python基础
生成式
列表生成式 格式 [表达式 for 表达式 in 迭代对象 (可加判断)]
原:
1 res1 = [] 2 for i in range(1,5): 3 res1.append(i) 4 print(res1)
改:
1 res2 = [i for i in range(1,5)] 2 print(res2)
字典生成式 格式 {key:value for 表达式 in 迭代对象 (可加判断)}
a = "adasdsasad" b = "asdasdasdg" dict = {x:y for x,y in zip(a,b) if x==y} print(dict)#{'a': 'a', 's': 's'}
集合生成式
ccc = {x for x in range(50) if x <20}
print(ccc)#{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19}
生成器推导式 (生成元祖) 一个生成器只能运行一次,只能迭代一次,第二次迭代就没了
t = (x for x in range(10) if x >2) print(t)#<generator object <genexpr> at 0x0000000001E992B0>生成器对象 print(tuple(t))#(3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) for i in t: print("再次使用生成器",i)#为空,因为生成器只能运行一次
模块
自定义模块
自己写的python代码组成的模块
常用模块
python自带的模块
https://www.cnblogs.com/RainBol/p/9505438.html
第三方模块
pip式傻瓜安装:python定义第三方的模块程序/命令
pip list 查看pip所有的安装模块
pip freeze>my_pip.txt 把所有的pip模块导出
pip install -r my_pip.txt 指定文件导入pip
手动安装:对应pip源下载
指定同一python版本:
xxx.tar.gz 下载下来,先解压找到setup.py文件,cmd,执行python setup.py install
xxx.whl 下载下来直接cmd,执行pip install xxxx.whl
指定对不同python版本安装:
python3.6 -m pip install xxxx.whl
python2.7 m pip install xxxx.whl
pycharm手动安装
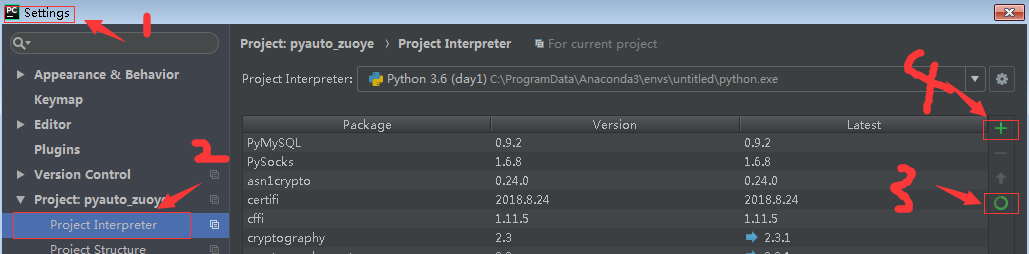
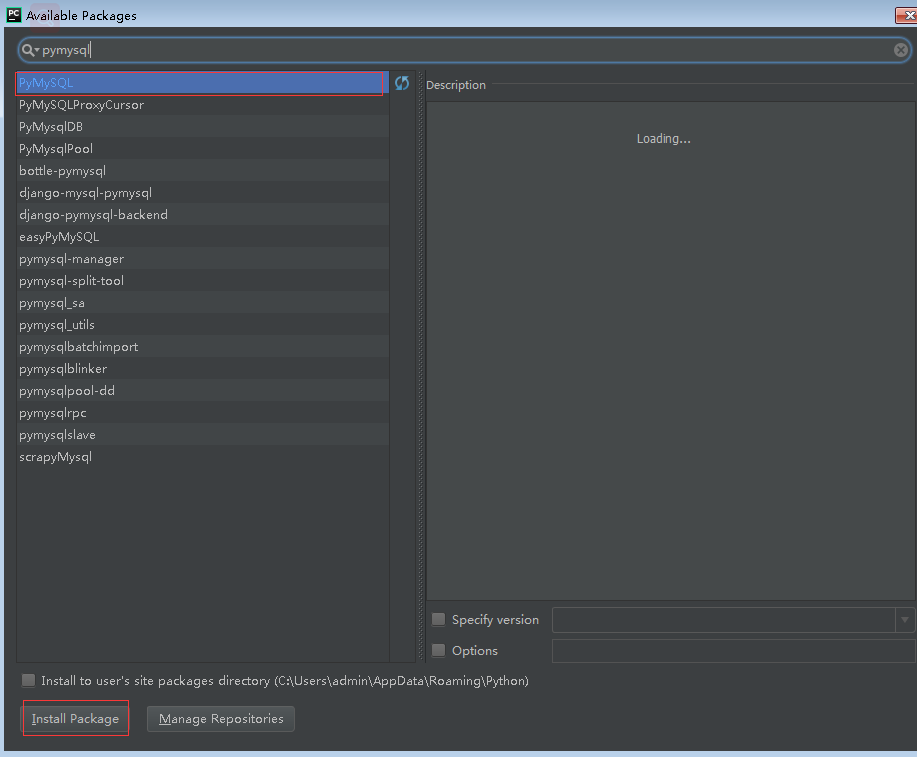
pipy上传 将自己写好的程序上传到pipy源上,以后我们只要pip install自己的源就可以了
1.注册pipy保证可用https://pypi.org/
2.下载需要打包的源:

''' @File : a.py @Copyright : Rainbol @Date : 2019/8/15 @Desc : ''' #!/usr/bin/env python """ Setuptools bootstrapping installer. Maintained at https://github.com/pypa/setuptools/tree/bootstrap. Run this script to install or upgrade setuptools. This method is DEPRECATED. Check https://github.com/pypa/setuptools/issues/581 for more details. """ import os import shutil import sys import tempfile import zipfile import optparse import subprocess import platform import textwrap import contextlib from distutils import log try: from urllib.request import urlopen except ImportError: from urllib2 import urlopen try: from site import USER_SITE except ImportError: USER_SITE = None # 33.1.1 is the last version that supports setuptools self upgrade/installation. DEFAULT_VERSION = "33.1.1" DEFAULT_URL = "https://pypi.io/packages/source/s/setuptools/" DEFAULT_SAVE_DIR = os.curdir DEFAULT_DEPRECATION_MESSAGE = "ez_setup.py is deprecated and when using it setuptools will be pinned to {0} since it's the last version that supports setuptools self upgrade/installation, check https://github.com/pypa/setuptools/issues/581 for more info; use pip to install setuptools" MEANINGFUL_INVALID_ZIP_ERR_MSG = 'Maybe {0} is corrupted, delete it and try again.' log.warn(DEFAULT_DEPRECATION_MESSAGE.format(DEFAULT_VERSION)) def _python_cmd(*args): """ Execute a command. Return True if the command succeeded. """ args = (sys.executable,) + args return subprocess.call(args) == 0 def _install(archive_filename, install_args=()): """Install Setuptools.""" with archive_context(archive_filename): # installing log.warn('Installing Setuptools') if not _python_cmd('setup.py', 'install', *install_args): log.warn('Something went wrong during the installation.') log.warn('See the error message above.') # exitcode will be 2 return 2 def _build_egg(egg, archive_filename, to_dir): """Build Setuptools egg.""" with archive_context(archive_filename): # building an egg log.warn('Building a Setuptools egg in %s', to_dir) _python_cmd('setup.py', '-q', 'bdist_egg', '--dist-dir', to_dir) # returning the result log.warn(egg) if not os.path.exists(egg): raise IOError('Could not build the egg.') class ContextualZipFile(zipfile.ZipFile): """Supplement ZipFile class to support context manager for Python 2.6.""" def __enter__(self): return self def __exit__(self, type, value, traceback): self.close() def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): """Construct a ZipFile or ContextualZipFile as appropriate.""" if hasattr(zipfile.ZipFile, '__exit__'): return zipfile.ZipFile(*args, **kwargs) return super(ContextualZipFile, cls).__new__(cls) @contextlib.contextmanager def archive_context(filename): """ Unzip filename to a temporary directory, set to the cwd. The unzipped target is cleaned up after. """ tmpdir = tempfile.mkdtemp() log.warn('Extracting in %s', tmpdir) old_wd = os.getcwd() try: os.chdir(tmpdir) try: with ContextualZipFile(filename) as archive: archive.extractall() except zipfile.BadZipfile as err: if not err.args: err.args = ('', ) err.args = err.args + ( MEANINGFUL_INVALID_ZIP_ERR_MSG.format(filename), ) raise # going in the directory subdir = os.path.join(tmpdir, os.listdir(tmpdir)[0]) os.chdir(subdir) log.warn('Now working in %s', subdir) yield finally: os.chdir(old_wd) shutil.rmtree(tmpdir) def _do_download(version, download_base, to_dir, download_delay): """Download Setuptools.""" py_desig = 'py{sys.version_info[0]}.{sys.version_info[1]}'.format(sys=sys) tp = 'setuptools-{version}-{py_desig}.egg' egg = os.path.join(to_dir, tp.format(**locals())) if not os.path.exists(egg): archive = download_setuptools(version, download_base, to_dir, download_delay) _build_egg(egg, archive, to_dir) sys.path.insert(0, egg) # Remove previously-imported pkg_resources if present (see # https://bitbucket.org/pypa/setuptools/pull-request/7/ for details). if 'pkg_resources' in sys.modules: _unload_pkg_resources() import setuptools setuptools.bootstrap_install_from = egg def use_setuptools( version=DEFAULT_VERSION, download_base=DEFAULT_URL, to_dir=DEFAULT_SAVE_DIR, download_delay=15): """ Ensure that a setuptools version is installed. Return None. Raise SystemExit if the requested version or later cannot be installed. """ to_dir = os.path.abspath(to_dir) # prior to importing, capture the module state for # representative modules. rep_modules = 'pkg_resources', 'setuptools' imported = set(sys.modules).intersection(rep_modules) try: import pkg_resources pkg_resources.require("setuptools>=" + version) # a suitable version is already installed return except ImportError: # pkg_resources not available; setuptools is not installed; download pass except pkg_resources.DistributionNotFound: # no version of setuptools was found; allow download pass except pkg_resources.VersionConflict as VC_err: if imported: _conflict_bail(VC_err, version) # otherwise, unload pkg_resources to allow the downloaded version to # take precedence. del pkg_resources _unload_pkg_resources() return _do_download(version, download_base, to_dir, download_delay) def _conflict_bail(VC_err, version): """ Setuptools was imported prior to invocation, so it is unsafe to unload it. Bail out. """ conflict_tmpl = textwrap.dedent(""" The required version of setuptools (>={version}) is not available, and can't be installed while this script is running. Please install a more recent version first, using 'easy_install -U setuptools'. (Currently using {VC_err.args[0]!r}) """) msg = conflict_tmpl.format(**locals()) sys.stderr.write(msg) sys.exit(2) def _unload_pkg_resources(): sys.meta_path = [ importer for importer in sys.meta_path if importer.__class__.__module__ != 'pkg_resources.extern' ] del_modules = [ name for name in sys.modules if name.startswith('pkg_resources') ] for mod_name in del_modules: del sys.modules[mod_name] def _clean_check(cmd, target): """ Run the command to download target. If the command fails, clean up before re-raising the error. """ try: subprocess.check_call(cmd) except subprocess.CalledProcessError: if os.access(target, os.F_OK): os.unlink(target) raise def download_file_powershell(url, target): """ Download the file at url to target using Powershell. Powershell will validate trust. Raise an exception if the command cannot complete. """ target = os.path.abspath(target) ps_cmd = ( "[System.Net.WebRequest]::DefaultWebProxy.Credentials = " "[System.Net.CredentialCache]::DefaultCredentials; " '(new-object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("%(url)s", "%(target)s")' % locals() ) cmd = [ 'powershell', '-Command', ps_cmd, ] _clean_check(cmd, target) def has_powershell(): """Determine if Powershell is available.""" if platform.system() != 'Windows': return False cmd = ['powershell', '-Command', 'echo test'] with open(os.path.devnull, 'wb') as devnull: try: subprocess.check_call(cmd, stdout=devnull, stderr=devnull) except Exception: return False return True download_file_powershell.viable = has_powershell def download_file_curl(url, target): cmd = ['curl', url, '--location', '--silent', '--output', target] _clean_check(cmd, target) def has_curl(): cmd = ['curl', '--version'] with open(os.path.devnull, 'wb') as devnull: try: subprocess.check_call(cmd, stdout=devnull, stderr=devnull) except Exception: return False return True download_file_curl.viable = has_curl def download_file_wget(url, target): cmd = ['wget', url, '--quiet', '--output-document', target] _clean_check(cmd, target) def has_wget(): cmd = ['wget', '--version'] with open(os.path.devnull, 'wb') as devnull: try: subprocess.check_call(cmd, stdout=devnull, stderr=devnull) except Exception: return False return True download_file_wget.viable = has_wget def download_file_insecure(url, target): """Use Python to download the file, without connection authentication.""" src = urlopen(url) try: # Read all the data in one block. data = src.read() finally: src.close() # Write all the data in one block to avoid creating a partial file. with open(target, "wb") as dst: dst.write(data) download_file_insecure.viable = lambda: True def get_best_downloader(): downloaders = ( download_file_powershell, download_file_curl, download_file_wget, download_file_insecure, ) viable_downloaders = (dl for dl in downloaders if dl.viable()) return next(viable_downloaders, None) def download_setuptools( version=DEFAULT_VERSION, download_base=DEFAULT_URL, to_dir=DEFAULT_SAVE_DIR, delay=15, downloader_factory=get_best_downloader): """ Download setuptools from a specified location and return its filename. `version` should be a valid setuptools version number that is available as an sdist for download under the `download_base` URL (which should end with a '/'). `to_dir` is the directory where the egg will be downloaded. `delay` is the number of seconds to pause before an actual download attempt. ``downloader_factory`` should be a function taking no arguments and returning a function for downloading a URL to a target. """ # making sure we use the absolute path to_dir = os.path.abspath(to_dir) zip_name = "setuptools-%s.zip" % version url = download_base + zip_name saveto = os.path.join(to_dir, zip_name) if not os.path.exists(saveto): # Avoid repeated downloads log.warn("Downloading %s", url) downloader = downloader_factory() downloader(url, saveto) return os.path.realpath(saveto) def _build_install_args(options): """ Build the arguments to 'python setup.py install' on the setuptools package. Returns list of command line arguments. """ return ['--user'] if options.user_install else [] def _parse_args(): """Parse the command line for options.""" parser = optparse.OptionParser() parser.add_option( '--user', dest='user_install', action='store_true', default=False, help='install in user site package') parser.add_option( '--download-base', dest='download_base', metavar="URL", default=DEFAULT_URL, help='alternative URL from where to download the setuptools package') parser.add_option( '--insecure', dest='downloader_factory', action='store_const', const=lambda: download_file_insecure, default=get_best_downloader, help='Use internal, non-validating downloader' ) parser.add_option( '--version', help="Specify which version to download", default=DEFAULT_VERSION, ) parser.add_option( '--to-dir', help="Directory to save (and re-use) package", default=DEFAULT_SAVE_DIR, ) options, args = parser.parse_args() # positional arguments are ignored return options def _download_args(options): """Return args for download_setuptools function from cmdline args.""" return dict( version=options.version, download_base=options.download_base, downloader_factory=options.downloader_factory, to_dir=options.to_dir, ) def main(): """Install or upgrade setuptools and EasyInstall.""" options = _parse_args() archive = download_setuptools(**_download_args(options)) return _install(archive, _build_install_args(options)) if __name__ == '__main__': sys.exit(main())
3.将步骤2 的代码放到一个py文件并执行
4.文件整理,将需要打包的文件放到一个文件统一文件夹中,里面要空的__init__.py文件
5.打包:在文件夹的同级目录再建立一个setup.py文件,里面写入代码,并执行python setup.py sdist,会生成一个dist文件和名字.egg-info文件

from setuptools import setup setup( name='你的项目源名称', #xxx version='项目版本',#1.0 description='项目的描述', #xxx author='作者',#rainbol author_email='xxx@qq.com', #邮箱 url='https://www.cnblogs.com/RainBol/', #相应的地址 py_modules=['rainbol.test']) #要打包的文件目录,我这里放在rainbol文件的test.py文件,也可以选择多个
6.pip install twine执行
7.上传命令 twine upload dist/* 输入pipy账号密码
8.查看
xpinyin模块 把中文变成中文拼音
import xpinyin s= xpinyin.Pinyin() print(s.get_pinyin("饕餮",""))
python操作mysql数据库模块
pip install pymysql
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host="192.168.1.1", password="123456", user="root", db="nihao", port=3306, charset="utf8", autocommit=True) cur = conn.cursor() # 建立游标,理解成取件员,cur = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)参数cursor表示选择字典游标类型
#循环游标 取到数据库的每行数据 劣势:占用大量内存,优势:减少每次连接mysql交互频率
for i in cur:
print(i)
# 查 cur.execute('show tables;') # 执行sql语句不会返回结果 print(cur.fetchall()) # 获取数据库中的结果,保存在二维元祖中 print(cur.fetchone()) # 获取一条数据,如果数据返回多条,直取第一条,返回一个一维元祖 fetchmany(n)表示想拿几条填几条 print(cur.description) # 获取表结构信息 # 增,删,改 sql = cur.execute('insert into xxx VALUES xxx') #单条单个
sql = cur.execute('insert into class(id,username,password) values(%s,%s,%s),('1','rainbol','123456')) #以传参的形式传给execute,单个参数不需要元祖形式,多个参数必须元祖形式,实现单条多个
list = (
('1','rainbol1','123456'),
('2','rainbol2','12345678')
('3','rainbol3','12345687')
)
sql = cur.executemany('insert into class(id,username,password) values(%s,%s,%s)',list) #executemany会自动把上面list列表中的参数循环传递,实现多条多个的情况
cur.execute(sql)
new_id = cur1.lastrowid #如果查询的表中有自增列,那这一行就可以获取最新的那个自增列的值,如果插入的是多条数据,那lastrowid取的是最后一个
sql = 'insert into xxx(k1,k2,k3,...)values(v1,v2,v3,...)'#很明显这样字段一多就要写死了,所以以下方法实现长字段插入
deal_sql = 'insert into xxx(%s)values(%s)'
key_list = []
value_list = []
for k, v in data.items():
key_list.append(k)
value_list.append('%%(%s)s' % k)
sql = sql % (','.join(key_list), ','.join(value_list))
cur.execut(deal_sql,data)
call_id1 = cur.callproc('p1') #callproc执行存储过程,无参数:pymysql调用mysql存储过程,p为存储过程函数名
cur.callproc('p2',args=(a,'123','b','asdf')) #有参数:pymysql调用mysql存储过程,获取存储过程的结果集并将返回值设置给@_p2_....;带参数写在一个元祖变量中,args中填写的是实参
#pymysql内部操作mysql
#set @_p2_0 = a
#set @_p2_1 = 123
#set @_p2_2 = b
@set @_p2_3 = asdf
res = cur.fetchall()#获取存储过程结果集,这里res没有返回mysql存储过程的返回值,但是通过上面的内部操作执行给了mysql,通过下面方式查询就可以拿到返回值
cur.execute('select @_p1_0,@_p1_1,@_p1_2,@_p1_3') #查询参数的执行返回值 @_为固定格式,p1为函数名,_1为参数序号,有几个就写几个
# conn.commit() # 提交数据,如果前面定义了autocommit=True,那就不用了 cur.close() # 关闭游标 conn.close() # 关闭连接
封装函数
def my_db(ip, user, password, db, sql, port=3306, charset='utf8'): conn = pymysql.connect(host=ip, password=password, user=user, db=db, port=port, charset=charset, autocommit=True) cur = conn.cursor() cur.execute(sql) res = cur.fetchall() cur.close() conn.close() return res
连接池PooledDB
pip install DBUtils
#db.conf
import pymysql
pool_info = { 'host': '127.0.0.1', # ip 'user': 'root', # username 'password': '123456', # password 'db': 'rainbol', # database 'port': 3306, # port 'charset': 'utf8', # coded set 'creator': pymysql, # 选择pymysql,这里库类,不是字符串 'maxconnections': 20, # 数据库连接池最大连接数 'mincached': 5, # 数据库连接池最小缓存数 'maxcached': 5, # 数据库连接池最大缓存数 'cursorclass': pymysql.cursors.DictCursor, # 返回方式dict形式 'blocking': True, # 当连接数达到最大的连接数时,在请求连接的时候, # 如果这个值是True,请求连接的程序会一直等待,直到当前连接数小于最大连接数,如果这个值是False,会报错 'maxshared': 20 # 当连接数达到这个数,新请求的连接会分享已经分配出去的连接 }
from config.db import pool_info from DBUtils.PooledDB import PooledDB pool = PooledDB(**pool_info) cur= self.pool.cursor() sql = 'select * from user' r = cur.execute(sql) res= cur.fetchall() print(res) cur.close() conn.close()
python操作excel
pip install xlwt pip install xlrd pip install xlutils
新增写excel:
import xlrd, xlutils, xlwt book = xlwt.Workbook() # 创建excel文件,可以指定路径,默认当前路径 sheet = book.add_sheet('sheet1') # 增加excel页,可以指定名称 sheet.write(0, 0, 'username') # 指定行和列,规律,当前行行不变,当前列列不变 sheet.write(1, 0, 'password') sheet.write(0, 1, 'admin') sheet.write(1, 1, '123456') book.save('世界你好.xls') # 保存文件并输出文件名,xlsx会打不开,wps可以打开
大批量数据循环嵌套
import xlwt all_shuzu = [ [1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3] ] book = xlwt.Workbook() sheet = book.add_sheet('sheet1') line = 0 for shuzu in all_shuzu: col = 0 for s in shuzu: sheet.write(line,col,s) col += 1 line += 1 book.save('世界你好.xls')
读excel:xlrd模块只能读不能写
import xlrd book = xlrd.open_workbook('世界你好.xls') sheet = book.sheet_by_index(0) # 根据编号找sheet1 # sheet = book.sheet_by_name("sheet1")#根据名字找sheet1 print(sheet.nrows) # 获取这个sheet1有多少行 print(sheet.ncols) # 获取这个sheet1有多少列 print(sheet.cell(0, 0).value) #获取到这个sheet1指定单元格内容 print(sheet.row_values(0)) #获取到这个sheet1指定整行的内容,返回list print(sheet.col_values(0)) #获取到这个sheet1指定整列的内容,返回list
修改excel:只能写,所以要和xlrd配合使用
import xlrd from xlutils import copy book = xlrd.open_workbook('世界你好.xls') # 读文件 new_book = copy.copy(book) # 复制文件句柄并放到一个新的文件中 sheet = new_book.get_sheet(0) # 获取sheet页面 sheet.write(0, 0, "我不好") new_book.save("世界你好.xls")
版权声明:本文原创发表于 博客园,作者为 RainBol 本文欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则视为侵权。
