前言
我用的是最原始的Spring MVC使用方式,基于XML文件配置。
项目结构
导入依赖:
-
spring-webmvc:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc
-
javax.servlet-api:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/javax.servlet-api
web.xml:
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<!-- 配置DispatcherServlet -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- 配置初始化参数 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
spring-mvc.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 告知Spring框架在创建核心容器时需要扫描的包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.gzy.springmvctest"/>
<!-- 配置视图解析器 -->
<bean id="internalResourceViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
<!-- 开启Spring MVC对注解的支持 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
</beans>
webapp文件夹结构:
相关组件
在Spring MVC中,HandlerMapping(处理器映射器)、HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器)、ViewResolver(视图解析器)成为Spring MVC三大组件。
配置<mvc:annotation-driven>标签会自动加载RequestMappingHandlerMapping(处理映射器)和RequestMappingHandlerAdapter(处理适配器),可在Spring MVC的XML配置文件中使用<mvc:annotation-driven>标签代替HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter的注解配置,但是别的组件不会自动加载。
DispatcherServlet(前端控制器)
作用:接收请求、响应结果。相当于转发器、中央处理器。有了DispatcherServlet就减少了其它组件之间的耦合度。
不需要工程师开发,由框架提供。用户请求到达前端控制器,它就相当于MVC模式中的C(Controller),dispatcherServlet是整个流程控制的中心,由它调用其它组件处理用户的请求,dispatcherServlet的存在降低了组件之间的耦合性。
HandlerMapping(处理器映射器)
作用:根据请求的URL查找Handler。
不需要工程师开发,由框架提供。HandlerMapping负责根据用户请求找到相应的Handler。
SpringMVC提供了不同的映射器实现不同的映射方式:
-
配置文件的方式。
-
实现接口的方式。
-
注解的方式。
HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器)
作用:按照特定规则(HandlerAdapter要求的规则)去执行Handler。
不需要工程师开发,由框架提供。
通过HandlerAdapter对Handler进行执行,这是适配器模式的应用,通过扩展适配器可以对更多类型的Handler进行执行。
Handler(处理器)
作用:处理用户具体的业务请求。
需要工程师开发。Handler是继DispatcherServlet前端控制器的后端控制器,在DispatcherServlet的控制下Handler对具体的用户请求进行处理。
由于Handler涉及到具体的用户业务请求,所以一般情况需要工程师根据业务需求开发Handler。
编写Handler时需要按照HandlerAdapter的要求去做,这样适配器才可以去正确地执行Handler。
ViewResolver(视图解析器)
作用:进行视图解析,根据逻辑视图名解析成真正的View。
不需要工程师开发,由框架提供。ViewResolver负责将处理的结果生成View,ViewResolver首先根据逻辑视图名解析成物理视图名(即具体的页面地址),再生成View对象,最后对View进行渲染并将处理结果通过页面展示给用户。
SpringMVC框架提供了很多的View类型:jstlView、freemarkerView、pdfView等。
View(视图)
需要工程师开发。View是一个接口,实现类支持不同的View类型(Jsp、Freemarker、pdf...)
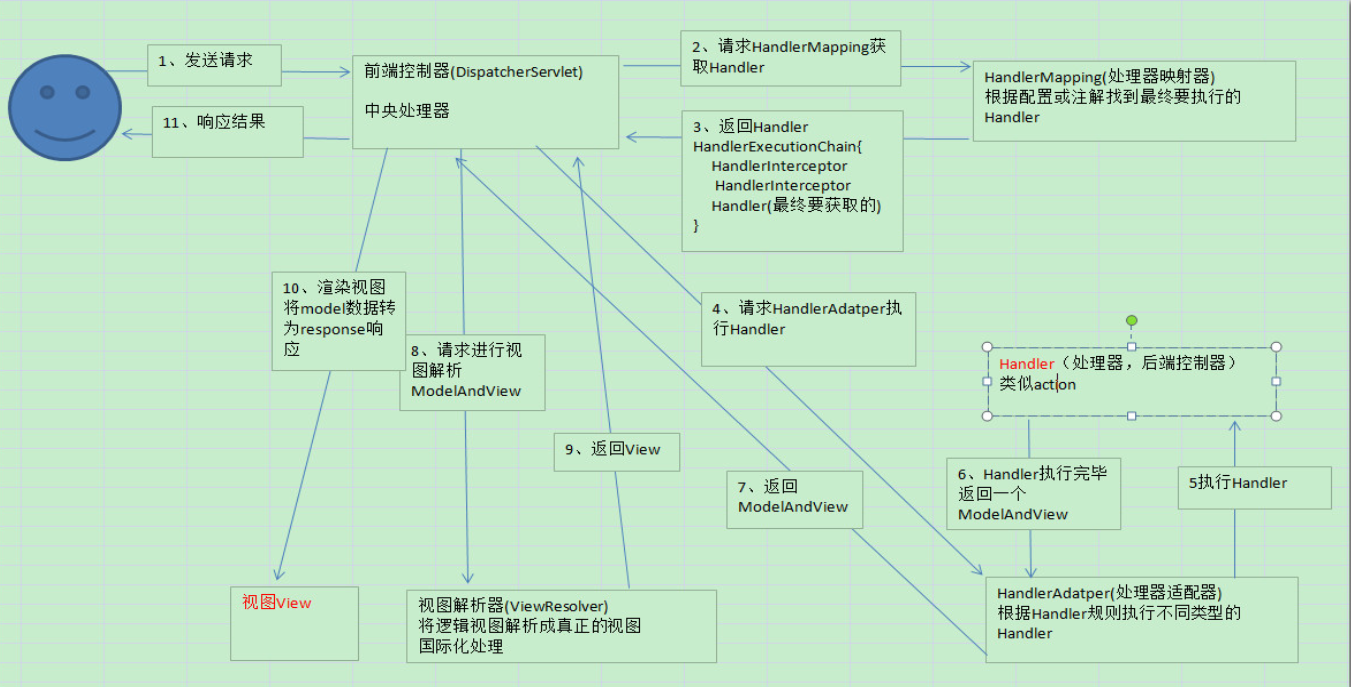
执行流程
Spring MVC是基于组件的方式来执行流程的。
源码分析
源码按Spring MVC的执行流程逐步分析(依照上面的流程图)。
第一步:
根据执行流程的步骤来,请求最先接触的是DispatcherServlet,它是整个Spring MVC的中央控制器。看名字可知它是一个Servlet,我这里没有指定<load-on-startup>参数,则默认是第一次访问时创建,所以当我第一次发送请求时才会创建DispatcherServlet。
既然DispatcherServlet是一个Servlet,我们来回顾一下Servlet的生命周期:
- 初始化:init方法。
- 处理请求:service方法。
- 销毁:destroy方法。
接下来看到DispatcherServlet的初始化init方法,它在间接父类HttpServletBean中,这个方法主要是进行一些最基础内容的初始化,并且提供了initServletBean方法供子类重写,FrameworkServlet类就对该方法进行了重写。
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// 设置DispatcherServlet的参数,就是<init-param>标签的内容
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// 子类重写
initServletBean();
}
接着寻找DispatcherServlet的service方法,它在父类FrameworkServlet中。先是获取请求的HTTP方法,并将其解析为一个HttpMethod对,HttpMethod是Spring MVC对HTTP方法的再封装。随后判断请求是否为PATCH方法,我们这里是GET方法,故进入父类(HttpServlet类)的service方法。
// FrameworkServlet类
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取请求的HTTP方法
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
在HttpServlet类的service方法中,其实也很简单,就是根据不同的HTTP方法进行不同的处理,我们这里进入的是doGet方法。
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
然后我们进入FramworkServlet类的doGet方法,里面没有什么逻辑,直接调用了另一个processRequest方法。而processRequest方法我们只需要关注它又调用了子类DispatcherServlet的doServlet方法。
// FrameworkServlet类
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 省略其他内容...
try {
// 子类DispatcherServlet实现了该方法
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
DispatcherServlet进到doService方法,这个方法也只需关注它调用了另一个doDispatch方法。
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 省略其他内容...
try {
// 分派处理请求的组件
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (requestPath != null) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.clearParsedRequestPath(request);
}
}
}
doDispatch是DispatcherServlet中最重要的方法,这个方法的主要作用是分派处理请求的组件。
// DispatcherServlet类
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
// 处理器执行链
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
// 是否为多部分类型请求
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
// 管理异步请求的处理
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
// 模型视图对象
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 检查是否需要将当前请求解析为多部分类型请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
// 是否解析为
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 决定使用哪个Handler来处理当前请求
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 决定使用哪个处理映射器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 获取当前请求的HTTP方法
String method = request.getMethod();
// 如果是GET或HEAD请求,就需要判断资源缓存是否过期
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 执行过前置拦截器
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 通过HandlerAdapter执行Handler
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 执行后置拦截器
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 视图解析器解析视图
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
我们先看到checkMultipart方法,它是用于检查是否需要将当前请求解析为多部分类型请求。先进行一个判断,如果multipartResolver(多部分请求解析器)不存在或者判断当前请求不是多部分类型的请求,就直接退出方法。反之则使用multipartResolver(多部分请求解析器)来解析该请求。
// DispatcherServlet类
// 检查是否需要将当前请求解析为多部分类型请求
protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
// 先判断是否有多部分类型解析器,只有当存在时才会解析当前请求
if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) {
if (WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class) != null) {
if (request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.REQUEST)) {
logger.trace("Request already resolved to MultipartHttpServletRequest, e.g. by MultipartFilter");
}
}
// 省略其他内容...
}
return request;
}
第二步:
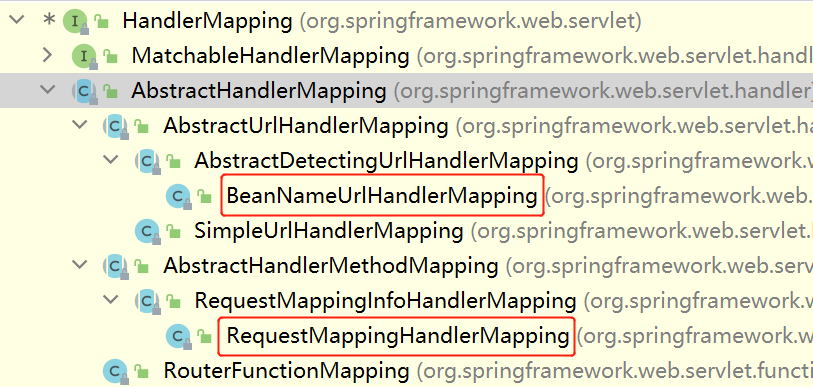
然后走到getHandler方法,第二步就是从该方法开始的。DispatcherServlet类中维护了一个名为handlerMappings的List集合,里面保存了两个默认的HandlerMapping(处理器映射器):一个是RequestMappingHandlerMapping,另个一个是BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping:用来处理通过注解来映射请求的Controller,例如@Controller、@RequestMapping等。
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:用来处理通过设置控制器Bean的name为请求URL路径的Controller。
getHandler方法会依次遍历每个HandlerMapping接口,直到某个HandlerMapping能获取到HandlerExecutionChain。因为我是使用注解配置的Controller,所以会使用RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现类。
// DispatcherServlet类
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
这里会有点绕!先进到RequestMappingHandlerMapping类间接抽象父类AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandler方法。然后会进入第一行代码的getHandlerInternal方法,这个方法在RequestMappingHandlerMapping类中,但是这方法又去到了父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的getHandlerInternal方法中。
HandlerMapping结构入下图所示:
// AbstractHandlerMapping类
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// 省略其他内容...
return executionChain;
}
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping类
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
request.removeAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
try {
return super.getHandlerInternal(request);
}
finally {
ProducesRequestCondition.clearMediaTypesAttribute(request);
}
}
先获取到请求的URL路径,然后通过lookupHandlerMethod方法来寻找Handler方法。
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 获取请求URL路径(这里是/hello)
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 根据请求的URL路径寻找Handler中对应的映射方法
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
暂停一下!这里需要先讲解一下mappingRegistry对象。
先介绍几个跟Handler方法有关的类:
- MappingRegistry:表示映射注册中心。里面保存了所有注册的映射(MappingRegistration)。
- MappingRegistration:表示一个映射。里面存有请求映射信息(RequestMappingInfo)以及映射方法(HandlerMethod)。
- HandlerMethod:表示Handler的一个映射方法。对Handler方法的封装,存有Handler方法的Method对象(用于反射)、方法参数、所在类的Class对象、所在类等信息。
- RequestMappingInfo:存有映射方法的映射信息,其实就是存储的@RequestMapping注解的属性。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
// Bean init前调用
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
// 初始化所有Handler方法
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
// 获取所有候选Bean然后依次判断是否是Handler Bean
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
// 真正处理Handler方法的初始化
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
// 获取所有候选Bean名称(其实就是IOC容器中所有的Bean的名称)
protected String[] getCandidateBeanNames() {
// detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts参数默认为false
return (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
// 从IOC容器中获取所有Bean(不管是否是Handler Bean)的名称,因为是根据Object类型的Bean
obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
}
// 判断该Bean是否是Handler Bean
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
// 通过Bean名称获取到对应Class对象
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
// isHandler方法作用就是判断是否为Handler
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
// 检测Handler中的方法是否为映射方法
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
// 省略其他内容...
}
isHandler方法主要作用是判断某个类是否是Handler(处理器),判断方法很简单,就是判断该类上是否标有@Controller或@RequestMapping注解。
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping类
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
detectHandlerMethods方法用来检测该指定Handler中的方法有哪些是映射方法,并将映射方法注册到一个名为mappingRegistry的Map集合中,其中Key为RequestMappingInfo,Value为MappingRegistration。
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
// 获取Handler的Class对象
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 筛选映射方法并存入Map集合中
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
// 将所有的映射方法处理后存入另一个Map集合中
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
// 注册进mappingRegistry集合中
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
// 注册Handler的映射方法
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping内部类MappingRegistry类
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
// 省略其他内容...
// 将一个映射存入映射注册中心
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directPaths, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
回到上面的lookupHandlerMethod方法,这里主要是通过请求的URL寻找对应的Handler映射方法。
Match:一个包装类,里面存有与请求匹配的RequestMappingInfo和对应的HandlerMethod。
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 存有与请求匹配的所有Match对象的集合
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
// 根据当前请求的URL获取所有对应的RequestMappingInfo对象的集合
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
// 在RequestMappingInfo对象的集合中再筛选出符合请求参数条件的,然后封装成Match添加至matches集合中
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
// 使用第一个匹配的Match对象
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
// 处理多个Match的情况
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 遍历当前请求URL所对应的所有HandlerMapping
for (T mapping : mappings) {
// 判断该HandlerMapping是否与当前请求所有参数都匹配,因为并不是通过URL获取的HandlerMapping都是符合要求的,请求还有其他的限制条件
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
// 将匹配的HandlerMapping与对应的HandlerMethod封装成一个Match对象,然后添加至matches集合中
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match,
this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().get(mapping).getHandlerMethod()));
}
}
}
第三步:
随后我们再次回到之前的getHandler方法中,通过getHandlerExecutionChain方法获取了一个包含Handler方法以及多个HandlerInterceptor(处理器拦截器)的HandlerExecutionChain(处理器执行链)。这里面涉及到一个类叫MappedInterceptor,这是映射拦截器,它带有路径模式匹配的HandlerInterceptor,也提供了匹配逻辑来测试拦截器是否适用于一个给定的请求路径。MappedInterceptor类被final关键字修饰,无法被继承,因此大多数的拦截器是否都是存在它内部,比如默认情况下Spring MVC会提供一个ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor(类型转换拦截器)并存入一个MappedInterceptor中,而所有的拦截器又会存储在AbstractHandlerMapping类的adaptedInterceptors集合中。
// AbstractHandlerMapping类
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
// 省略其他内容...
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
// 日志打印
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
// 判断是否要处理跨域问题
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);
config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config);
}
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
}
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
// 获取处理器执行链
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 初始化处理器执行链
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
// 遍历adaptedInterceptors集合中的拦截器,依次添加进HandlerExecutionChain的interceptorList集合中
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(request)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
谈谈这个HandlerExecutionChain,该类里面存储了Handler方法以及装有对应拦截器的List集合,还有前置处理方法、后置处理方法和完成触发方法。
public class HandlerExecutionChain {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(HandlerExecutionChain.class);
// Handler方法
private final Object handler;
// 拦截器
private final List<HandlerInterceptor> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>();
private int interceptorIndex = -1;
// 省略其他内容...
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptorList.size(); i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
return true;
}
void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable ModelAndView mv)
throws Exception {
for (int i = this.interceptorList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv);
}
}
void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Exception ex) {
for (int i = this.interceptorIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
try {
interceptor.afterCompletion(request, response, this.handler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
logger.error("HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion threw exception", ex2);
}
}
}
}