一、回顾
1、Linux程序包管理的实现,rpm包管理器
2、rpm命令实现程序管理
安装: -ivh,--nodeps,--replacepkgs
卸载:-e,--nodeps
升级:-Uvh(即能升级又能安装),-Fvh(只能升级),--nodeps,--oldpackage
查询:-q,-qa,-qf,-qi,-qd,-qc,-q --scripts,-q --changlog,-q --provides,-q --requires
校验:-V
导入GPG密钥:--import,-K(直接检验一个程序包来源合法性和包完整性),--nodigest(校验时不检查完整性),--nosignature(校验时不检查来源合法性)
数据库重建:--initdb,--rebuilddb
二、Linux程序包管理
1、CentOS:yum,dnf。
a、yum所需要的文件访问机制是一个C/S架构。当我们要安装程序包时我们会首先到远程服务器上拉取远程服务器程序包仓库的程序包元数据文件并缓存到本地,然后找我们需要安装的程序包,当找到后就在远程服务器上下载我们对应的程序包进行安装。当我们再次要安装程序包时我们本地服务器又会对比本地缓存的元数据文件和远程仓库服务器的元数据文件的校验码,若是一致的就不会再下载相应的元数据文件,若不一致就会重新下载远程服务器上的元数据文件。
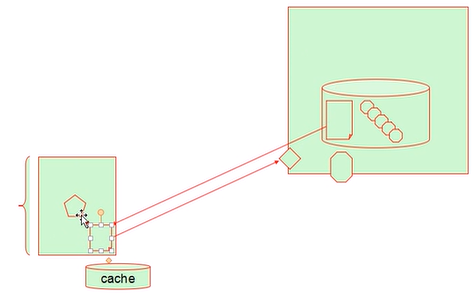
b、YUM早些时候是yellow dog研发的而不是redhat提供。YUM的全称为Yellowdog Update Modifier
c、yum repository:yum repo,也就是yum仓库,其存储了众多的rpm包,以及包的相关的元数据文件(放置于特定目录下:repodata),repodata所在的目录的位置就是这个仓库应该指向的路径
2、yum仓库所提供的访问方式
a、ftp://
b、http://
c、nfs://
d、file://
3、yum客户端
a、我们查看yum的配置文件,可以看到主配置文件/etc/yum.conf,其还有一个配置文件路径为 /etc/yum.repos.d/*.repo
/etc/yum.conf :为所有仓库提供公共配置
/etc/yum.repos.d/*.repo :为每一个仓库提供特有配置
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qc yum /etc/logrotate.d/yum /etc/yum.conf /etc/yum/version-groups.conf
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/yum.conf [main] cachedir=/var/cache/yum/$basearch/$releasever keepcache=0 #本地缓存的文件在使用完以后要不要保存下来 debuglevel=2 #调试级别 logfile=/var/log/yum.log #yum的日志文件 exactarch=1 #安装程序包时要不要进行精确的平台匹配 obsoletes=1 # gpgcheck=1 #装某一个包时是否要检查其完整性和来源合法性 plugins=1 #是否支持插件机制 installonly_limit=5 #支持同时安装几个程序包 bugtracker_url=http://bugs.centos.org/set_project.php?project_id=23&ref=http://bugs.centos.org/bug_report_page.php?category=yum distroverpkg=centos-release # This is the default, if you make this bigger yum won't see if the metadata # is newer on the remote and so you'll "gain" the bandwidth of not having to # download the new metadata and "pay" for it by yum not having correct # information. # It is esp. important, to have correct metadata, for distributions like # Fedora which don't keep old packages around. If you don't like this checking # interupting your command line usage, it's much better to have something # manually check the metadata once an hour (yum-updatesd will do this). # metadata_expire=90m # PUT YOUR REPOS HERE OR IN separate files named file.repo # in /etc/yum.repos.d
4、仓库的定义
a、定义格式
[repositoryID]
name=Some name for this repository
baseurl=url://path/to/repository/
url2://path/to/repository
url3://path/to/repository (#多个url的写法)
enabled={1|0}表示是否启用此仓库,1表示启用,0表示禁用
gpgcheck={1|0}表示是否检查仓库完整性和来源合法性
gpgkey=URL 指明密钥文件,这个密钥文件有可能是对方仓库提供的,这个URL就是指向仓库密钥文件的路径
enablegroups={1|0} 是否支持在此仓库上使用组来批量管理程序包,默认是1
failovermethod={roundrobin|priority} 轮询或优先级,默认为轮询,意为随机挑选
cost= #开销,默认为1000
b、实战
首先我们看我们对应的配置文件路径下的文件
[root@localhost ~]# ls /etc/yum.repos.d/ CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Sources.repo CentOS-Vault.repo
然后我们将该路径下的repo文件备份并自己创建repo文件
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/Centos-local.repo [base] name=Base Repo on 172.16.0.1 baseurl=http://172.16.0.1/cobbler/ks_mirror/CentOS-6.6-x86_64/ gpgcheck=0 [epel] name=Fedora EPEL for EL6 x86_64 baseurl=http://172.16.0.1/fedora-epel/6/x86_64/ gpgcheck=0
然后我们通过命令yum repolist列出所有的yum仓库

我们可以看到他首先会去服务器上下载primary_db这个文件,然后会列出对应的repo的id和 repo名字,status表示当前仓库中有多少个程序包
5、yum命令
a、显示仓库列表
repolist [all|enabled|disabled] 。默认显示启用的,如果要显示所有就显示all
yum repolist all #显示所有仓库列表
yum repolist disabled #显示禁用的仓库列表
yum repolist | yum repolist enabled #显示启用的仓库列表
b、显示程序包
list
yum list all #显示所有
yum list available|installed|updates #显示仓库中所有 可用的 | 有但是还没有安装的 | 所有可升级的
c、安装程序包
install
yum install package1 package2 ...
默认会装最新版本的包,若要安装指定版本的需要加上版本号
d、升级程序包
yum update package1 package2
降级程序包
yum downgrade package1 package2
e、检查可用升级
yum check-update
f、卸载程序包
yum remove package1 package2
g、查看程序包的信息
yum info package
[root@localhost ~]# yum info gcc Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.aliyun.com * extras: mirror.lzu.edu.cn * updates: mirrors.cn99.com Installed Packages Name : gcc Arch : x86_64 Version : 4.8.5 Release : 39.el7 Size : 37 M Repo : installed From repo : base Summary : Various compilers (C, C++, Objective-C, Java, ...) URL : http://gcc.gnu.org License : GPLv3+ and GPLv3+ with exceptions and GPLv2+ with exceptions and LGPLv2+ and BSD Description : The gcc package contains the GNU Compiler Collection version 4.8. : You'll need this package in order to compile C code.
h、查看指定的特性(可用是某文件)是由哪个程序包所提供,相当于rpm -qf
yum provides package
[root@localhost ~]# yum provides gcc Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.aliyun.com * extras: mirror.lzu.edu.cn * updates: mirrors.cn99.com gcc-4.8.5-39.el7.x86_64 : Various compilers (C, C++, Objective-C, Java, ...) Repo : base gcc-4.8.5-39.el7.x86_64 : Various compilers (C, C++, Objective-C, Java, ...) Repo : @base
i、清理本地缓存
yum clean [ packages | metadata | expire-cache | rpmdb | plugins | all ]
yum clean all #直接清理所有即可
j、构建缓存
yum makecache
k、搜索
yum search string1 string2
以指定的关键字搜索程序包名及sumary信息
l、重新安装程序包
yum reinstall package1 package2
m、查看对应程序包依赖哪些其它包
yum deplist package
n、yum的每次更新操作都会启动yum事务,而history可以查看相关的更新信息
history [info|list|packages-list|packages-info|summary|addon-info|redo|undo|rollback|new|sync|stats]
yum history #即可查看所有信息
o、安装及升级本地程序包(现在直接使用install,可以不用localinstall)
* localinstall rpmfile1 [rpmfile2] [...]
(maintained for legacy reasons only - use install)
* localupdate rpmfile1 [rpmfile2] [...]
(maintained for legacy reasons only - use update)
6、包组管理的相关命令
yum groupinstall group1 group2 #安装包组
yum grouplist #列出有哪些包组
yum groupdate group1 group2 #升级相应包组
yum groupremove group1 group2 #移除相应包组
yum groupinfo group1 group2 #查看相应的包组的信息
7、Centos7制作本地镜像yum源
[root@localhost /]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/local.repo [base-local] name=CentOS 7 Release 7 baseurl=file:///mnt enable=1 gpgcheck=0
....