来实现去除年龄重复的 4 HashSet<Student> hs=new HashSet<Student>(); 5 Student s1=new Student("a",12); 6 Student s2=new Student("b",15); 7 Student s3=new Student("c",12); 8 hs.add(s1); 9 hs.add(s2); 10 hs.add(s3); 11 for(Student stu:hs) 12 System.out.println("名字是:"+stu.getName()+",年龄是:"+stu.getAge()); 13 } 14 }
输出结果:
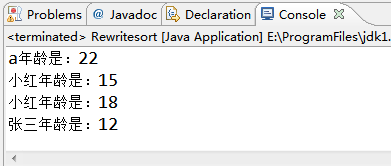
通过重写compare()方法来实现根据姓名排序,若姓名重复则根据年龄排序的测试类:
1 public class Rewritesort { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 Student s1=new Student("小红",18); 4 Student s2=new Student("张三",12); 5 Student s3=new Student("小红",15); 6 Student s4=new Student("a",22); 7 List<Student> lt=new ArrayList<Student>(); 8 lt.add(s1); 9 lt.add(s2); 10 lt.add(s3); 11 lt.add(s4); 12 //根据姓名和年龄进行排序 13 Collections.sort(lt,new Student()); 14 for(Student stu:lt){ 15 System.out.println(stu.getName()+"年龄是:"+stu.getAge()); 16 } 17 } 18 }
输出结果: