一、Spring的演进
二、SpringBoot约定优于配置的体现
三、Bean的自动装载
首先思考一个问题:在SpringBoot项目内使用redis、mybatis或者mongodb组件时,我们是怎么引入及配置的?
- 首先pom.xml文件内引入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 之后resources目录下application.properties配置文件内配置redis相关陪配置
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
spring.redis.port=xxx
- 最后,项目内直接注入即可
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
/**
* 为什么能用?
* 说明已经在IOC容器内注入了;
* 那是怎么样实现自动装载的?
*/
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/hi")
public String say() {
String vl = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("k1");
return vl;
}
}
在这例子中,其实可以看出Spring Boot集成redis等组件非常方便,完全不需要像Spring之前版本那样引入xml配置、配置文件等一系列操作,那SpringBoot具体又是如何实现的呢?
1. Spring Bean的动态装载
Spring Boot提供了以下两种方式支持Bean的动态装载:
- ImportSelector: DeferredImportSelector
- Registator : ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
其实我们可以简单直接的从@SpringBootApplication注解入手,查看其源码流程大致如下
-> org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication
-> @EnableAutoConfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration
-> @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector
-> org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector#selectImports
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector#getAutoConfigurationEntry
-> org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector#getCandidateConfigurations
-> org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader#loadFactoryNames
-> org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader#loadSpringFactories
1. 首先启动类的注解 @SpringBootApplication
内部存在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration注解
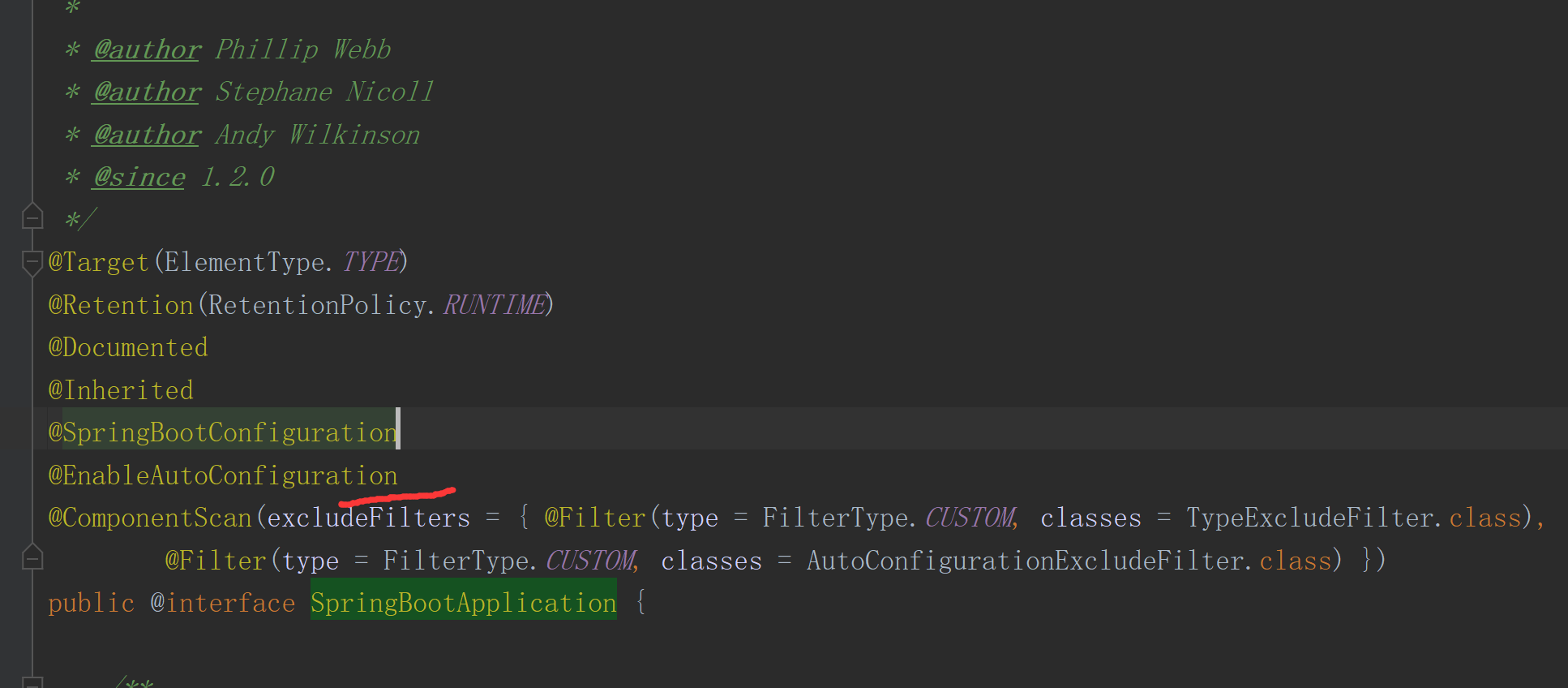
2. @EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解内使用@Import引入了org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector类
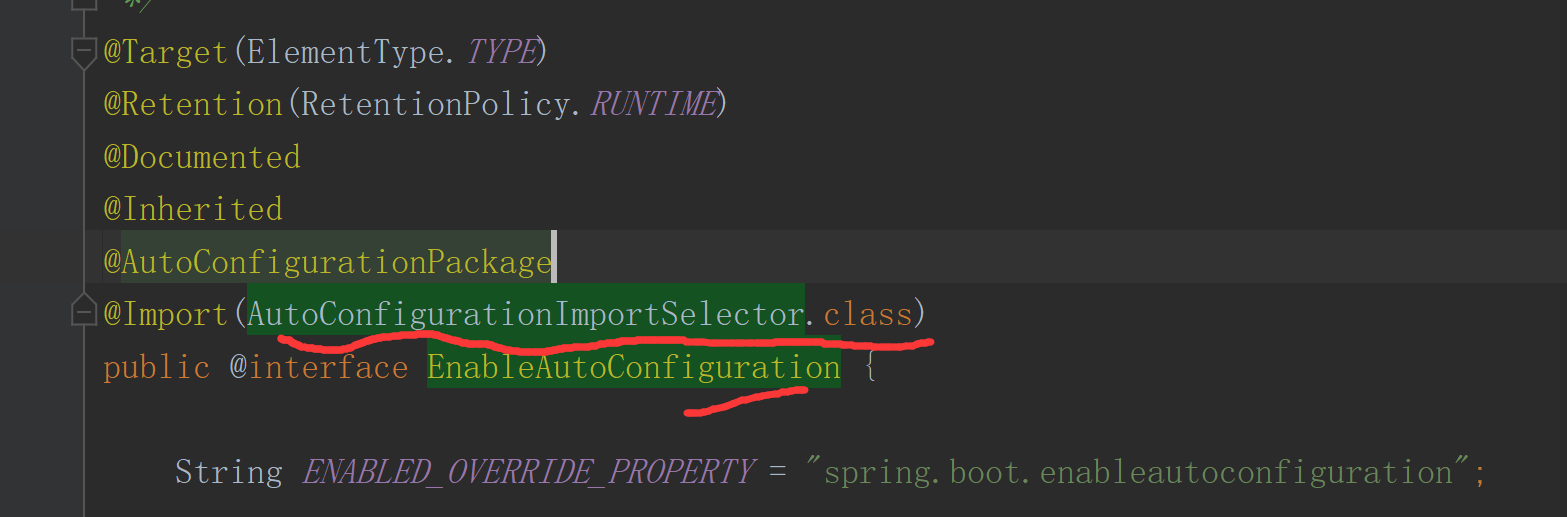
3. AutoConfigurationImportSelector类内实现了自动装配的逻辑
AutoConfigurationImportSelector类实现了DeferredImportSelector接口,该接口继承于ImportSelector接口;重写了org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportSelector#selectImports方法
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector#selectImports
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered {
...
...
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
...
...
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
...
...
}
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportSelector#getCandidateConfigurations
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
...
...
org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader#loadFactoryNames
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
...
org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader#loadSpringFactories
...
...
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
...
我们可以在getAutoConfigurationEntry()方法内加上断点,调试一下加了哪些配置,如下 内部包含了redis、mongodb的Configuration
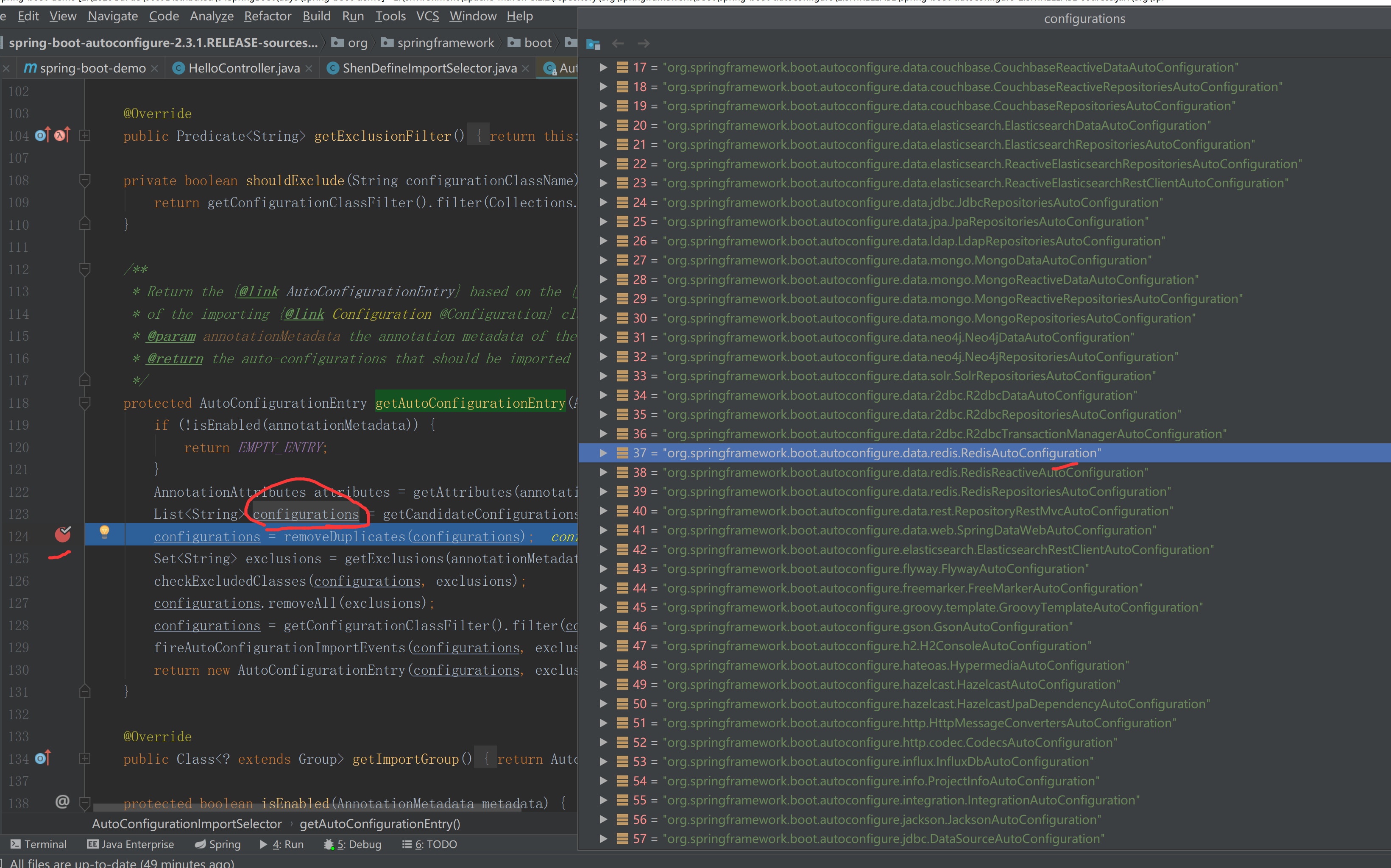
redis对应Configuration为:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration
而在org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader#loadSpringFactories源码内可以看到,SpringBoot启动时会固定从META-INF/spring.factories内读取解析配置文件,实现默认的自动装配的配置及加载。
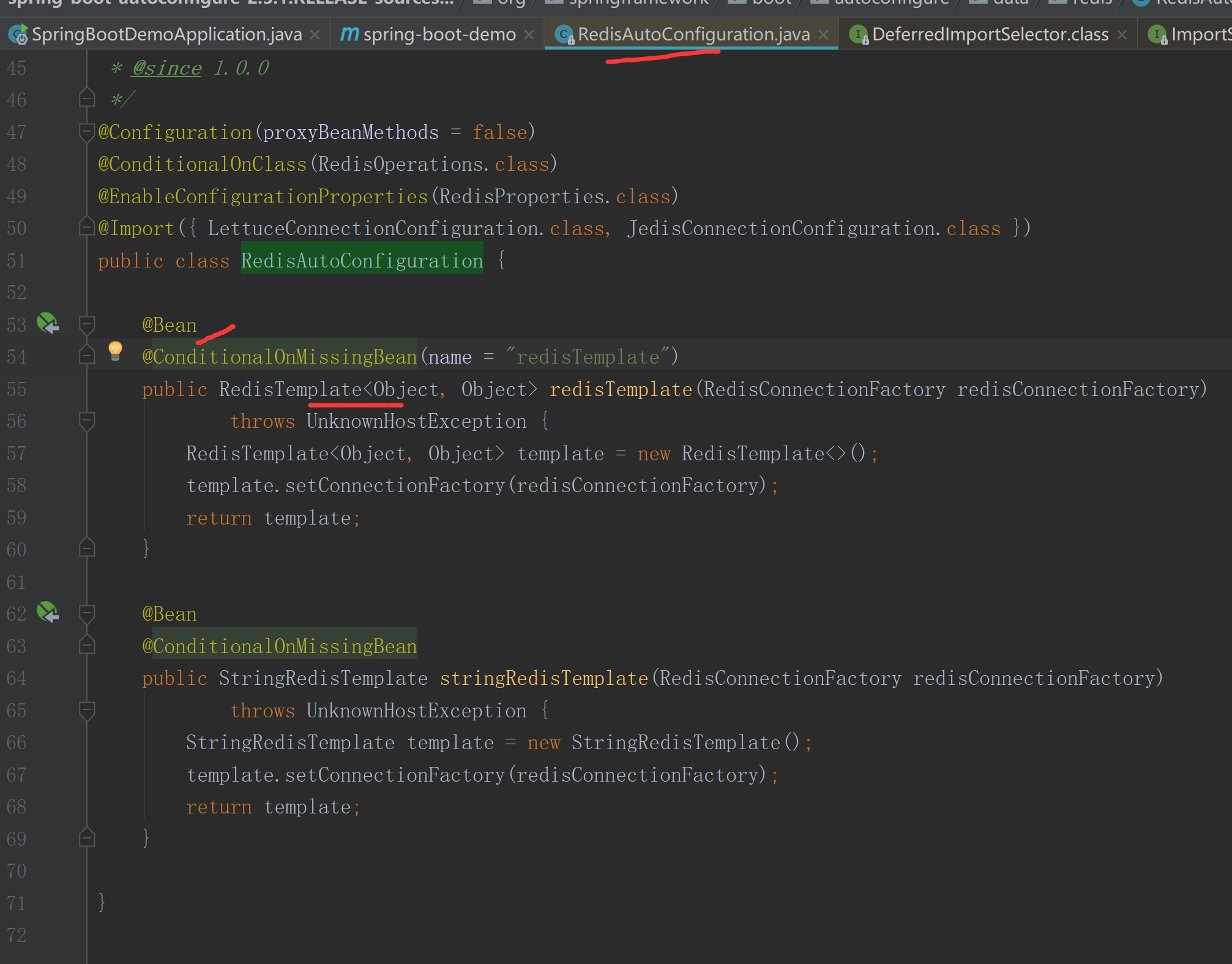
4. RedisAutoConfiguration配置类
内部通过@Bean将RedisTemplate注入IOC容器
5. 约定优于配置 spring.factories
在Spring装配Bean的演进中,核心目标其实一直是为了让我们Bean的装载更加简单,所以SpringBoot定义了很多约定由于配置的体现,此处的一个体现就是在classpath*:META-INF/spring.factories内提供自动装配的Bean的定义
org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader#loadSpringFactories
/**
* The location to look for factories.
* <p>Can be present in multiple JAR files.
*/
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
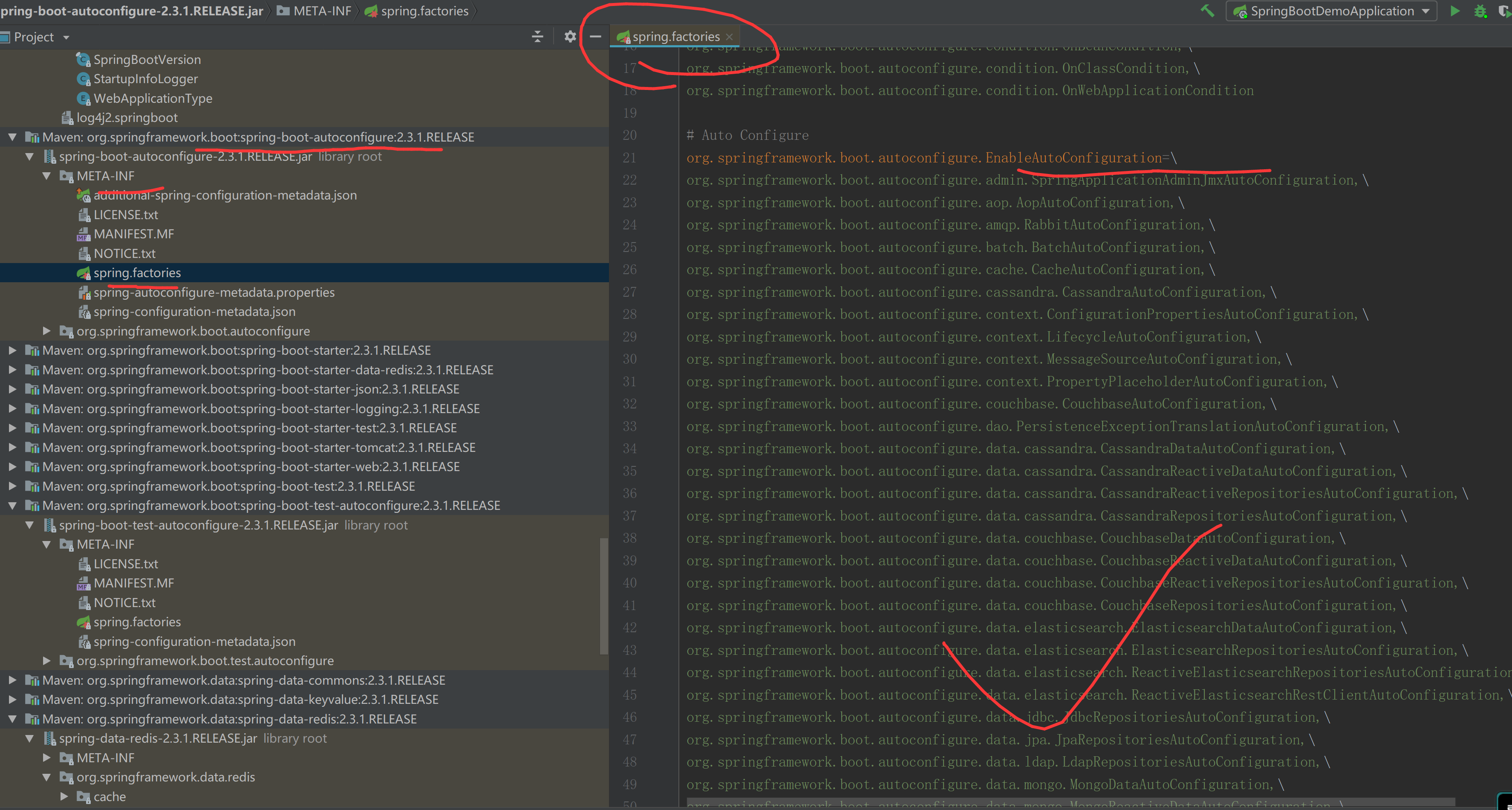
在spring.factories配置文件内定义了一系列的可以自动装配的Bean的xxxConfiguration,这些Configuration类内部定义了像Redis、MQ等各种组件的Bean。
简单来说:自动装配是SpringBoot的一种约定由于配置的体现,通过在spring.factories配置文件内定义自动需要装配的Bean或者Configuration,然后SpringBoot容器在启动后自动从classpath下的META-INF下的spring.factories文件内读取配置,实现动态加载Bean至IOC容器的目的。
2. SPI机制(Service Provider Interface)
SPI机制:为接口寻找服务实现类。
提供的SPI机制的组件需满足一下条件:
- 需要在classpath目录下创建一个 META-INF/services
- 在该目录下创建一个以服务接口全路径命名的文件为,文件内填写接口的具体实现
- 文件编码格式为UTF-8
- 通过
java.util.ServiceLoader进行加载
当服务的提供者,提供了服务接口的一种实现之后,在jar包的META-INF/services/目录里同时创建一个以服务接口命名的文件。该文件里就是实现该服务接口的具体实现类。而当外部程序装配这个模块的时候,就能通过该jar包META-INF/services/里的配置文件找到具体的实现类名,并装载实例化,完成模块的注入。
我们以第三方的角色来实现官方驱动为例:
1.首先模拟官方的jar包及内部驱动接口
<groupId>com.bigshen.spi</groupId>
<artifactId>DataBaseDriver</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
public interface DataBaseDriver {
String buildConnect(String host, int port);
}
2.此时我们需要自定义jar包来对接口进行实现
首先创建自定义项目
<groupId>com.bigshen.driver</groupId>
<artifactId>shen-driver</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
项目pom内引入官方依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.bigshen.spi</groupId>
<artifactId>DataBaseDriver</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
项目内进行接口实现
import com.bigshen.spi.DataBaseDriver;
public class ShenSqlDriver implements DataBaseDriver {
@Override
public String buildConnect(String s, int i) {
return "ShenSql的驱动实现: " + s;
}
}
最后,根据SPI机制在相应路径下创建接口文件
在resources下创建META-INF/services/目录,创建文件、名称为官方接口名com.bigshen.spi.DataBaseDriver,内部写自定义接口实现类:com.bigshen.driver.ShenSqlDriver
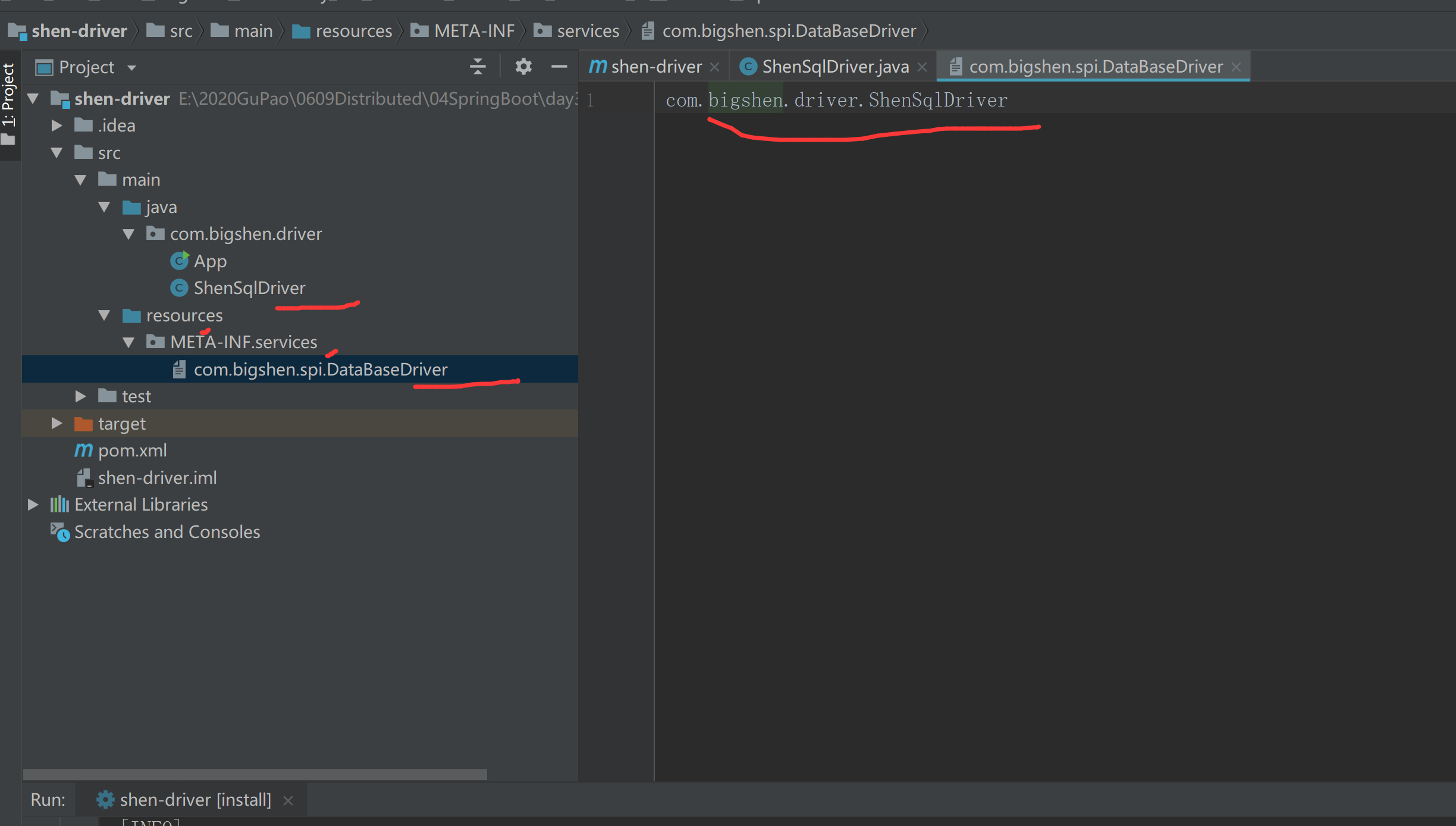
至此,我们提供的满足SPI机制的第三方组件已经实现,打包入maven仓库。
3. 使用ServiceLoad进行加载
在外部组件项目内,可以使用我们提供的驱动实现:
引入:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.bigshen.driver</groupId>
<artifactId>shen-driver</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
java.util.ServiceLoader加载
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ServiceLoader<DataBaseDriver> dataBaseDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(DataBaseDriver.class);
for (DataBaseDriver el : dataBaseDrivers) {
System.out.println(el.buildConnect("ip", 111));
}
}
... 输出结果
ShenSql的驱动实现: ip
可见,在外部组件内的DataBaseDriver接口实现已经是我们的自定义实现ShenSqlDriver了。
3. SpringBoot自动装配的条件控制
- 对于官方的starter组件 spring-boot-starter-xxx
不需要通过配置spring.factories配置文件来自动装配,而是通过@Conditional注解控制,且官方实现的自动装配是统一在spring-boot-autoconfigurejar包内的spring.factories内配置的
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
以spring-boot-starter-data-redis为例,这个jar包内就没有sprinig.factories配置文件,但引入这个jar包后我们就可以直接在项目中注入RedisTemplate,这就是因为在spring-boot-autoconfigure-x.y.z.jar下的spring.factories内已经维护了org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(RedisOperations.class) // ConditionalOnClass进行条件判断,判断 RedisOperations类是否存在,存在的话才会自动装配
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class)
@Import({ LettuceConnectionConfiguration.class, JedisConnectionConfiguration.class })
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
在RedisAutoConfiguration 类上存在@ConditionalOnClass(RedisOperations.class)注解,ConditionalOnClass会进行条件判断,判断 RedisOperations类是否存在,存在的话才会自动装配。
而RedisOperations其实是在jar包spring-data-redis-x.y.z.jar内存在的。
通过spring.factories和@ConditionalOnClass的结合来实现官方starter组件的自动装配。
- 第三方包 xxx-spring-boot-starter
遵循META-INF/spring.factories规范,内部定义Configuration来实现自动装配
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
com.bigshen.autoconfiguration.demo.ShenConfiguration
ShenConfiguration内使用@Bean定义Bean的实现
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ShenConfiguration {
@Bean
public ShenEduBean shenEduBean(){
return new ShenEduBean();
}
}
之后将该组件打成jar包放入maven仓库,其余项目引入依赖实现ShenEduBean的自动注入。