运行环境:vs2012+opencv320
sift 需要的头文件为 <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
bool refineMatchesWithHomography(
const std::vector<cv::KeyPoint>& queryKeypoints,
const std::vector<cv::KeyPoint>& trainKeypoints,
float reprojectionThreshold,
std::vector<cv::DMatch>& matches,
cv::Mat& homography)
{
const int minNumberMatchesAllowed = 8;
if (matches.size() < minNumberMatchesAllowed)
return false;
// Prepare data for cv::findHomography
std::vector<cv::Point2f> srcPoints(matches.size());
std::vector<cv::Point2f> dstPoints(matches.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++) {
srcPoints[i] = trainKeypoints[matches[i].trainIdx].pt;
dstPoints[i] = queryKeypoints[matches[i].queryIdx].pt;
}
// Find homography matrix and get inliers mask
std::vector<unsigned char> inliersMask(srcPoints.size());
homography = cv::findHomography(srcPoints, dstPoints, CV_FM_RANSAC,reprojectionThreshold, inliersMask);
std::vector<cv::DMatch> inliers;
for (size_t i = 0; i < inliersMask.size(); i++) {
if (inliersMask[i])
inliers.push_back(matches[i]);
}
matches.swap(inliers);
return matches.size() > minNumberMatchesAllowed;
}
bool comp(vector<DMatch>& a,vector<DMatch>& b)
{
return a[0].distance/a[1].distance < b[0].distance/b[1].distance;
}
void main()
{
Ptr<xfeatures2d::SIFT>feature=xfeatures2d::SIFT::create();
Mat input1 = imread("sift_img\16.png",1);
Mat input2 = imread("sift_img\11.png",1);
vector<KeyPoint>kp1,kp2;
Mat des1,des2;
Mat output1,output2;
feature->detectAndCompute(input1,cv::noArray(),kp1,des1);
drawKeypoints(input1,kp1,output1);
feature->detectAndCompute(input2,cv::noArray(),kp2,des2);
drawKeypoints(input2,kp2,output2);
vector<DMatch>matches;
vector<vector<DMatch> >Dmatches;
Ptr<cv::DescriptorMatcher> matcher_knn = new BFMatcher();
Ptr<cv::DescriptorMatcher> matcher = new BFMatcher(NORM_L2,true);
matcher->match(des1,des2,matches);
matcher_knn->knnMatch(des1,des2,Dmatches,2);
sort(Dmatches.begin(),Dmatches.end(),comp);
vector<DMatch> good;
for(int i=0;i<Dmatches.size();i++){
if(Dmatches[i][0].distance < 0.75*Dmatches[i][1].distance)
good.push_back(Dmatches[i][0]);
}
Mat imResultOri;
drawMatches(output1, kp1, output2, kp2, matches, imResultOri,CV_RGB(0,255,0), CV_RGB(0,255,0));
Mat matHomo;
refineMatchesWithHomography(kp1, kp2, 3, matches, matHomo);
cout << "[Info] Homography T : " << endl << matHomo << endl;
Mat imResult;
drawMatches(output1, kp1, output2, kp2, matches, imResult,CV_RGB(0,255,0), CV_RGB(0,255,0));
Mat Mgood;
drawMatches(output1, kp1, output2, kp2, good, Mgood,CV_RGB(0,255,0), CV_RGB(0,255,0));
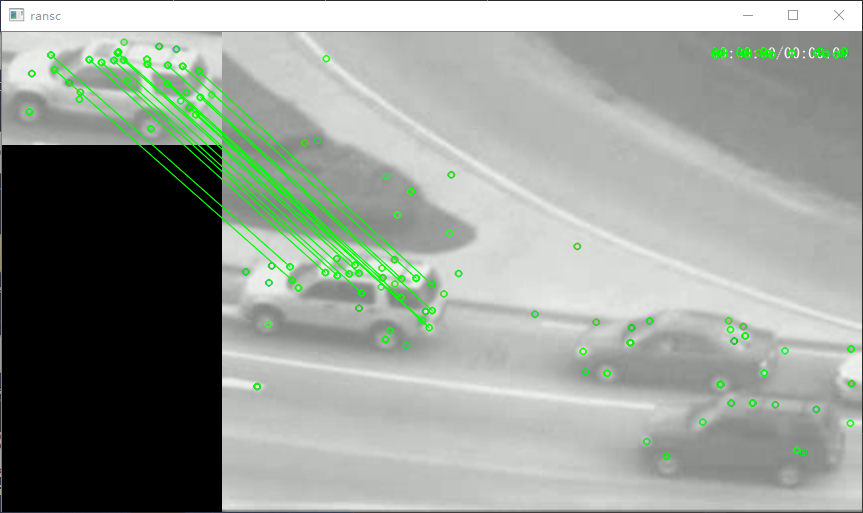
imshow("ransc",imResult);
imshow("knn_match",Mgood);
waitKey(0);
return;
}