— I experienced so many great things.
— You gave me memories like dreams... But I have to leave now...
— One last request, can you...
— Help me solve a Codeforces problem?
— ......
— What?
Chtholly has been thinking about a problem for days:
If a number is palindrome and length of its decimal representation without leading zeros is even, we call it a zcy number. A number ispalindrome means when written in decimal representation, it contains no leading zeros and reads the same forwards and backwards. For example 12321 and 1221 are palindromes and 123 and 12451 are not. Moreover, 1221 is zcy number and 12321 is not.
Given integers k and p, calculate the sum of the k smallest zcy numbers and output this sum modulo p.
Unfortunately, Willem isn't good at solving this kind of problems, so he asks you for help!
The first line contains two integers k and p (1 ≤ k ≤ 105, 1 ≤ p ≤ 109).
Output single integer — answer to the problem.
2 100
33
5 30
15
In the first example, the smallest zcy number is 11, and the second smallest zcy number is 22.
In the second example, 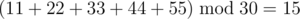 .
.
回文数系列题目(经典算法): http://blog.csdn.net/computer_liuyun/article/details/27967963
【题意】:求前k个偶数位回文数之和%p的值。
【分析】:POJ 1150/2402/3247同类题目。直接写个判断偶数位回文数的函数,将整数n逆转,逆转的方法就是利用求余%和/的思想,此题总有一个常错的地方,就是m的平方和立方可能会超范围所以一定要用long long 或者_int64即可。或者用字符串表示,可能更加通俗易懂。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; ll n,m,sum; ll a[15000]; ll huiwen(ll n)//倒过来和的数与原来相等,那么就是回文数 { ll ans=n,t=n;//ll ans=n 若不分偶数位,则为ans=0; while(t) { ans=ans*10+t%10; t/=10; } return ans; } int main() { cin>>n>>m; for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++) { sum=(sum+huiwen(i))%m; } printf("%lld ",sum%m); }

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e5+10; typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int,int> P; LL k,p; LL getnow(LL n) { char str[20] = {0}; sprintf(str,"%lld",n); int len = strlen(str); for(int i=len;i<len+len;i++) str[i] = str[2*len-i-1]; LL cnt = 0; sscanf(str,"%lld",&cnt); return cnt; } void solve() { LL ans = 0; for(int i=1;i<=k;i++) ans = (ans+getnow(i)) % p; // cout<<getnow(k)<<endl; cout<<ans<<endl; } int main() { // IO; cin>>k>>p; solve(); return 0; }
