一棵简单能用的左偏树
左偏树是一种可并堆,它查询最小值是(O(1)),合并是(O(log n))。Push 和 pop 操作都可以用合并来实现(分别是并入一个只有一个节点的堆和合并该堆根节点的左右两个子树),所以 push 和 pop 都是 (O(n log n))。
在学习左偏树的性质之前,我们需要知道左偏树中一个重要的定义:距离(dis)。它表示一个节点到最近的叶子节点的距离。
左偏树的性质(以大根堆为例):
- 它是一棵二叉树
- 父亲节点的值比儿子节点大
- 左儿子的dis >= 右儿子的dis(所以一个节点的dis等于右儿子的dis +1)
左偏树的最重要操作是“合并”。
当我们将两棵左偏树X, Y合并的时候:
- 如果 X, Y 中有一个为空,则合并结果是另一个;
- 否则让“根节点较小的左偏树”与“根节点较大的左偏树的右子树”合并,成为合并结果的右子树。
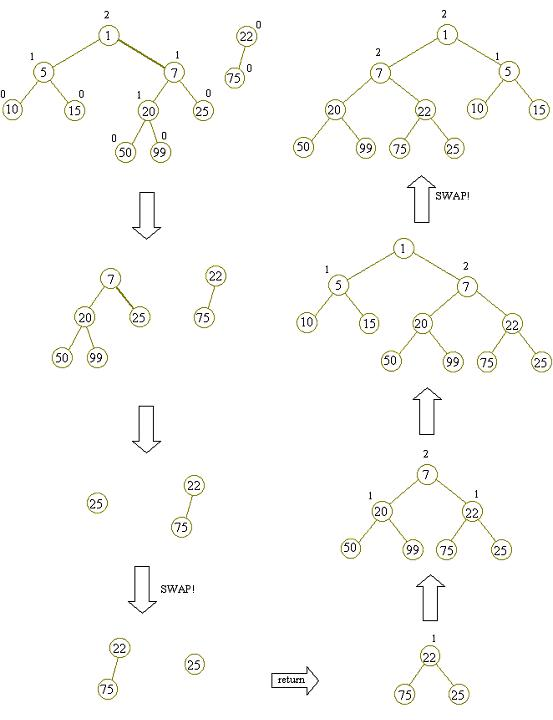
在每次合并之后,合并结果的右子树的dis可能增加,增加过多可能超过左子树的dis,这时为了维护左偏树的性质,要调换左右子树。
因为右子树的dis不超过(log n),每次递归合并的时候,X, Y 中有一个dis会减少,所以合并的复杂度是(O(log n))。
一道例题:BZOJ 2809
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define space putchar(' ')
#define enter putchar('
')
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
template <class T>
void read(T &x){
char c;
bool op = 0;
while(c = getchar(), c < '0' || c > '9')
if(c == '-') op = 1;
x = c - '0';
while(c = getchar(), c >= '0' && c <= '9')
x = x * 10 + c - '0';
if(op) x = -x;
}
template <class T>
void write(T x){
if(x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x;
if(x >= 10) write(x / 10);
putchar('0' + x % 10);
}
const int N = 100005, M = 80000005;
int n, m, adj[N], nxt[N];
int cost[N], lead[N];
int que[N], qr, fa[N];
ll ans;
struct node {
node *ls, *rs;
int dis, sze, val;
ll sum;
node(): ls(NULL), rs(NULL), dis(0), sze(0), val(0), sum(0){}
node(int x): ls(NULL), rs(NULL), dis(0), sze(1), val(x), sum(x){}
node *upt(){ //update函数:适时交换左右儿子,更新dis,更新sze,更新sum
if(!ls || ls -> dis < rs -> dis) swap(ls, rs);
dis = rs ? rs -> dis + 1 : 0;
sze = (ls ? ls -> sze : 0) + (rs ? rs -> sze : 0) + 1;
sum = (ls ? ls -> sum : 0) + (rs ? rs -> sum : 0) + val;
return this;
}
} *tr[N];
node *merge(node *x, node *y){
if(!x) return y;
if(!y) return x;
if(x -> val < y -> val) swap(x, y);
x -> rs = merge(x -> rs, y);
return x -> upt();
}
void pop(node *&x){
while(x -> sum > m)
x = merge(x -> ls, x -> rs);
}
void add(int u, int v){
nxt[v] = adj[u];
adj[u] = v;
}
void bfs(){
que[qr = 1] = 1;
for(int ql = 1; ql <= qr; ql++){
int u = que[ql];
for(int v = adj[u]; v; v = nxt[v])
que[++qr] = v;
}
for(int ql = qr; ql >= 1; ql--){
int v = que[ql], u = fa[v];
ans = max(ans, (ll)lead[v] * tr[v] -> sze);
if(u) tr[u] = merge(tr[u], tr[v]), pop(tr[u]);
}
}
int main(){
read(n), read(m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
read(fa[i]), read(cost[i]), read(lead[i]);
add(fa[i], i);
tr[i] = new node(cost[i]);
}
bfs();
write(ans), enter;
return 0;
}