题目
机器人在形状为green house立方体的5个表面移动进行打扫,初始位置为表面1上的某个给定位置,输入一串由123组成的连续指令(1:向前移动1个单位;2:右转方向;3:左转方向)操作机器人,判断最后机器人所处表面(1/2/3/4/5)。
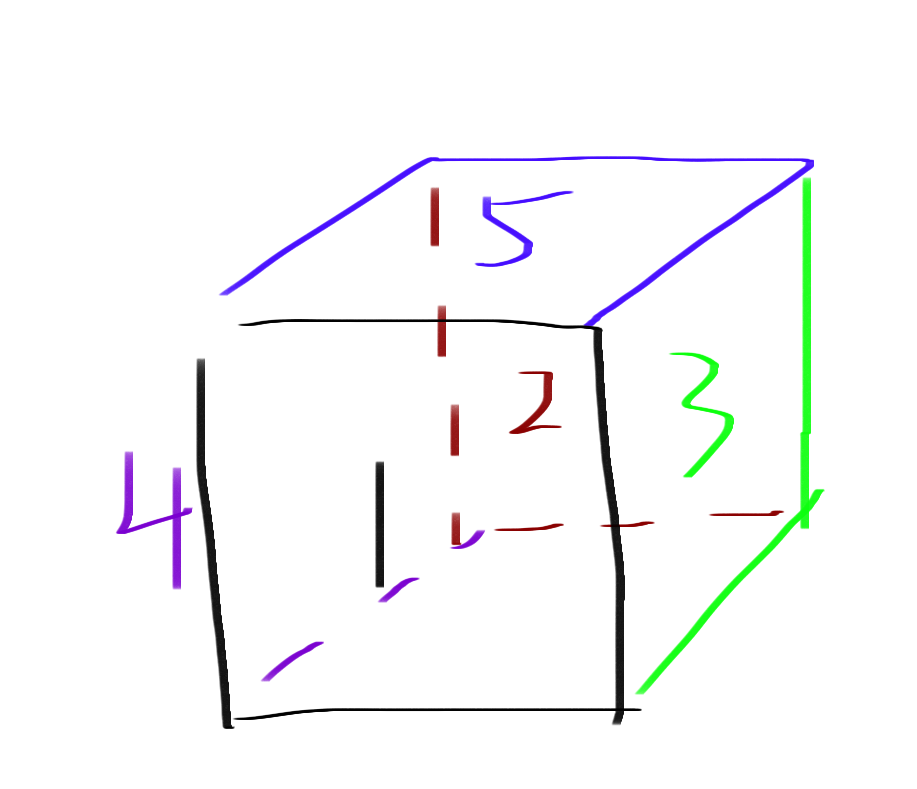
细节
1) 当移动到当前表面边界时执行前移操作(op=1)时会这样移动到对应毗邻的表面:
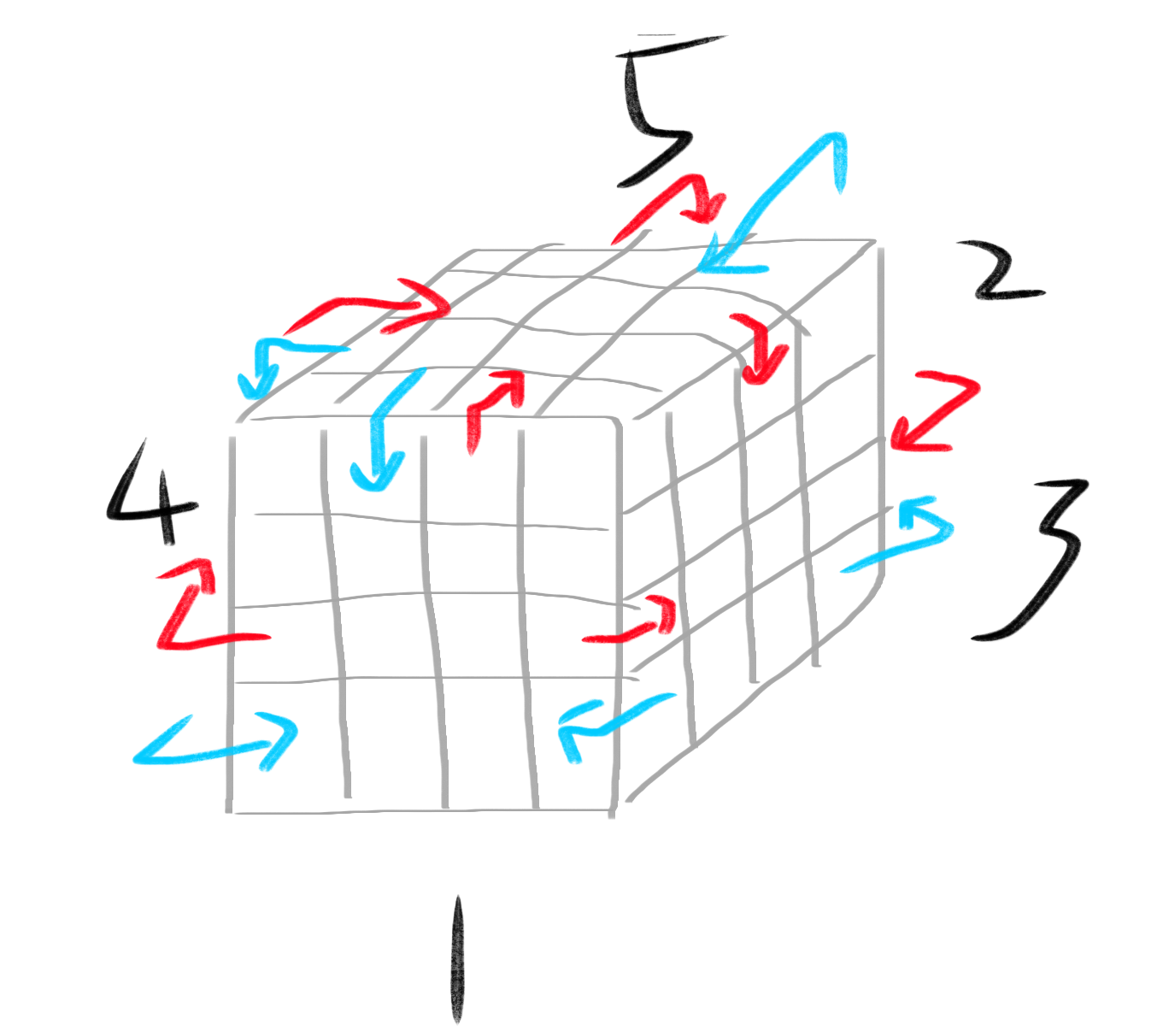 好难画啊口区
好难画啊口区
2) 机器人位于表面1、2、3、4的底层边缘时试图往下移动的操作将会失败,位置不变。
i.e.
输入:N(int,立方体棱长)、location_r(int,初始位置竖直坐标)、loation_c(int,初始位置水平坐标)、 ops(int[200],由1/2/3组成的指令串);
输出:执行完所有指令后机器人所在的表面编号。
例子:N=4,初始位置为3,2(注意题目的输入以1为起点),输入长度25的指令1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 3, 1, 1, 3, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1。
轨迹:
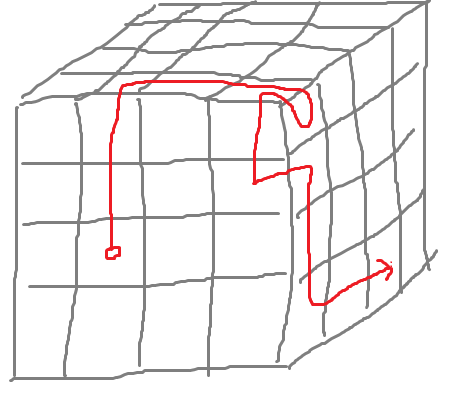
好丑啊救命
思路
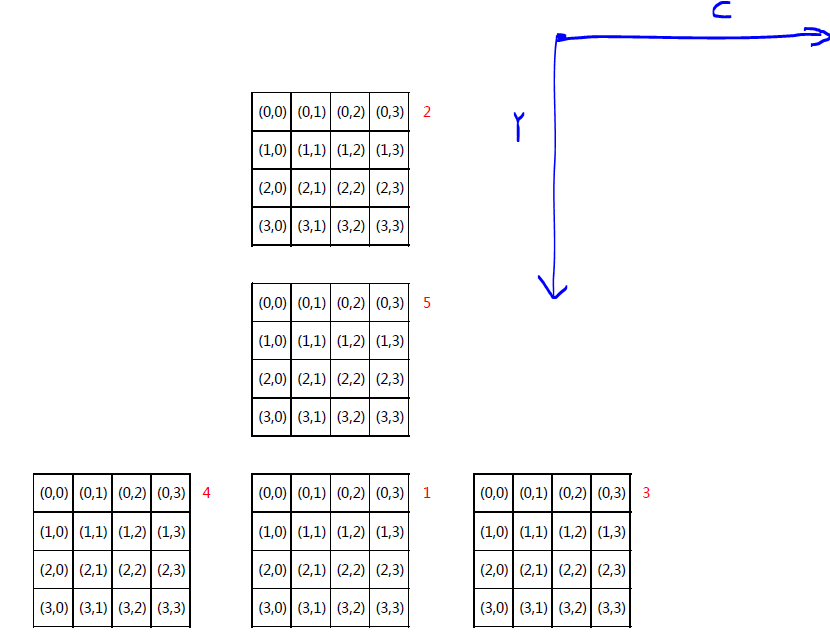
[1] 把立方体表面展开并设定绝对方向;
绝对方向: 展开后的二维空间上的方向,只有上下左右4个。counterpart应该不能叫相对方向吧,反正是三维空间中根据当前所在具体平面+平面上的方向所确定的∈R3的向量吧阿没关系啦反正这个跟解题应该没什么关系
e.g. N=4,展开立方体并以表面1方向为基准,每个表面以左上角为坐标原点。//也可以按别的方式展开 看个人偏好
[2] 用4个int变量grid, location_r, location_c, direction追踪机器人每执行完一个指令后的状态。
grid: 机器人当前所在表面编号
location_r: 机器人当前所在行坐标 //我个人是以0为起始的
location_c: 机器人当前所在列坐标
direction: 机器人当前朝向 //这里关联前面提到的绝对方向
[3] 指令处理:可分为 向前移动机器人 和 转动方向
[3-1] 转动方向
当op为2或3的时候相应的顺时针/逆时针改变方向 e.g. 当前方向为up时,收到指令3,逆时针转动90度所以方向更新为left。
实现的时候可以考虑用4个整形常量0 1 2 3标记上下左右 或者逆时针 上左下右 或者顺时针 上右下左 随便啦反正后面不要突然弄混就是了 但我觉得这样做可读性不是很强,我个人偏向用枚举enum directions{up, left, down, right}虽然考试系统的编译器比较垃圾不认识enum所以我最后又只能默默改回用整数罢了
[3-2] 向前移动机器人
只要看当前的绝对方向是什么再对坐标做相应的更新(先不管可能会遇到坐标越界需要更换所在表面的问题),e.g.direction为up时坐标r轴+=-1 c轴+=0
实现建议 上如果先前是用简单的连续整数标记4个方向比如0/1/2/3分别表示up/left/down/right那么可以用一个4*2的二维数组存储坐标更新的可能delta值:deltas[4][2]={{0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}},这样就可以直接用方向值作为下表获取坐标更新的delta值直接递增在原坐标上计算
当然如果题目想要再复杂一点可能一次不是只移动一格那么deltas里的值也可以改不过我也不想考虑这么无聊的情况了hehe
e.g.
enum directions {up, left, down, right}; int deltas[4][2]={{0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}}; //operates, change direction or move or whatever ... //get an op==1 indicates that you need to move forward location_r+=deltas[direction][0]; location_c+=deltas[direction][1];
如果更新后的坐标值是合法的 i.e. 在0和N-1之间 (当然如果是从1起始就是在1和N之间啊我为什么要打这些废话)那就完了
如果更新后的坐标值不合法说明它可能要移动到另一个平面 或者 试图移动到最底下那个不能到达的平面但没有成功,那就要对坐标值进行再次更新使它合法,有时候方向也要根据情况进行更新。
[3-2-2] 合法化非法坐标 //听起来为什么这么诡异
根据之前的展开图找规律进行相应变更
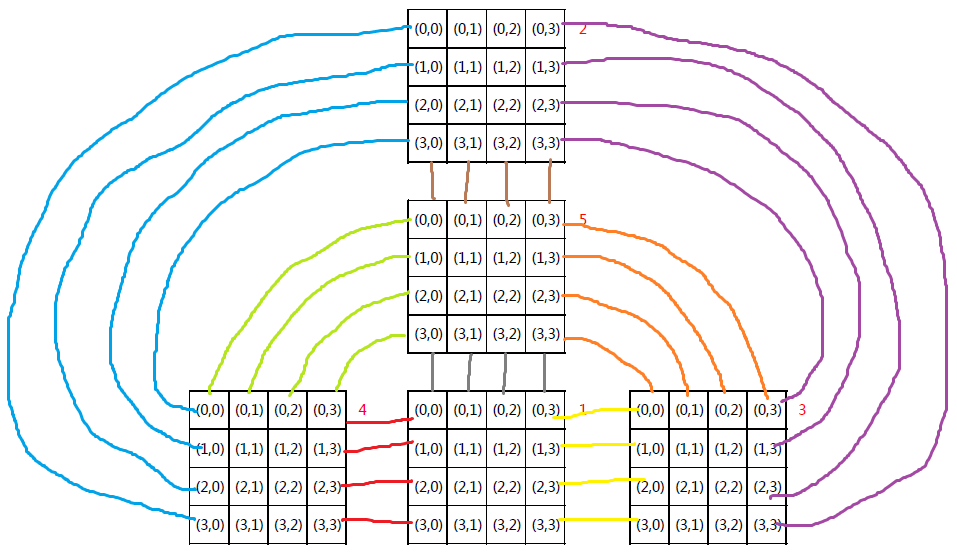
e.g. 当在表面5时location_c<0时,说明机器人实际上已经移动到表面4的上侧,对应的规律就是r变为0【因为反正题目中只移动一步所以确定是在表面4的第一行】而c变为原本的r值。direction也会从原来的left变为down。 其他情况以此类推。
当在与底面毗邻的表面1/2/3/4试图往底面移动时(e.g. grid==2, location_r<0)时会失败,把当前非法的坐标值更新为边界值,方向不变。
[4] 最后返回当前记录的grid值
关于grid location和directon的追踪
实现全部在main里写也是没问题,但是我比较喜欢分成几个函数来写。这样的话为了保证函数中做的变更能更新到main里的表面/坐标/方向的变量值就需要把它们按引用传递而不是按值传递, C/C++可以把参数设为引用或者指针,java的话好像基本数据类型参数是默认按值传递的,但好像也有个什么途径可以把它们封装成对象就能按引用传递了。
如果你们直接把它们用作返回值当我没说
用全局变量也可以啦但我不是很喜欢
总体
int grid = 1, location_r, location_c, direction; void robot_move(int& location_r, int& location_c, int& direction); bool locationInvalid(const int location_r, const int location_c, const int N); void robot_rectify(int& grid, int& location_r, int& location_c, int& direction, const int N); void changeDirection(int& direction, const int op); //依此执行输入指令 for (int op : ops) { switch (op) { case 1: //move forward robot_move(location_r, location_c, direction); //update location if (locationInvalid(location_r, location_c, N)) robot_rectify(grid, location_r, location_c, direction, N); //rectify the illegal location values and udpate direction perhaps break; case 2: case 3: changeDirection(direction, op); break; } }
完整代码:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; enum directions { up, left, down, right }; int deltas[4][2] = { { -1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, 1 } }; void robot_move(int& location_r, int& location_c, int& direction) { //increment locations with specific delta according to the current direction location_r += deltas[direction][0]; location_c += deltas[direction][1]; } bool locationInvalid(const int location_r, const int location_c, const int N) { return location_r < 0|| location_r >= N || location_c < 0 || location_c >= N; } void robot_rectify(int& grid, int& location_r, int& location_c, int& direction, const int N) { switch (grid) { case 1: if (location_r < 0) { grid = 5; location_r = N - 1; } else if (location_r >= N) { location_r = N - 1; } else if (location_c < 0) { grid = 4; location_c = N - 1; } else if (location_c >= N) { grid = 3; location_c = 0; } break; case 2: if (location_r < 0) { location_r = 0; } else if (location_r >= N) { grid = 5; location_r = 0; } else if (location_c < 0) { grid = 4; direction = directions::right; location_r = N - 1 - location_r; location_c = 0; } else if (location_c >= N) { grid = 3; direction = directions::left; location_r = N - 1 - location_r; location_c = N - 1; } break; case 3: if (location_r < 0) { grid = 5; direction = directions::left; location_r = N-1-location_c; location_c = N - 1; } else if (location_r >= N) { location_r = N - 1; } else if (location_c < 0) { grid = 1; location_c = N - 1; } else if (location_c >= N) { grid = 2; direction = directions::right; location_r = N - 1 - location_r; location_c = N - 1; } break; case 4: if (location_r < 0) { grid = 5; direction = directions::right; location_r = location_c; location_c = 0; } else if (location_r >= N) { location_r = N - 1; } else if (location_c < 0) { grid = 2; direction = directions::right; location_r = N - 1 - location_r; location_c = 0; } else if (location_c >= N) { grid = 1; location_c = 0; } break; case 5: if (location_r < 0) { grid = 2; location_r = N - 1; } else if (location_r >= N) { grid = 1; location_r = 0; } else if (location_c < 0) { grid = 4; direction = directions::down; location_c = location_r; location_r = 0; } else if (location_c >= N) { grid = 3; direction = directions::down; location_c = N-1-location_r; location_r = 0; } break; } } void changeDirection(int& direction, const int op) { switch (op) { case 2://turn right if (direction == directions::up) direction = directions::right; else --direction; break; case 3://turn left if (direction == directions::right) ++direction; else ++direction; break; } } int main() { //input & initialization int N, grid, location_r, location_c, direction, k, ops[200]; cin >> N >> location_r >> location_c >> k; --location_r; --location_c; for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) cin >> ops[i]; /* test case int N = 4, grid, location_r = 2, location_c = 1, direction, k = 25; int ops[200] = { 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 3, 1, 1, 3, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1 }; */ grid = 1; direction = directions::up; //依次执行输入指令 for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { switch (ops[i]) { case 1: //move forward robot_move(location_r, location_c, direction); //update location if (locationInvalid(location_r, location_c, N)) robot_rectify(grid, location_r, location_c, direction, N); //rectify the illegal location values and udpate direction perhaps break; case 2: case 3: changeDirection(direction, ops[i]); break; } } cout << grid << endl; return 0; }