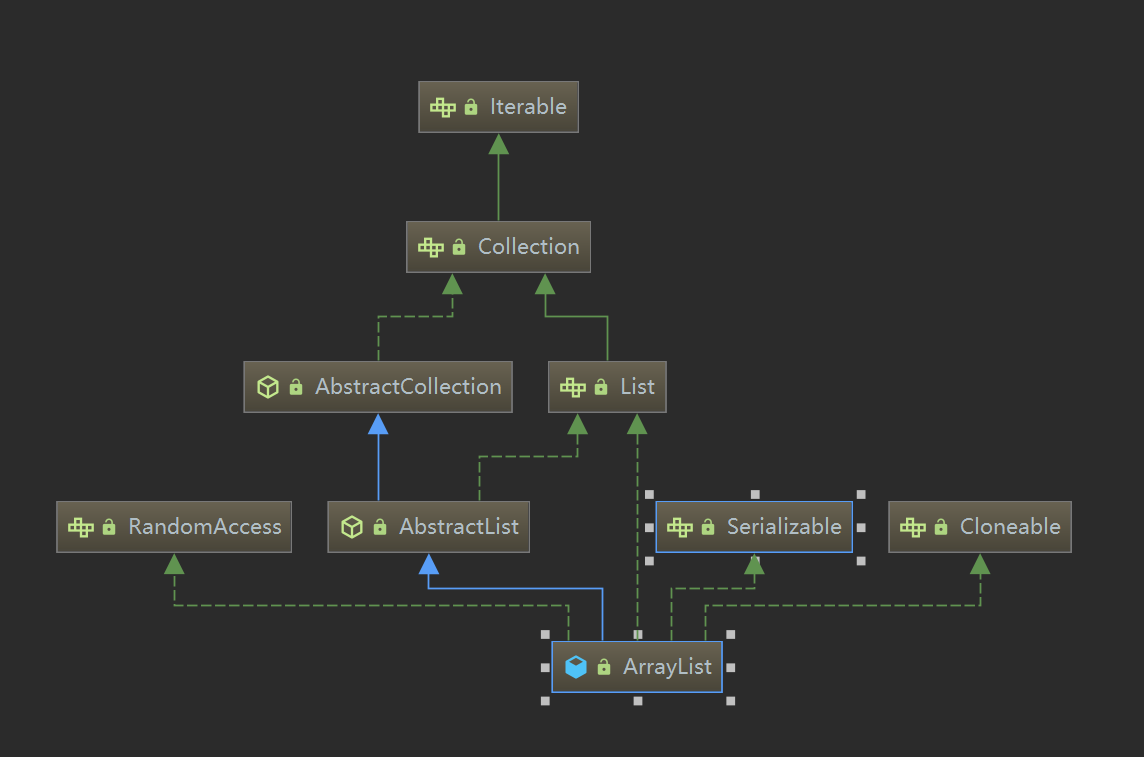
UML
主要代码
ArrayList实现了List、RandomAccess、Cloneable、Serializable,继承了AbstractList。
为什么继承了AbstractList还要实现List接口?
AbstractList中已经实现了List接口,这里其实是没有必要再实现List接口的,这个获取是为了体现面向接口编程。
RandomAccess接口:该接口在jdk中是一个空实现,是一个标记接口。文档指明实现了RandomAccess说明List支持随机访问。这个接口的主要目的是允许普通算法对随机方法或者连续访问List时,改变其行为,以获得较好的性能。
默认初始容量为10,每次扩容1.5倍,底部存储使用数组。
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
// 默认容量10
private static final int DAFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
// 当传入的容量大小为0时,使用该空的常量数组对象来初始化底层数组elementData
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
// 当未指定容量大小时,使用该空的常量数组对象来初始化底层数组elementData,,这时,当第一次添加元素时,将会默认创建一个容量为10的默认容量数组。
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
// 存储ArrayList中的元素,使用transient是为了不序列化这个字段
transiemt Object[] elementData;
// 集合中元素的个数, 不是底层数组elementData的长度
private int size;
// 最大容量,即elementData数组的最大长度,超过该长度将会抛出OutOfMemoryError
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
// 结构性修改次数,定义在AbstractList中
protected transient int modCount = 0;
/**
* 构造一个指定容量的集合
* 根据参数大小做为容量来实例化底层的数组对象,当参数等于0时,用空的常量数组对象EMPTY_ * ELEMENTDATA来初始化底层数组elementData
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if(initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[intialCapacity];
}else if(initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacityy : " + initialCapacity);;
}
}
/**
* 构造一个初始容量为10的空集合
* 这里并没有指定容量,那么我们怎么知道是10呢?答案请看add(E e)
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENT;
}
/**
* 将容器Collection转化为数组赋值给底层数组elementData
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 集合转化为数组
elelementData = c.toArray();
if((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// 将c.toArray()返回的是不是Object[]类型,如果不是重新拷贝生成Object[]类型
if(elementData.getClass != Object[].class) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(lementData, size, Ojbect[].class);
}
}else {
// 如果是空集合,则初始化为空数组EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
/**
* 将指定元素e添加到list的末尾,平均时间时间复杂度O(1)
* 1.计算最小容量minCapacity
* 如果elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,最小容量为max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)
* 否则为size + 1
* 2.检查当前elementData容量是否够minCapacity,不够进行扩容
* 3.将size位置的元素设置e
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
// 检查是否需要进行扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
// 将size位置设置为e,并将size++;
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* 添加元素到指定位置
* 1.检查是否越界 0 <= index <= size
* 2.检查是否需要扩容
* 3.将index之后的元素后移一位
* 4.设置index位置的元素为elementData
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
// addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)、addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) 逻辑与add(int index, E element)相似
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensuerCapacityInternal(size + numNew);
int numMoved = size - index;
if(numMoved > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numMoved , numMoved);
}
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
/**
* 设置index位置的元素为element
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 获取指定位置index上的元素
*/
public E get(int index) {
// 检查是否越界 0 <= index < this.size
rangeCheck(index);
// 返回底层数组index位置的元素
return elementData[index];
}
/**
* 从头开始查找对象o在list中的索引位置
* 查找分o为null和非null两种情况,没有找到返回-1
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if(o == null) {
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if(elementData[i] == null) {
return i;
}
}
}else {
for(int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
if(o.equals(elementData[i])) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 从尾部开始查找对象o所在索引位置
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 移除index位置的元素
* 1.检查index是否越界
* 2.结构性修改次数加1
* 3.将index后面的元素向前移动一位
* 4.将最后一位置为空,并返回移除的元素
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData[index];
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if(numMoved > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, numMoved);
}
elementData[--size] = null;
return oldValue;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if(o == null) {
for(int index = 0; index < size; index++) {
if(elementData == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for(int index = 0; index < size; index++) {
if(o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 移除指定集合c中元素
*/
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
// c不能为null
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
/**
* 对list中的所有元素执行operator.apply()
*/
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> oprator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final int size = this.size;
for(int i = 0; modCount == expectedCount && i < size; i++) {
elementData[i] = operator.apply((E)element[i]);
}
if(modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
/**
* list排序,直接调用Arrays.sort()。只对0,size之间的元素进行排序
*/
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
Array.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c);
if(modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModification Exception();
}
modCount++;
}
/**
* elementData使用了transient,所以序列化时不会将elementData序列化,
* 这里将ArrayList写入到序列化流中
*/
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
s.writeInt(size);
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
s.writeObject(elementData[i]);
}
if(modCount != elementModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* 从流中反序列化
*/
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s) throws IOEception, ClassNotFoundException {
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
s.defaultReadObject();
s.readInt();
if(size > 0) {
int capacity = calculateCapacity(elementData, size);
Shared.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity);
ensureCapacityInternal(size);
Object[] a = elementData;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
a[i] = s.readObject();
}
}
}
private void fastRemove(index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if(numMoved > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, numMoved);
}
elementData[--size] = null;
}
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
int r = 0; w = 0;
boolean modified = false;
try {
for(; r < size; r++) {
if(c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) {
// 如果list中该元素不存在与collection中,就放入elementData
elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
}
}finally {
if(r != size) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r);
w += size - r;
}
// 如果list中确实有collection中的元素,那么w一定不等于size
if(w != size) {
// 将其他元素设置为null,这样elementData中就只有不在collection中的元素了,并且多余的索引位置并设置为了null
for(int i = w; i < size; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
// 修改次数
modCount += size -w;
// size等于w
size = w;
// 移除过元素
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
/**
* 计算最小容量
* 1,如果elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,那么取DEFAULT_CAPACITY和minCapacity中的较大者
* 2.取minCapacity
*/
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPCITY, minCapacity);
}
return capacity;
}
/**
* 如果所需的最小容量大于底层数组elementData的容量大小,进行扩容,否则直接返回
*/
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 结构性修改次数—+1
modCount++;
// 如果所需的最小容量大于elementData的容量,进行扩容
if(minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) {
// 进行扩容
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
/**
* 扩容
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// 当前数组容量
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 新数组容量为旧数组容量的1.5倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if(newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) {
// 如果新数组容量还是不够(也有可能是溢出了),赋值新数组容量为所需的最小数组容量
newCapacity = minCapacity;
}
if(newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
// 如果新数组容量比MAX_ARRAY_SIZE大,并且所需的minCapacity也大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,设置新容量为Integer.MAX_VALUE,否则设置为MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
}
// 将旧数组拷贝到新数组
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if(minCapacity < 0) {
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
}
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > this.size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
}
}