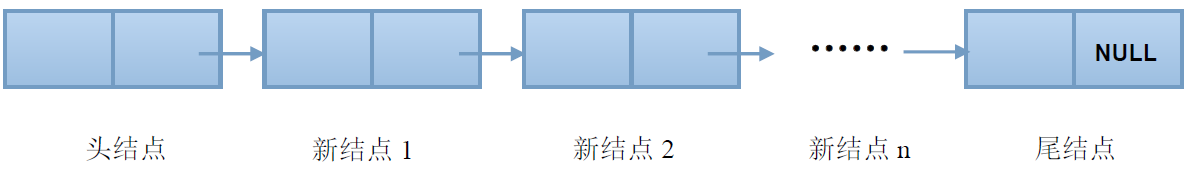
建立非循环单链表的过程总览
因为链表是离散存储的,每一个结点之间通过指针来链接。所以要想创建一个非循环单链表,应当首先确定一个头结点,在确定一个尾结点,在中间不断的开辟新的结点并存储相应的内容。
注意:本文中提到的头结点中不存储有效数值,尾结点的指针域为空,开辟新节点使用malloc函数实现。为了简便,在数据域中仅仅存储整型数据。开辟后的链表如图所示:
假设单链表中节点的结构体
typedef struct NODE { int data; // 数据域 struct NODE * Next; // 指针域 }Node, *pNode;
建立头结点和尾结点并循环创建中间结点
在创建链表过程中,不断的在头结点和尾结点之间插入新的结点,使用图解释为:
struct Node * 等价于下文代码中的 pNode struct Node 等价于下文代码中的 Node

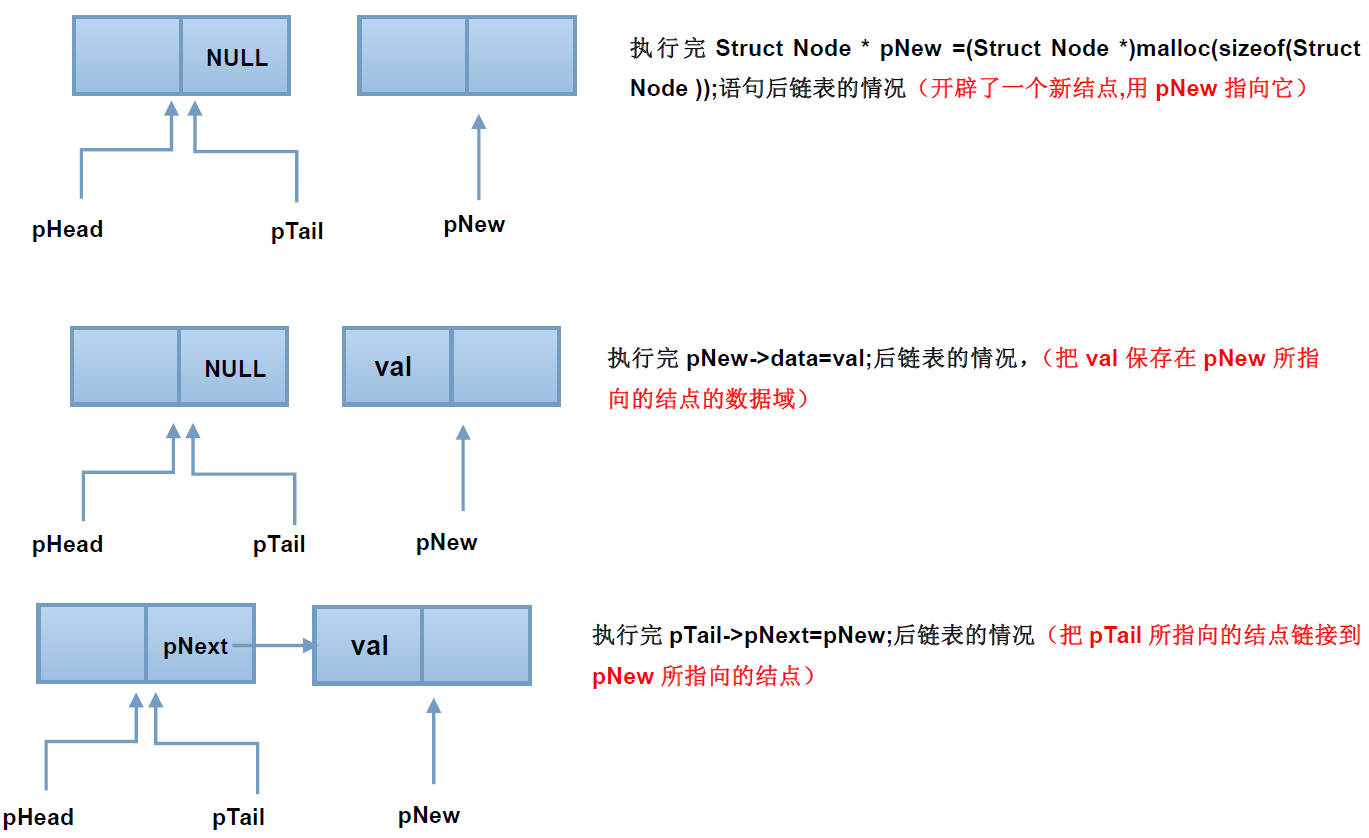
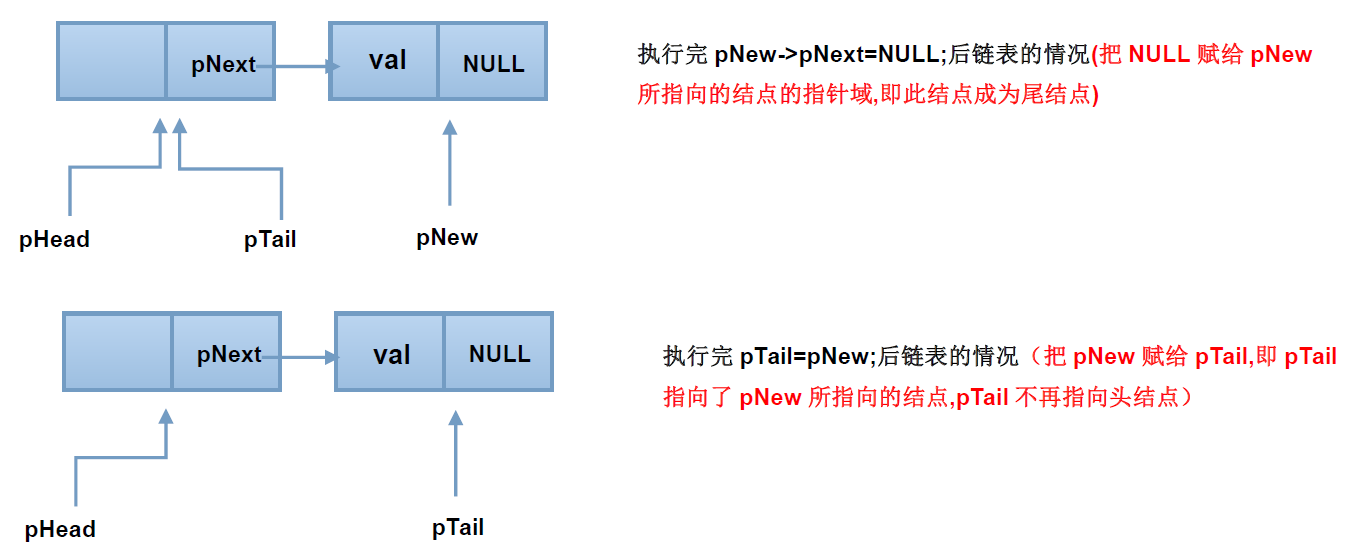

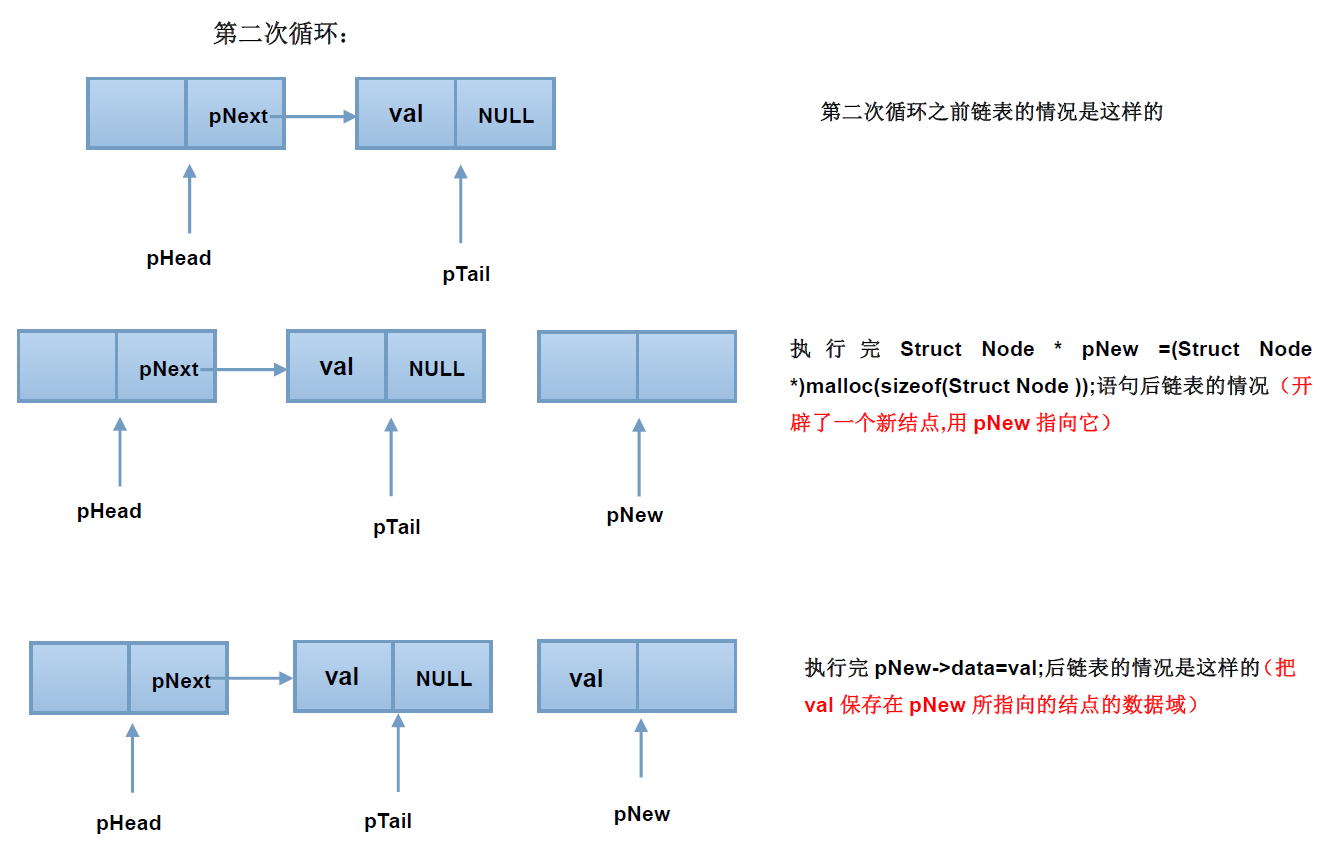
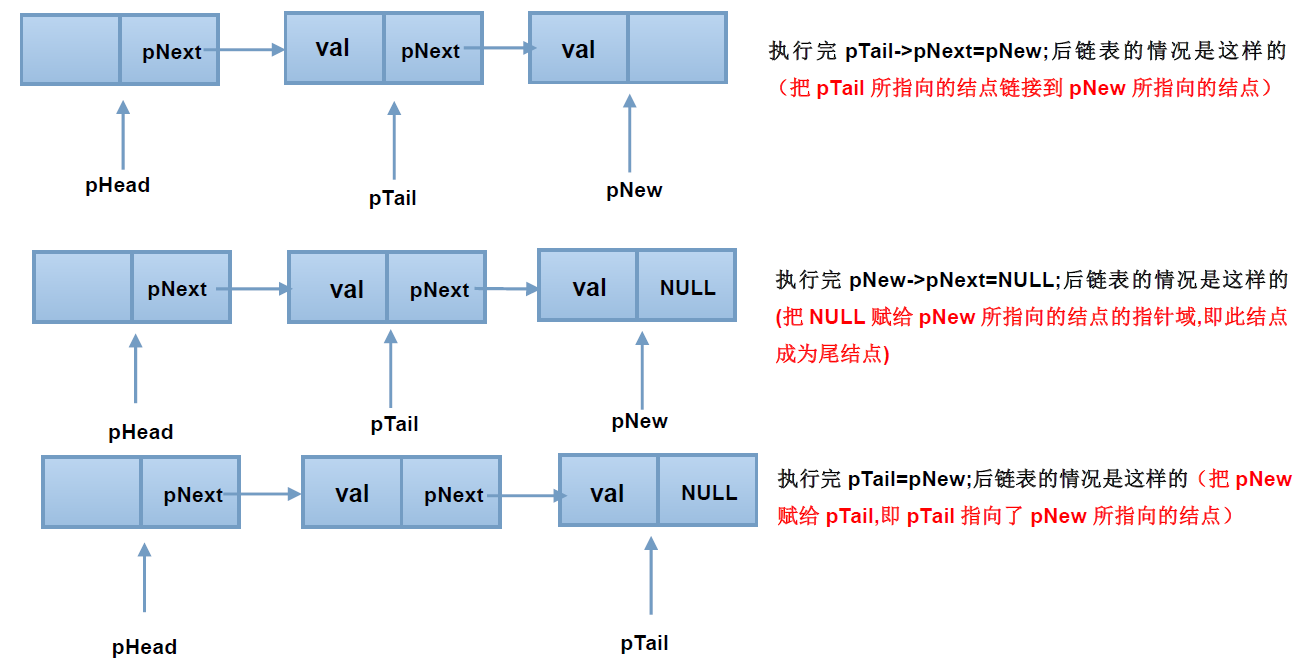
可以看到,新建店结点挂到了链表的最后,成为了尾结点,并且为指针pTail指向了它,在整个操作过程中,pNew只是个临时变量。
单链表基本函数:
创建一个非循环的单链表,采用后插入的方式
pNode Creat_List(void)//创建一个非循环的单链表,采用后插入的方式
{
int i, len, val;
pNode pHead, pTail, pNew; // pTail永远指向尾节点
pHead = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (NULL == pHead)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
pTail = pHead;
pTail->Next = NULL; // 置尾结点指针域为空
printf("请输入想要创建节点个数:len = ");
scanf("%d",&len);
for (i=0; i<len; i++)
{
pNew = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (NULL == pNew)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
printf("请输入插入节点%d的数值:val = ",i);
scanf("%d",&val);
pTail->Next = pNew;
pNew->data = val;
pTail = pNew;
pNew->Next = NULL;
}
return pHead;
}
遍历整个链表
void traverse_list(pNode pHead)//遍历整个链表
{
pNode p = pHead->Next;
while (NULL != p)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->Next;
}
}
在表头添加元素
void insert_pre_list(pNode pHead, int val)//在表头添加元素
{
pNode pNew = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (NULL == pNew)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
pNew->data = val;
pNew->Next = pHead->Next;
pHead->Next = pNew;
return;
}
在链表最后添加元素
void append_list(pNode pHead, int val) // 在链表最后添加元素
{
pNode pNew = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
pNode p = pHead;
if (NULL == pNew)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
pNew->data = val;
while (NULL != p->Next)
{
p = p->Next;
}
p->Next = pNew;
pNew->Next = NULL;
return;
}
目前已有元素的个数
int number_list(pNode pHead)// 目前已有元素的个数
{
int len = 0;
while (NULL != pHead->Next)
{
len++;
pHead = pHead->Next;
}
return len;
}
在某个位置前插入特定元素
int insert_list(pNode pHead, int loc, int val)// 在某个位置前插入特定元素
{
int len = number_list(pHead);
int i;
if (loc<1 || loc>len)
{
printf("查找位置失败!插入元素失败!
");
return 0;
}
pNode pNew;
pNew = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (NULL == pNew)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
for (i=0; i<loc-1; i++)
pHead = pHead->Next;
pNew->data = val;
pNew->Next = pHead->Next;
pHead->Next = pNew;
return 1;
}
判断链表是否为空
int is_NULL_list(pNode pHead) // 判断链表是否为空
{
if (NULL == pHead->Next)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
元素的排序
void sort_list(pNode pHead) // 元素的排序
{
pNode p, q;
int temp;
for (p=pHead->Next; p!=NULL; p=p->Next)
for (q=p->Next; q!=NULL; q=q->Next)
if (p->data > q->data)
{
temp = p->data;
p->data = q->data;
q->data = temp;
}
free(p);
free(q);
return;
}
查找是否存在特定数值的元素,并将元素第一次出现的位置下标返回主函数
int find_number_list(pNode pHead, int number, int * val) // 查找是否存在特定数值的元素,并将元素第一次出现的位置下标返回主函数
{
pNode p = pHead->Next;
int i = 0;
while (NULL != p)
{
i++;
if (p->data == number)
{
*val = i;
return 1;
}
p = p->Next;
}
free(p);
return 0;
}
删除某一个位置的元素,并将删除的元素返回主函数
int delete_loc_list(pNode pHead, int loc, int * val) // 删除某一个位置的元素,并将删除的元素返回主函数
{
pNode p;
int i;
if (loc<1 || loc>number_list(pHead) )
{
printf("删除第%d个元素失败!
",loc);
return 0;
}
for (i=0; i<loc-1; i++)
pHead = pHead->Next;
p = pHead->Next;
*val = p->data;
pHead->Next = p->Next;
free(p);
return 1;
}
显示某一个元素的前驱 注:元素不存在返回-1,前驱不存在返回0, 其余返回1
int pre_element_list(pNode pHead, int number, int * val) // 显示某一个元素的前驱 注:元素不存在返回-1,前驱不存在返回0, 其余返回1
{
int loc, i;
if (find_number_list(pHead, number, &loc))
{
if (1 == loc)
return 0;
for (i=0; i<loc-1; i++)
pHead = pHead->Next;
*val = pHead->data; // 前驱的数据域
return 1;
} else
return -1;
}
显示某一个元素的后继 注:元素不存在返回-1,后继不存在返回0, 其余返回1
int nex_element_list(pNode pHead, int number, int * val) // 显示某一个元素的后继 注:元素不存在返回-1,后继不存在返回0, 其余返回1
{
int loc, i;
if (find_number_list(pHead, number, &loc))
{
if (loc == number_list(pHead))
return 0;
for (i=0; i<loc+1; i++)
pHead = pHead->Next;
*val = pHead->data; // 后继的数据域
return 1;
} else
return -1;
}
销毁整个链表
void destroy_list(pNode pHead) // 销毁整个链表
{
pNode p;
while (NULL != pHead->Next)
{
p = pHead->Next;
pHead->Next = p->Next;
free(p);
}
printf("链表销毁成功!
");
}
整体表示:
Link.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct NODE
{
int data; // 数据域
struct NODE * Next; // 指针域
}Node, *pNode;
pNode Creat_List(void);//创建一个非循环的单链表,采用后插入的方式
void traverse_list(pNode pHead);//遍历整个链表
void insert_pre_list(pNode pHead, int val); //在表头添加元素
void append_list(pNode pHead, int val); // 在链表最后添加元素
int number_list(pNode pHead);// 目前已有元素的个数
int insert_list(pNode pHead, int loc, int val);// 在某个位置前插入特定元素
int is_NULL_list(pNode pHead);// 判断链表是否为空
void sort_list(pNode pHead);// 元素的排序
int find_number_list(pNode pHead, int number, int * val);// 查找是否存在特定数值的元素,并将元素第一次出现的位置下标返回主函数
int delete_loc_list(pNode pHead, int loc, int * val);// 删除某一个位置的元素,并将删除的元素返回主函数
int pre_element_list(pNode pHead, int number, int * val);// 显示某一个元素的前驱 注:元素不存在返回-1,前驱不存在返回0, 其余返回1
int nex_element_list(pNode pHead, int number, int * val);// 显示某一个元素的后继 注:元素不存在返回-1,后继不存在返回0, 其余返回1
void destroy_list(pNode pHead);// 销毁整个链表
Link.c
#include "Link.h"
pNode Creat_List(void)//创建一个非循环的单链表,采用后插入的方式
{
int i, len, val;
pNode pHead, pTail, pNew; // pTail永远指向尾节点
pHead = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (NULL == pHead)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
pTail = pHead;
pTail->Next = NULL; // 置尾结点指针域为空
printf("请输入想要创建节点个数:len = ");
scanf("%d",&len);
for (i=0; i<len; i++)
{
pNew = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (NULL == pNew)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
printf("请输入插入节点%d的数值:val = ",i);
scanf("%d",&val);
pTail->Next = pNew;
pNew->data = val;
pTail = pNew;
pNew->Next = NULL;
}
return pHead;
}
void traverse_list(pNode pHead)//遍历整个链表
{
pNode p = pHead->Next;
while (NULL != p)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->Next;
}
}
void insert_pre_list(pNode pHead, int val)//在表头添加元素
{
pNode pNew = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (NULL == pNew)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
pNew->data = val;
pNew->Next = pHead->Next;
pHead->Next = pNew;
return;
}
void append_list(pNode pHead, int val) // 在链表最后添加元素
{
pNode pNew = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
pNode p = pHead;
if (NULL == pNew)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
pNew->data = val;
while (NULL != p->Next)
{
p = p->Next;
}
p->Next = pNew;
pNew->Next = NULL;
return;
}
int number_list(pNode pHead)// 目前已有元素的个数
{
int len = 0;
while (NULL != pHead->Next)
{
len++;
pHead = pHead->Next;
}
return len;
}
int insert_list(pNode pHead, int loc, int val)// 在某个位置前插入特定元素
{
int len = number_list(pHead);
int i;
if (loc<1 || loc>len)
{
printf("查找位置失败!插入元素失败!
");
return 0;
}
pNode pNew;
pNew = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (NULL == pNew)
{
printf("动态内存分配失败!程序终止!
");
exit(-1);
}
for (i=0; i<loc-1; i++)
pHead = pHead->Next;
pNew->data = val;
pNew->Next = pHead->Next;
pHead->Next = pNew;
return 1;
}
int is_NULL_list(pNode pHead) // 判断链表是否为空
{
if (NULL == pHead->Next)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
void sort_list(pNode pHead) // 元素的排序
{
pNode p, q;
int temp;
for (p=pHead->Next; p!=NULL; p=p->Next)
for (q=p->Next; q!=NULL; q=q->Next)
if (p->data > q->data)
{
temp = p->data;
p->data = q->data;
q->data = temp;
}
free(p);
free(q);
return;
}
int find_number_list(pNode pHead, int number, int * val) // 查找是否存在特定数值的元素,并将元素第一次出现的位置下标返回主函数
{
pNode p = pHead->Next;
int i = 0;
while (NULL != p)
{
i++;
if (p->data == number)
{
*val = i;
return 1;
}
p = p->Next;
}
free(p);
return 0;
}
int delete_loc_list(pNode pHead, int loc, int * val) // 删除某一个位置的元素,并将删除的元素返回主函数
{
pNode p;
int i;
if (loc<1 || loc>number_list(pHead) )
{
printf("删除第%d个元素失败!
",loc);
return 0;
}
for (i=0; i<loc-1; i++)
pHead = pHead->Next;
p = pHead->Next;
*val = p->data;
pHead->Next = p->Next;
free(p);
return 1;
}
int pre_element_list(pNode pHead, int number, int * val) // 显示某一个元素的前驱 注:元素不存在返回-1,前驱不存在返回0, 其余返回1
{
int loc, i;
if (find_number_list(pHead, number, &loc))
{
if (1 == loc)
return 0;
for (i=0; i<loc-1; i++)
pHead = pHead->Next;
*val = pHead->data; // 前驱的数据域
return 1;
} else
return -1;
}
int nex_element_list(pNode pHead, int number, int * val) // 显示某一个元素的后继 注:元素不存在返回-1,后继不存在返回0, 其余返回1
{
int loc, i;
if (find_number_list(pHead, number, &loc))
{
if (loc == number_list(pHead))
return 0;
for (i=0; i<loc+1; i++)
pHead = pHead->Next;
*val = pHead->data; // 后继的数据域
return 1;
} else
return -1;
}
void destroy_list(pNode pHead) // 销毁整个链表
{
pNode p;
while (NULL != pHead->Next)
{
p = pHead->Next;
pHead->Next = p->Next;
free(p);
}
printf("链表销毁成功!
");
}
main.c
#include "Link.h"
int main()
{
int val;
/* =======创建一个简单的单链表======== */
pNode pHead = NULL;
pHead = Creat_List(); //创建一个非循环的单链表,采用后插入的方式
traverse_list(pHead); //遍历整个链表
/* =========在表头添加元素========== */
insert_pre_list(pHead, 99);//在表头添加元素
traverse_list(pHead); //遍历整个链表
/* =========在表末尾添加元素========== */
append_list(pHead, 88); // 在链表最后添加元素
traverse_list(pHead); //遍历整个链表
/* =========在某个位置前插入特定元素========== */
if ( insert_list(pHead, 4, 22) ) // 在某个位置前插入特定元素
printf("插入元素成功!
");
traverse_list(pHead); //遍历整个链表
/* =========链表的长度========== */
printf("该链表拥有%d个元素!
",number_list(pHead));
/* =========链表排序========== */
sort_list(pHead);
traverse_list(pHead); //遍历整个链表
/* =========链表中查找目标元素========== */
if ( find_number_list(pHead, 9, &val) )
printf("目标元素的下标是:%d
",val);
else
printf("目标元素不存在!
");
/* =========链表中删除目标元素========== */
if ( delete_loc_list(pHead, 3, &val) )
printf("删除元素成功,删除的元素是:%d
",val);
traverse_list(pHead); //遍历整个链表
/* =========链表中查找目标元素前驱========== */
if ( 0 == pre_element_list(pHead, 9, &val) )
printf("目标元素前驱不存在!
");
else if (-1 == pre_element_list(pHead, 9, &val))
printf("查找元素失败!目标元素不存在!
",val);
else
printf("目标元素的前驱是:%d
",val);
/* =========链表中查找目标元素后继========== */
if ( 0 == nex_element_list(pHead, 9, &val) )
printf("目标元素后继不存在!
");
else if (-1 == nex_element_list(pHead, 9, &val))
printf("查找元素失败!目标元素不存在!
",val);
else
printf("目标元素的后继是:%d
",val);
/* =========销毁整个链表========== */
destroy_list(pHead);
traverse_list(pHead); //遍历整个链表
return 0;
}
参考文献:
[1] https://wenku.baidu.com/view/9efe250bc281e53a5802ffc3.html
RR