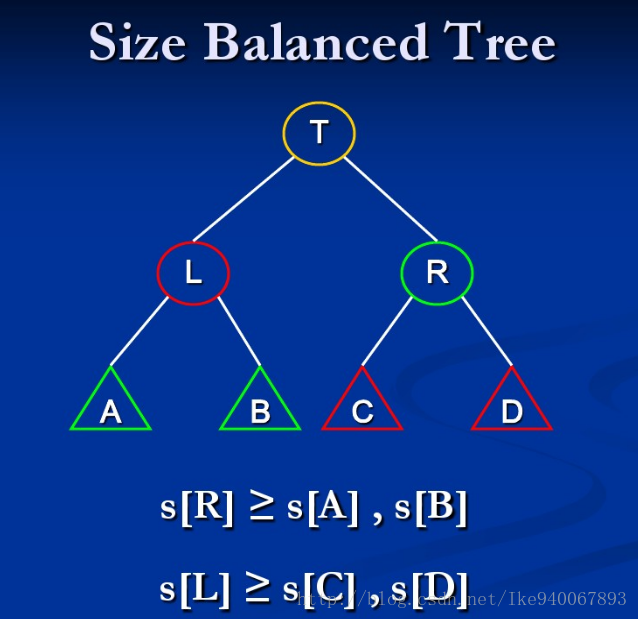
SBT(Size Balance Tree), 即一种通过子树大小(size)保持平衡的BST
SBT的基本性质是:每个节点的size大小必须大于等于其兄弟的儿子的size大小:
当我们插入或者删除一个节点之后,SBT的性质会有所改变,此时需要函数maintain(mt)来维持平衡
mt(T)用于修复以T为根的子树的SBT 调用mt(T)的前提是T的子树都已经是SBT了
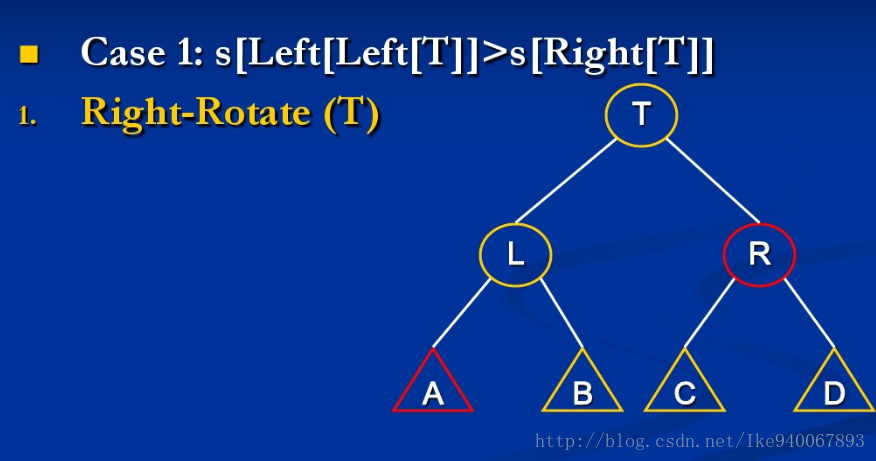
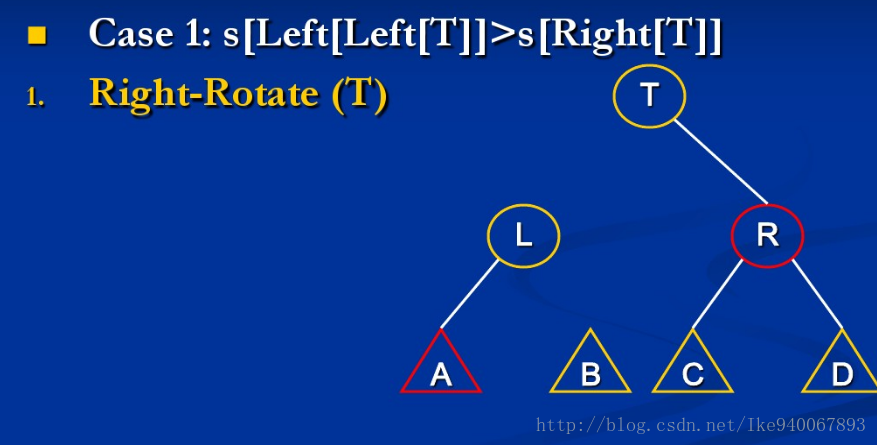
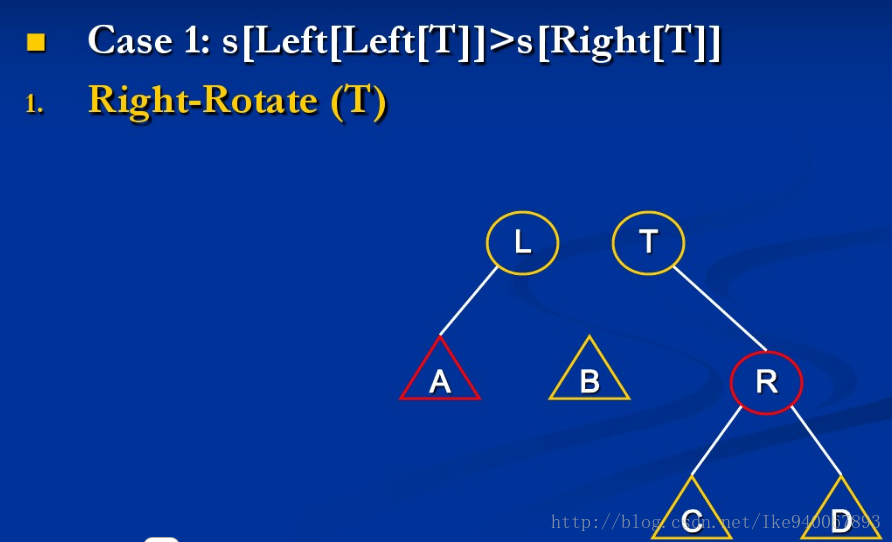
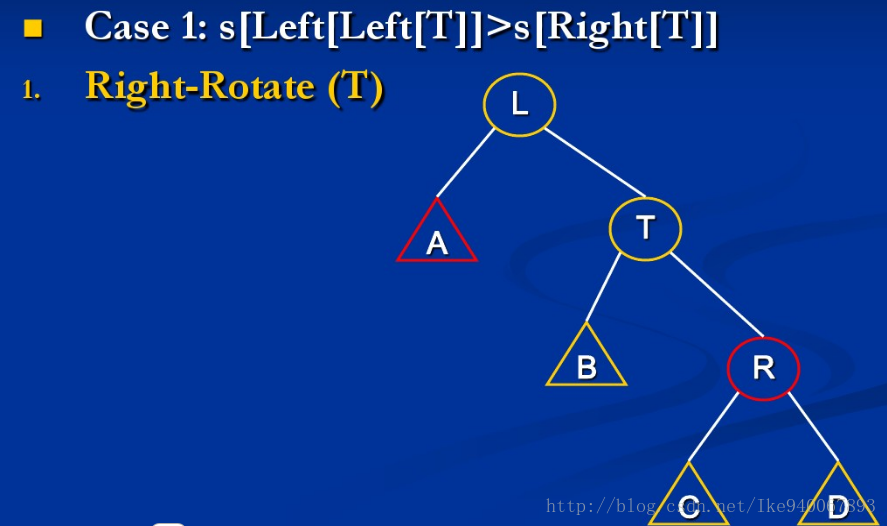
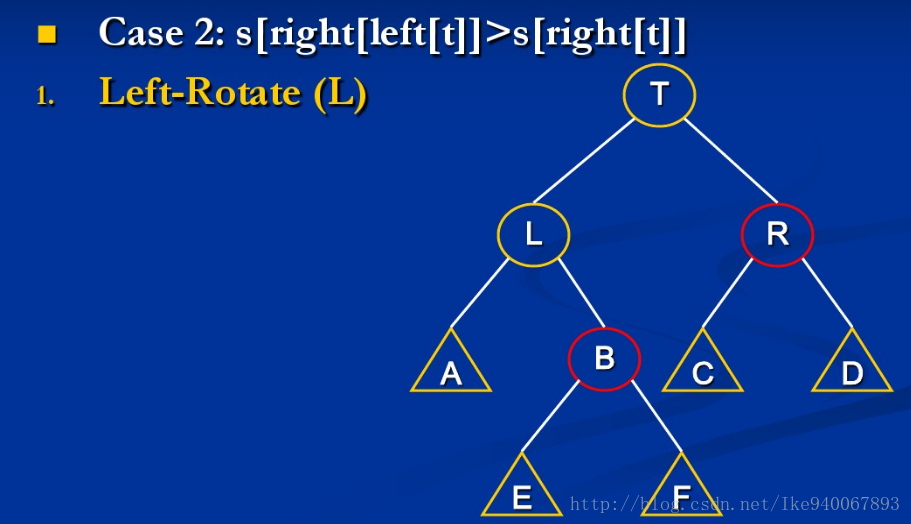
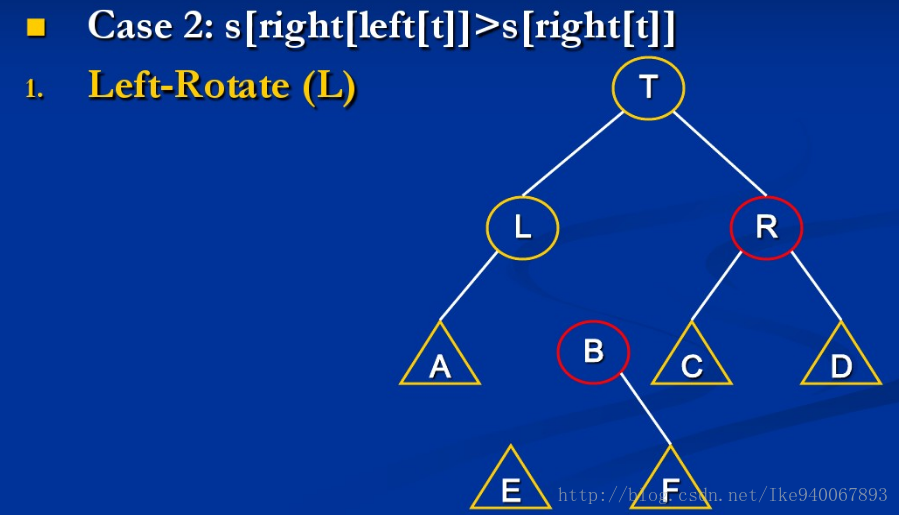
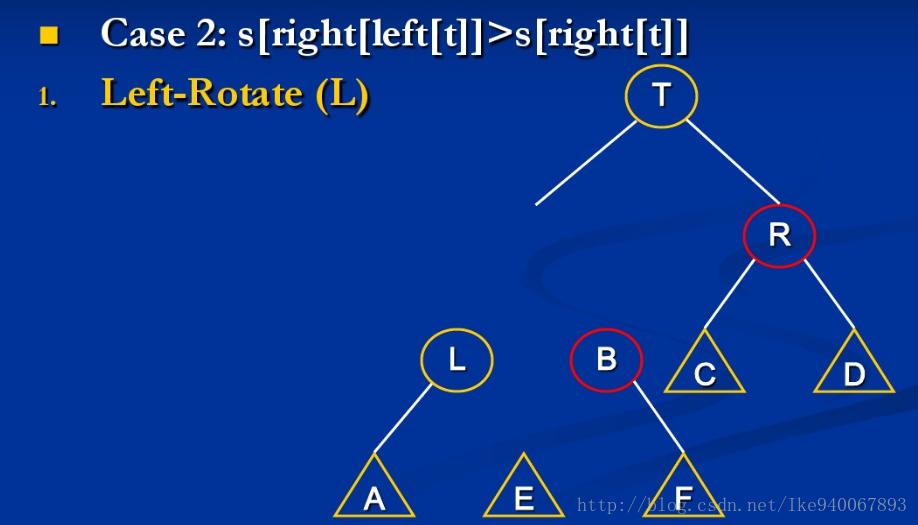
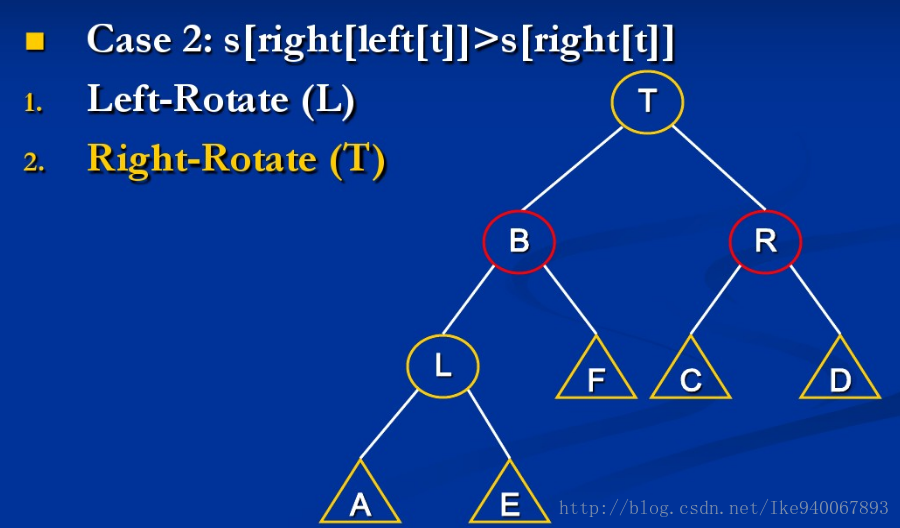
{由于左右对称,这里只讨论关于上图第一个不等式不成立的例子}
情形1:size[A] > size[R]
此时只需继续mt(A)与mt(L)就行
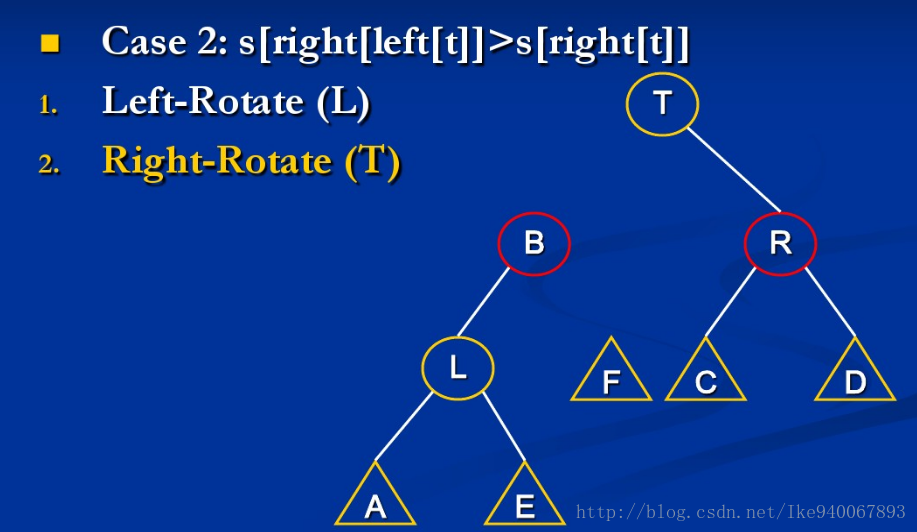
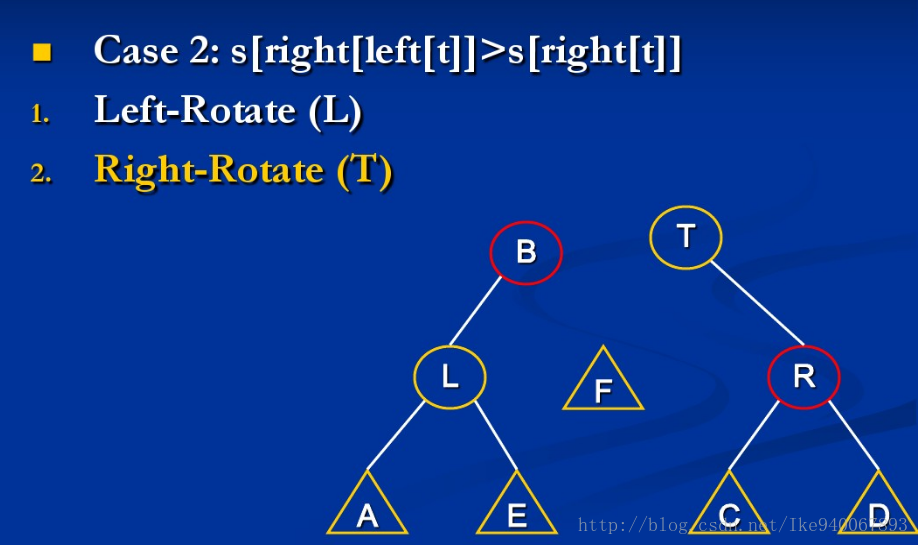
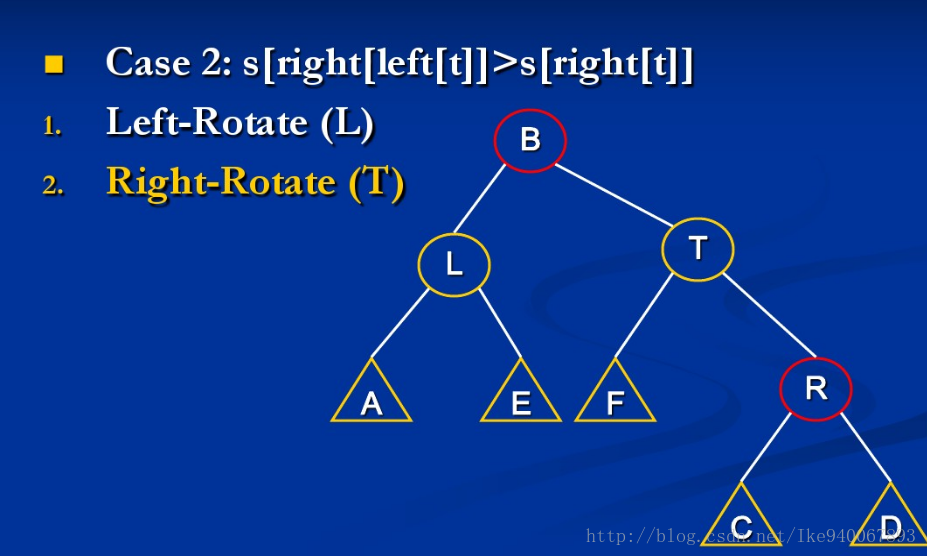
情形2:size[B] > size[R]
此时继续mt(L)与mt(B)
综上,Maintain代码如下:
inline void update(node* r) { r->sz = r->lc->sz + r->rc->sz + 1; }
void rotate(node* &r, bool f) {
node *t = r->ch[f];
r->ch[f] = t->ch[!f];
t->ch[!f] = r;
t->sz = r->sz;
update(r);
r = t;
}
void mt(node* &r, bool f) { //利用左右对称带上参数f同时减去不必要的检查
if(r == NILL) return; //NILL 为空指针
if(r->ch[f]->ch[f]->sz > r->ch[!f]->sz)
rotate(r, f);
else if(r->ch[f]->ch[!f]->sz > r->ch[!f]->sz)
rotate(r->ch[f], !f), rotate(r, f);
else return;
mt(r->ch[f], f);
mt(r, f);
}Analysis of Height
F[H]:高度为H最大结点个数,有定理:
F[H] = Fibonacci[H+2]-1
∴N个结点的SBT的最坏深度最大满足(F[H]<=N)的H,因此:
根据各种分析之后可得:Maintain的单次操作为O(1) SBT的其他操作时间复杂度都为为log(n)
所以SBT被称为目前最快的二叉平衡树!贴上模板题的代码(普通平衡树):
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define lc ch[0]
#define rc ch[1]
const int MAXN = 500000;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct node {
node* ch[2];
int sz, v;
node(){}
}SBT[MAXN+10], *NILL=new node, *root=NILL, *tot=SBT;
int getint() {
int ret = 0; bool f = 0; char ch;
while((ch=getchar()) < '0' || ch > '9')if(ch == '-') f = !f;
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') ret = ret * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
return f ? -ret : ret;
}
void init() {
NILL->lc = NILL;
NILL->rc = NILL;
NILL->sz = 0;
}
inline void update(node* r) { r->sz = r->lc->sz + r->rc->sz + 1; }
node* newnode() {
tot->lc = tot->rc = NILL;
tot->sz = 1;
return tot++;
}
void rotate(node* &r, bool f) {
node *t = r->ch[f];
r->ch[f] = t->ch[!f];
t->ch[!f] = r;
t->sz = r->sz;
update(r);
r = t;
}
void mt(node* &r, bool f) {
if(r == NILL) return;
if(r->ch[f]->ch[f]->sz > r->ch[!f]->sz)
rotate(r, f);
else if(r->ch[f]->ch[!f]->sz > r->ch[!f]->sz)
rotate(r->ch[f], !f), rotate(r, f);
else return;
mt(r->ch[f], f);
mt(r, f);
}
void insert(node* &r, int v) {
if(r == NILL) {
r = newnode();
r->v = v;
return;
}
r->sz++;
bool k = v > r->v;
insert(r->ch[k], v);
mt(r, k);
}
int del(node* &r, int x) {
int ret;
r->sz--;
if(r->v == x || (r->lc == NILL && x < r->v) || (r->rc == NILL && x > r->v)) {
ret = r->v;
if(r->lc == NILL || r->rc == NILL)
r = r->lc==NILL ? r->rc : r->lc;
else r->v = del(r->lc, x);
}
else ret = del(r->ch[x>=r->v], x);
return ret;
}
int sel(int val) {
int ret = 1;
node* p = root;
while(p != NILL) {
if(val <= p->v)
p = p->lc;
else {
ret += p->lc->sz + 1;
p = p-> rc;
}
}
return ret;
}
int rk(int x)
{
node* p = root;
while(p != NILL){
if(x == p->lc->sz + 1)
return p->v;
if(x <= p->lc->sz)
p = p->lc;
else {
x -= p->lc->sz + 1;
p = p->rc;
}
}
return INF;
}
int query(int v, bool f)
{
node* p = root;
int ret = f ? INF : -INF;
while(p != NILL) {
if(p->v != v && (f == (p->v > v) && f == (ret > p->v)))
ret = p->v;
if(v == p->v)
p = p->ch[f];
else p = p->ch[v > p->v];
}
return ret;
}
int main () {
init();
int kase = getint();
while(kase--) {
int opt = getint(), x = getint();
switch(opt) {
case 1:insert(root, x); break;
case 2:del(root, x); break;
case 3:printf("%d
", sel(x)); break;
case 4:printf("%d
", rk(x)); break;
case 5:printf("%d
", query(x, 0)); break;
case 6:printf("%d
", query(x, 1)); break;
}
}
}但可能还是没有avl快