
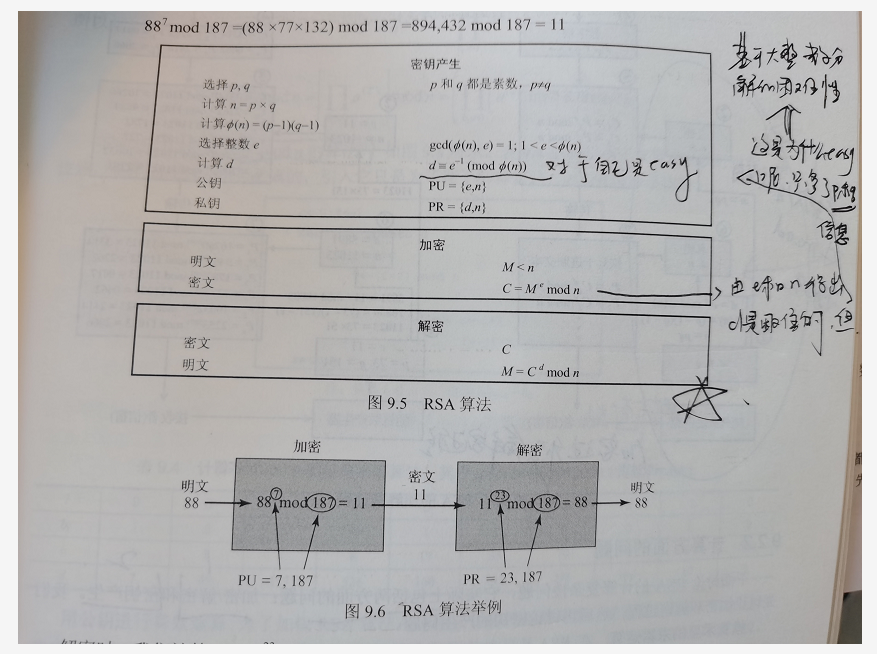
生成RSA公钥和私钥源代码:
# RSA Key Generator # http://inventwithpython.com/hacking (BSD Licensed) import random, sys, os, rabinMiller, cryptomath def main(): # create a public/private keypair with 1024 bit keys print('Making key files...') makeKeyFiles('My_al_sweigart', 1024) print('Key files made.') def generateKey(keySize): # Creates a public/private key pair with keys that are keySize bits in # size. This function may take a while to run. # Step 1: Create two prime numbers, p and q. Calculate n = p * q. print('Generating p prime...') p = rabinMiller.generateLargePrime(keySize) print('Generating q prime...') q = rabinMiller.generateLargePrime(keySize) n = p * q # Step 2: Create a number e that is relatively prime to (p-1)*(q-1). print('Generating e that is relatively prime to (p-1)*(q-1)...') while True: # Keep trying random numbers for e until one is valid. e = random.randrange(2 ** (keySize - 1), 2 ** (keySize)) if cryptomath.gcd(e, (p - 1) * (q - 1)) == 1: break # Step 3: Calculate d, the mod inverse of e. print('Calculating d that is mod inverse of e...') d = cryptomath.findModInverse(e, (p - 1) * (q - 1)) publicKey = (n, e) privateKey = (n, d) print('Public key:', publicKey) print('Private key:', privateKey) return (publicKey, privateKey) def makeKeyFiles(name, keySize): # Creates two files 'x_pubkey.txt' and 'x_privkey.txt' (where x is the # value in name) with the the n,e and d,e integers written in them, # delimited by a comma. # Our safety check will prevent us from overwriting our old key files: if os.path.exists('%s_pubkey.txt' % (name)) or os.path.exists('%s_privkey.txt' % (name)): sys.exit('WARNING: The file %s_pubkey.txt or %s_privkey.txt already exists! Use a different name or delete these files and re-run this program.' % (name, name)) publicKey, privateKey = generateKey(keySize) print() print('The public key is a %s and a %s digit number.' % (len(str(publicKey[0])), len(str(publicKey[1])))) print('Writing public key to file %s_pubkey.txt...' % (name)) fo = open('%s_pubkey.txt' % (name), 'w') fo.write('%s,%s,%s' % (keySize, publicKey[0], publicKey[1])) fo.close() print() print('The private key is a %s and a %s digit number.' % (len(str(publicKey[0])), len(str(publicKey[1])))) print('Writing private key to file %s_privkey.txt...' % (name)) fo = open('%s_privkey.txt' % (name), 'w') fo.write('%s,%s,%s' % (keySize, privateKey[0], privateKey[1])) fo.close() # If makeRsaKeys.py is run (instead of imported as a module) call # the main() function. if __name__ == '__main__': main()
输出:
Making key files... Generating p prime... Generating q prime... Generating e that is relatively prime to (p-1)*(q-1)... Calculating d that is mod inverse of e... Public key: (20568209143252677078119058168035601492144407205238081134389623947553300520383618030722441824670851677422189702723379242411514807896505490593597921854779812062674476053726125420344205324094301464457020885689767121622218081530221054583979666503684425034850236608787337390539929601328218742032586632310678202364192746115447681548961879236126659198967246772560575411272270150281454124957024847454345144448492422499505523531063723013182118490082160576108092986312864068701483352352201348133176665929675070200383558450958684876765269246633232579765908427132470253986564733180661636578698481528251410808656000495485885064431, 177181900604485385859089278995336054349195227209474666610202818353053441867040090258520032166314961421663592461885970774558513073204274276330590792406481442045089473007396586708371196053951107573163533459940834178409635777108403047324843946055420755897292458294340939921932071421000515446556064026169271234081) Private key: (20568209143252677078119058168035601492144407205238081134389623947553300520383618030722441824670851677422189702723379242411514807896505490593597921854779812062674476053726125420344205324094301464457020885689767121622218081530221054583979666503684425034850236608787337390539929601328218742032586632310678202364192746115447681548961879236126659198967246772560575411272270150281454124957024847454345144448492422499505523531063723013182118490082160576108092986312864068701483352352201348133176665929675070200383558450958684876765269246633232579765908427132470253986564733180661636578698481528251410808656000495485885064431, 7544297804112911499835595438087786244369293759362340426923724898724129142903334627532565872658504657521094004289475130282101086721496339841763432746059520461931838529840299232037775380093296293819701492727284536815962451803964299140089004238048627952122461961009066850182817277670646751222914605884206560142748298012655939192075865725846086784942443603911613591811516706031116496827201593383652693058605818812988727083044414499024334725416252854928022025717438652365028432440776312271001450594807555403586614201310624921975796215190494396608061113848000305749355551768849965813180689089873683173378913796765576813577) The public key is a 617 and a 309 digit number. Writing public key to file My_al_sweigart_pubkey.txt... The private key is a 617 and a 309 digit number. Writing private key to file My_al_sweigart_privkey.txt... Key files made.
P.S.
- 这个算法用到了RabinMiller算法生成质数
- 用到了扩展欧几里得算法findModInverse来找到模逆
- 生成文件代码
os.path.exists('%s_pubkey.txt' % (name))检查文件name.txt是否存在

fo = open('%s_pubkey.txt' % (name), 'w') fo.write('%s,%s,%s' % (keySize, publicKey[0], publicKey[1])) fo.close()
注意,RSA加密算法是分组加密。每一组为一个(明文密文)块,而且,RSA只能加密文本文件,而不能加密二进制文件
但是,所有的数据都是以数字的形式保存在计算机中的, 那么就需要一个字符到数字的映射:
ASCII美国信息交换标准代码:
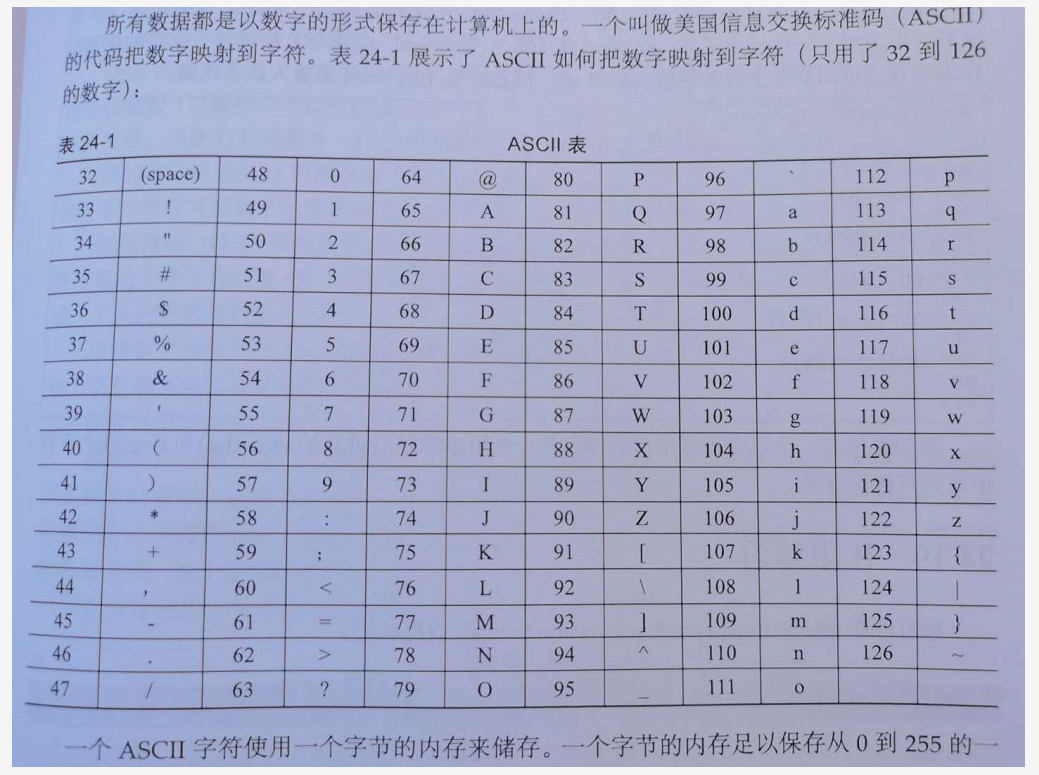
一个ASCII字符使用一个字节的内存来存储。
chr() 和 ord():字符和数字之间的转化
>>> chr(88) 'X' >>> chr(333) 'ō' >>> chr(3335) 'ഇ' >>> chr(33357) '艍' >>> ? File "<stdin>", line 1 ? ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax >>> ord('A') 65 >>> chr(ord('A')) 'A' >>> ord('AW') Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> TypeError: ord() expected a character, but string of length 2 found >>>
但是chr() 和 ord()只能是做到单个字符的转化。所以必须有一种字符串的转化。
区块
密码学中,“区块” 是 固定长度的位。 (p.s. 常有128字节 1024字节)
在RSA加密中,要求区块大小等于或者小于密钥大小
我们的区块如果是128个字节,那么它可以表示0到256^128(不含)的任何一个整数,可以想象,RSA中到处是大整数
为什么要用区块,和大整数?
如果使用单个字符的话,相同的消息会被加密成相同的结果,就有点像是仿射和凯撒加密法了。从安全性角度说,
RSA的安全性是基于大整数分解成两个素数的困难
现在问题就涉及了如何把字符串转化成一个大整数,即:
把ASCII整数合并成一个大的数字!===========把字符串编码成区块
举个栗子:编码'Hello World!'
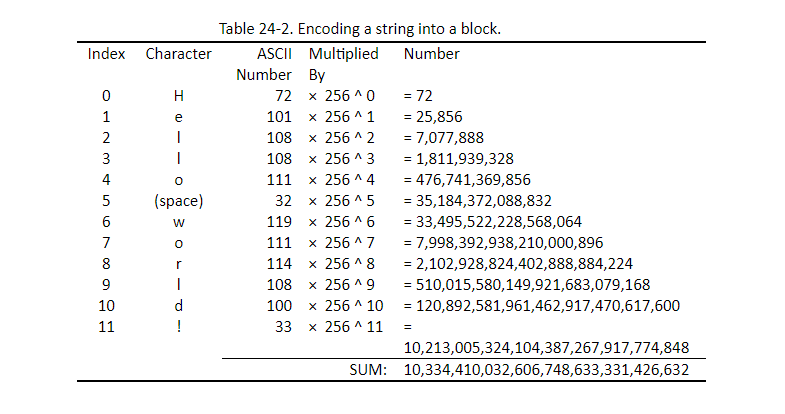
这个最后的整数和就是密文的区块!!!
因为我们的区块是设置了128个字节,所以在一个区块里最多只能加密128个字符。
所以如果消息超过了128个字符,必须对其进行分组从而加密多个区块,RSA会用逗号‘,’来间隔不同的区块
encode()字符串方法
encode()字符串方法将返回一个"Bytes"对象,是普通字符串值前面加上一个'b' b和后面的字符串之间没有空格
>>> spam = 'hello'.encode('ascii') >>> spam b'hello' >>> list(spam) [104, 101, 108, 108, 111] >>> len(spam) 5 >>> spam[2] 108 >>>
可以通过调用bytes()函数来创建"Bytes"对象
>>> spam = bytes([123, 854, 25, 69, 255]) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> ValueError: bytes must be in range(0, 256) >>> spam = bytes([123, 85, 25, 69, 255]) >>> spam b'{Ux19Exff' >>> spam = b'World' >>> spam b'World' >>> list(spam) [87, 111, 114, 108, 100] >>>
decode()• bytes对象方法
在一个"bytes"对象上调用decode()方法,返回这个bytes对象里保存的字符串
>>> spam = bytes([104, 101, 108, 108, 111]) >>> spam b'hello' >>> spam.decode('ascii') 'hello' >>>
insert()列表方法
insert()列表方法可以把一个值插入到列表中的任何一个地方,第一个参数是插入到的地方的索引,第二个参数是要插入的值
>>> spam = [2, 5, 9, 99] >>> spam.insert(0, 555) >>> spam [555, 2, 5, 9, 99] >>> spam.insert(7, 777) >>> spam [555, 2, 5, 9, 99, 777] >>> spam.insert(6, 7777777) >>> spam [555, 2, 5, 9, 99, 777, 7777777] >>> spam.insert(0, 'dsdasd') >>> spam ['dsdasd', 555, 2, 5, 9, 99, 777, 7777777] >>>
加密源码:
# RSA Cipher # http://inventwithpython.com/hacking (BSD Licensed) import sys # IMPORTANT: The block size MUST be less than or equal to the key size! # (Note: The block size is in bytes, the key size is in bits. There # are 8 bits in 1 byte.) # DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE = 128 # 128 bytes # 一个字节可以保存0 - 255 中的任意一个数共256个数 BYTE_SIZE = 256 # One byte has 256 different values. def main(): # Runs a test that encrypts a message to a file or decrypts a message # from a file. filename = 'encrypted_file.txt' # the file to write to/read from mode = 'decrypt' # set to 'encrypt' or 'decrypt' if mode == 'encrypt': message = '''"Journalists belong in the gutter because that is where the ruling classes throw their guilty secrets." -Gerald Priestland "The Founding Fathers gave the free press the protection it must have to bare the secrets of government and inform the people." -Hugo Black''' pubKeyFilename = 'al_sweigart_pubkey.txt' print('Encrypting and writing to %s...' % (filename)) encryptedText = encryptAndWriteToFile(filename, pubKeyFilename, message) print('Encrypted text:') print(encryptedText) elif mode == 'decrypt': privKeyFilename = 'al_sweigart_privkey.txt' print('Reading from %s and decrypting...' % (filename)) decryptedText = readFromFileAndDecrypt(filename, privKeyFilename) print('Decrypted text:') print(decryptedText) # 把消息转成区块,很多个区块, def getBlocksFromText(message, blockSize=DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE): # Converts a string message to a list of block integers. Each integer # represents 128 (or whatever blockSize is set to) string characters. messageBytes = message.encode('ascii') # convert the string对象 to bytes对象 # 每个区块转换成一个很大的整数,保存到blockInts中 blockInts = [] for blockStart in range(0, len(messageBytes), blockSize): # 正在创建区块的索引 第一个区块索引为0,第一个区块索引为128(取决于blockSize), 第一个区块索引为256, 区块的索引小于len(messageBytes) # Calculate the block integer for this block of text blockInt = 0 for i in range(blockStart, min(blockStart + blockSize, len(messageBytes))): #因为最后一个区块可能是刚好128个字符,但通常会小于128个字符len(messageBytes)-1正是messageBytes的最后一个索引 #blockInt是一个大整数 messageBytes[i] * (BYTE_SIZE ** (i % blockSize))是字符的sacii乘以256^(每个块中的字符索引) blockInt += messageBytes[i] * (BYTE_SIZE ** (i % blockSize)) #BYTE_SIZE = 256 (i % blockSize)是0~字符串长度 blockInts.append(blockInt) return blockInts # 把很多个区块转换成字符消息 必须要messageLength参数为了最后一个区块需要 def getTextFromBlocks(blockInts, messageLength, blockSize=DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE): # Converts a list of block integers to the original message string. # The original message length is needed to properly convert the last # block integer. # 注意最后这是一个message字符列表 最后需要建立连接 message = [] for blockInt in blockInts: blockMessage = [] # 从blockInt提取sacii数字的方式是反向进行的,从blockSize - 1开始,每个迭代-1,直到-1(不包括) for i in range(blockSize - 1, -1, -1): if len(message) + i < messageLength: # Decode the message string for the 128 (or whatever # blockSize is set to) characters from this block integer. asciiNumber = blockInt // (BYTE_SIZE ** i) # 既然我们已经计算了这个字符,就需要移除,通过blockInt除以(BYTE_SIZE ** i)取余得到,yeap 逆向嘛 blockInt = blockInt % (BYTE_SIZE ** i) # 一个一个字符asciiNumber 0~255插入 blockMessage.insert(0, chr(asciiNumber)) message.extend(blockMessage) return ''.join(message) def encryptMessage(message, key, blockSize=DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE): # Converts the message string into a list of block integers, and then # encrypts each block integer. Pass the PUBLIC key to encrypt. encryptedBlocks = [] n, e = key for block in getBlocksFromText(message, blockSize): # ciphertext = plaintext ^ e mod n encryptedBlocks.append(pow(block, e, n)) # C = M^e mod n return encryptedBlocks def decryptMessage(encryptedBlocks, messageLength, key, blockSize=DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE): # Decrypts a list of encrypted block ints into the original message # string. The original message length is required to properly decrypt # the last block. Be sure to pass the PRIVATE key to decrypt. decryptedBlocks = [] n, d = key for block in encryptedBlocks: # plaintext = ciphertext ^ d mod n decryptedBlocks.append(pow(block, d, n)) # M = C^d mod n return getTextFromBlocks(decryptedBlocks, messageLength, blockSize) def readKeyFile(keyFilename): # Given the filename of a file that contains a public or private key, # return the key as a (n,e) or (n,d) tuple value. fo = open(keyFilename) content = fo.read() fo.close() keySize, n, EorD = content.split(',') return (int(keySize), int(n), int(EorD)) def encryptAndWriteToFile(messageFilename, keyFilename, message, blockSize=DEFAULT_BLOCK_SIZE): # Using a key from a key file, encrypt the message and save it to a # file. Returns the encrypted message string. keySize, n, e = readKeyFile(keyFilename) # Check that key size is greater than block size. if keySize < blockSize * 8: # * 8 to convert bytes to bits sys.exit('ERROR: Block size is %s bits and key size is %s bits. The RSA cipher requires the block size to be equal to or greater than the key size. Either decrease the block size or use different keys.' % (blockSize * 8, keySize)) # Encrypt the message encryptedBlocks = encryptMessage(message, (n, e), blockSize) # Convert the large int values to one string value. for i in range(len(encryptedBlocks)): encryptedBlocks[i] = str(encryptedBlocks[i]) encryptedContent = ','.join(encryptedBlocks) # Write out the encrypted string to the output file. encryptedContent = '%s_%s_%s' % (len(message), blockSize, encryptedContent) fo = open(messageFilename, 'w') fo.write(encryptedContent) fo.close() # Also return the encrypted string. return encryptedContent def readFromFileAndDecrypt(messageFilename, keyFilename): # Using a key from a key file, read an encrypted message from a file # and then decrypt it. Returns the decrypted message string. keySize, n, d = readKeyFile(keyFilename) # Read in the message length and the encrypted message from the file. fo = open(messageFilename) content = fo.read() messageLength, blockSize, encryptedMessage = content.split('_') messageLength = int(messageLength) blockSize = int(blockSize) # Check that key size is greater than block size. if keySize < blockSize * 8: # * 8 to convert bytes to bits sys.exit('ERROR: Block size is %s bits and key size is %s bits. The RSA cipher requires the block size to be equal to or greater than the key size. Did you specify the correct key file and encrypted file?' % (blockSize * 8, keySize)) # Convert the encrypted message into large int values. encryptedBlocks = [] for block in encryptedMessage.split(','): encryptedBlocks.append(int(block)) # Decrypt the large int values. return decryptMessage(encryptedBlocks, messageLength, (n, d), blockSize) # If rsaCipher.py is run (instead of imported as a module) call # the main() function. if __name__ == '__main__': main()
输出:
加密 mode='encrypt'
Encrypting and writing to encrypted_file.txt... Encrypted text: 262_128_9926158891891412924886952141356136142542943862695072991250598006600270898300155338706636681856461575090075284572263362618218739769545313477249608401485234147843064609273929706353514554444810285427183303767133366827434264155196422091782649929928244535021903927052585385716925680743931745588143336997344189661596414349468058963048024948132923217849247276941269579027325396701709129191510084539012275457327046892059514600198713235394985023008043572425418307615110483262279656839322893000061931573893934153492056320331481641996204470201622784975235041470244964996075123464854629954207517620745550909143567815440815430367,6684261355384175628979536129678576912290902989264360857554803434400959272554726558432523319331127651229226379236001569105754247234449664301393066887072563919911914664504822721492217530056774346964092597494522555496959638903763181124233744530745204194891726109468870800424574799803024463576184984561160905385692143883155534327512132834866466005840402451465709012175029417109925035724824080741967623225446680099823178790059243202224297039960462494558200472899766913932921695002362188199621771371349477094464441789497029364384034674419241261434600801973782901186703144271104078294839144290043228508639879193883889311384,7277016624458973047704080668015657545528557043555314379029981553323365606133331342297139093317529026058177734586887567745897370142270546218412444852855142060252694055284415945350850536174716382559790627193026256934316461174349640238168693204610463496242533658473621140628689617878612045411645907503868803711923465905950382446525719000159190942639677572746105141288262702033570490198413350331921834181220670294175801373024013553583624428117568253845170657841567369678118510784447456725765265002966285445904361732332706663086388760638687504068870937711285114415078149377285832325922978358897651126143551277531003851780
解密:mode='decrypt'
Reading from encrypted_file.txt and decrypting... Decrypted text: "Journalists belong in the gutter because that is where the ruling classes throw their guilty secrets." -Gerald Priestland "The Founding Fathers gave the free press the protection it must have to bare the secrets of government and inform the people." -Hugo Black
我们为什么不能破译RSA
太多可能的密钥,暴力破解攻击NO
密钥基于数字,字典攻击NO
因为区块的引入,相同的明文加密成不同的东东西取决于区块在哪里,单词模式攻击NO
单个加密区块表示多个字符,频率分析NO
要解开一切并破译RSA,找出n的因数, n = p * q 再计算d,但这在数学上是困难的。
完结撒花♠♣♥♦,继续努力✊✊✊✊✊✊✊✊