基本示例
这里有一个 Vue 组件的示例:
// 定义一个名为 button-counter 的新组件
Vue.component('button-counter', {
data: function () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
template: '<button v-on:click="count++">You clicked me {{ count }} times.</button>'
})
组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,且带有一个名字:在这个例子中是 <button-counter>。
我们可以在一个通过 new Vue 创建的 Vue 根实例中,把这个组件作为自定义元素来使用:
<div id="components-demo">
<button-counter></button-counter>
</div>
new Vue({ el: '#components-demo' })
因为组件是可复用的 Vue 实例,所以它们与 new Vue 接收相同的选项,例如 data、computed、watch、methods 以及生命周期钩子等
。仅有的例外是像 el 这样根实例特有的选项。
own:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>组件的创建</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div class="header"></div> <!-- 组件可复用性强 --> <Vheader></Vheader> <Vheader></Vheader> </div> <script src="./js/vue.js" type="text/javascript"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> //组件的创建 Vue.component('Vheader', { data: function () { //必须要return,哪怕是空对象 return { } }, template: ` <div clss='header'> <div clss ='w'> <div class='w-1'> <img src='./images/6.png'> </div> <div class='w-r'> <button>登录</button> <button>注册</button> </div> </div> </div> ` }) var app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { }, methods: { }, computed: { } }) </script> </body> </html>
具体页面使用
1.引入子组件

2.在 components 中配置子组件不然不显示

3.放到页面上使用
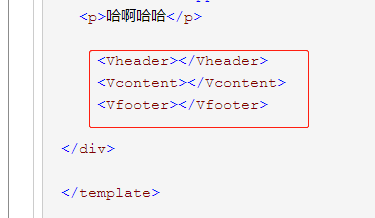
<!--一个组件有三部分组成-->
<!-- 页面的结构 -->
<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>{{ msg }}</h3>
<div class="app"></div>
<p>哈啊哈哈</p>
<Vheader></Vheader>
<Vcontent></Vcontent>
<Vfooter></Vfooter>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 1.引入子组件
import Vheader from './components/Vheader'
import Vcontent from './components/Vcontent'
import Vfooter from './components/Vfooter'
//页面的业务逻辑
export default {
name:'App',
data(){
return{
msg:'Hello 组件'
}
},
methods:{
},
computed:{
},
//配置子组件不然不显示
components:{
Vheader,
Vcontent,
Vfooter,
}
}
</script>>
<style >
</style>
子组件页面(头,内容,页脚):
头:
<template>
<header class="wrap">
<h3>头标题</h3>
</header>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'Vheader',
data(){
return{
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
h3{
color: red
}
</style>
内容:
<template> <content class="wrap"> <h4>我是中心内容</h4> </content> </template> <script> export default { name:'Vcontent', data(){ return{ } } } </script> <style> h4{ color: blue } </style>
页脚:
<template> <footer class="wrap"> <h5> 我是footer页脚</h5> </footer> </template> <script> export default { name:'Vfooter', data(){ return{ } } } </script> <style> h5{ color: blueviolet } </style>
组件的复用
你可以将组件进行任意次数的复用:
<div id="components-demo">
<button-counter></button-counter>
<button-counter></button-counter>
<button-counter></button-counter>
</div>

注意当点击按钮时,每个组件都会各自独立维护它的 count。
因为你每用一次组件,就会有一个它的新实例被创建。
data 必须是一个函数
当我们定义这个 <button-counter> 组件时,你可能会发现它的 data 并不是像这样直接提供一个对象:
data: {
count: 0
}
取而代之的是,一个组件的 data 选项必须是一个函数,因此每个实例可以维护一份被返回对象的独立的拷贝:
data: function () {
return {
count: 0
}
}
如果 Vue 没有这条规则,点击一个按钮就可能会像如下代码一样影响到其它所有实例:

组件的组织
通常一个应用会以一棵嵌套的组件树的形式来组织:

例如,你可能会有页头、侧边栏、内容区等组件,每个组件又包含了其它的像导航链接、博文之类的组件。
为了能在模板中使用,这些组件必须先注册以便 Vue 能够识别。
这里有两种组件的注册类型:全局注册和局部注册。至此,我们的组件都只是通过 Vue.component 全局注册的:
Vue.component('my-component-name', {
// ... options ...
})
全局注册的组件可以用在其被注册之后的任何 (通过 new Vue) 新创建的 Vue 根实例,
也包括其组件树中的所有子组件的模板中。
到目前为止,关于组件注册你需要了解的就这些了,
