Just because we're experts doesn't mean we know how to help other people also become experts. (we are experts in using computer, but we may not be experts in helping others using is)
In my experience, many people look at HCI like this. The red dot represents what they know and the black circle represents what they think there's to know. They know there's probably somethings they don't know yet, but they're already pretty at it, and it wouldn't be too hard to become an expert.
After studying HCI for a bit though, they look more like this. You can see that they've increased what they know buttheir perception of what there is to kn
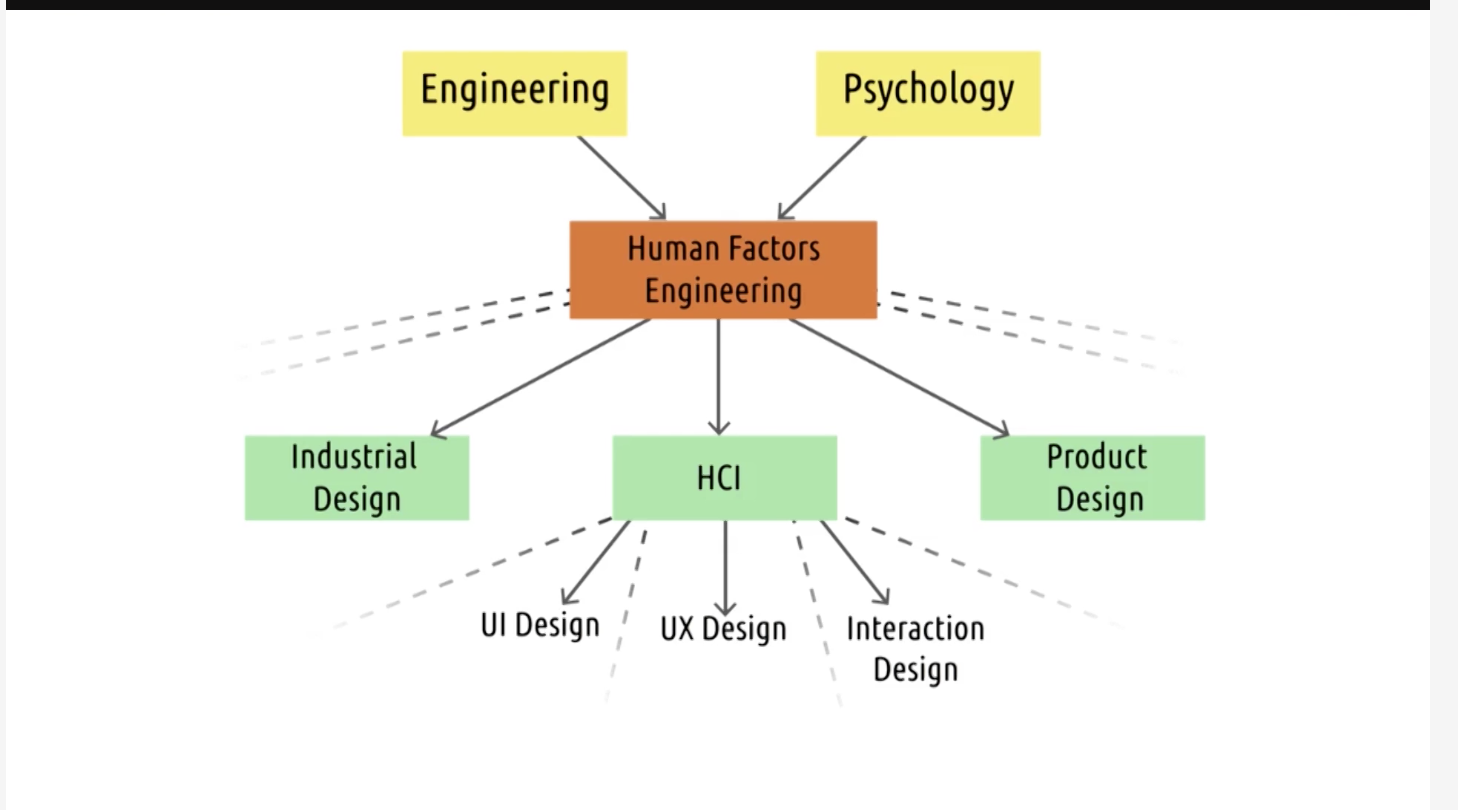
Human factors
Human factors is interested in designing interactions between people and products, systems or devices.
HCI is interested interested in interactions between computers. Although computers are also a part of products or systems, but human factors also care about non-computing part.
Interaction Design
But in HCI, we're interested in things that go beyond the user's interaction with a single screen. Technically, you an cover that in UI design as well, but traditionally most of the UI design classes I see focus on on-screen interaction. In HCI, we'll talk about the more general methods that apply to.
User Experience Design
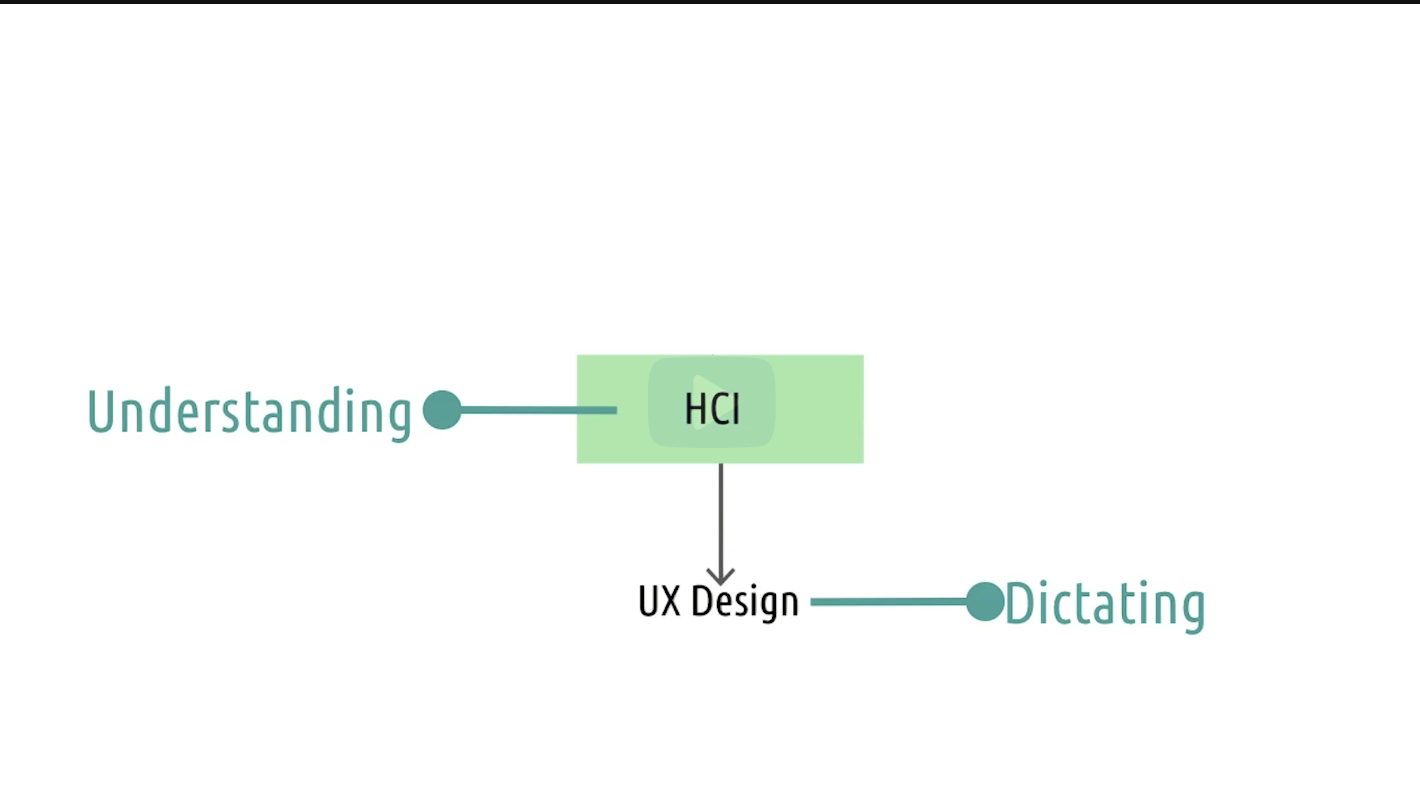
HCI is more about understanding the users interactions while UX about dictating. However, understanding informs dictating, and the result of dictating conducts the research ( feedback cycle ).
Psychology
Symbyotic. Psychology helps better understand human interface design and the results help us better know human.

What HCI is ?
About general principles and methods for designing and researching all of these things, eg : smart phones and smart watch, or some kind of touch or gesture based system.

About this class
First, we want you to understand some of the common principles in human computer interaction.
Second, we want you to understand design life cycle.
Third, we want you to understand the expense of the human computer inherent interaction field and the current applications available for HCI.
The first part of this learning outcome is to design. Well for us design is going to take two forms.
First, design is an activity where you're appl known principles to a new problem.
But design is a second form as well, design is also a process where you gather information, use it to develop design alternatives, evaluate them with users and revise them accordingly.
The second part is effectiveness. (usability/research/change).
The third part is between humans and computer. Instead of just designing interfaces, we designing tasks.

So, the same principles we discussed for designing good representations, apply directly to designing good visualizations.
Technology:
VR
AR
Ubicomp and wearables
robotics
mobile
Idea:
Context-sensitive
Gesture-based interaction
pen and touch based interaction
information visualization
CSCW
Social Computing
Domain:
Special Needs
Education
HealthCare
Security
Games
MacKenzie, I.S. (2013). Chapter 1: Historical Context. Human-Computer Interaction: An Empirical Research Perspective. (pp. 1-26). Waltham, MA: Elsevier.
Norman, D. (2013). Chapter 1: The Psychopathology of Everyday Things. In The Design of Everyday Things: Revised and Expanded Edition. (pp. 1-36). Arizona: Basic Books.