面向过程与面向对象

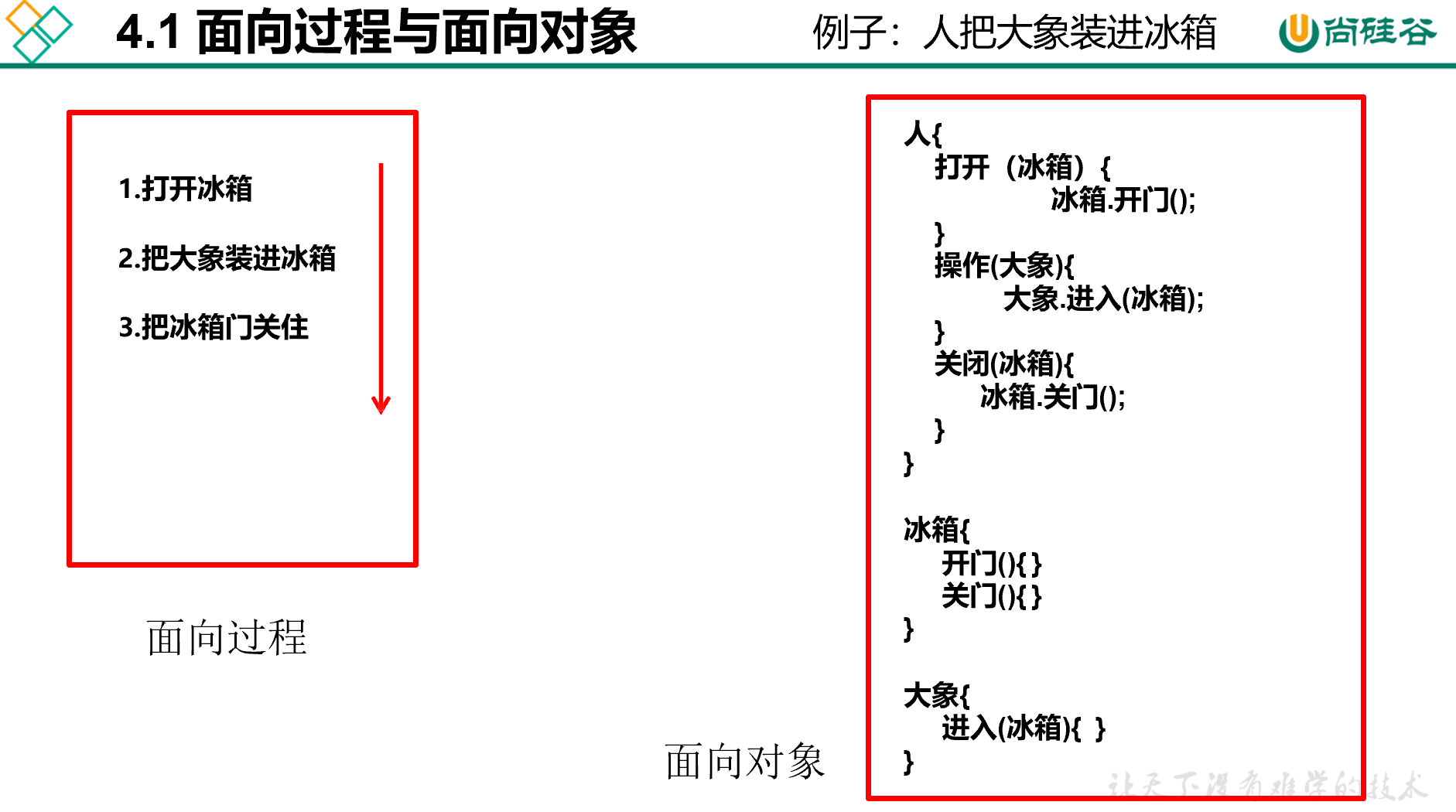

- Java类及类的成员:属性、方法、构造器;代码块、内部类
- 面向对象的三大特征:封装性、继承性、多态性、(抽象性)
类和对象

- 一、设计类,其实就是设计类的成员
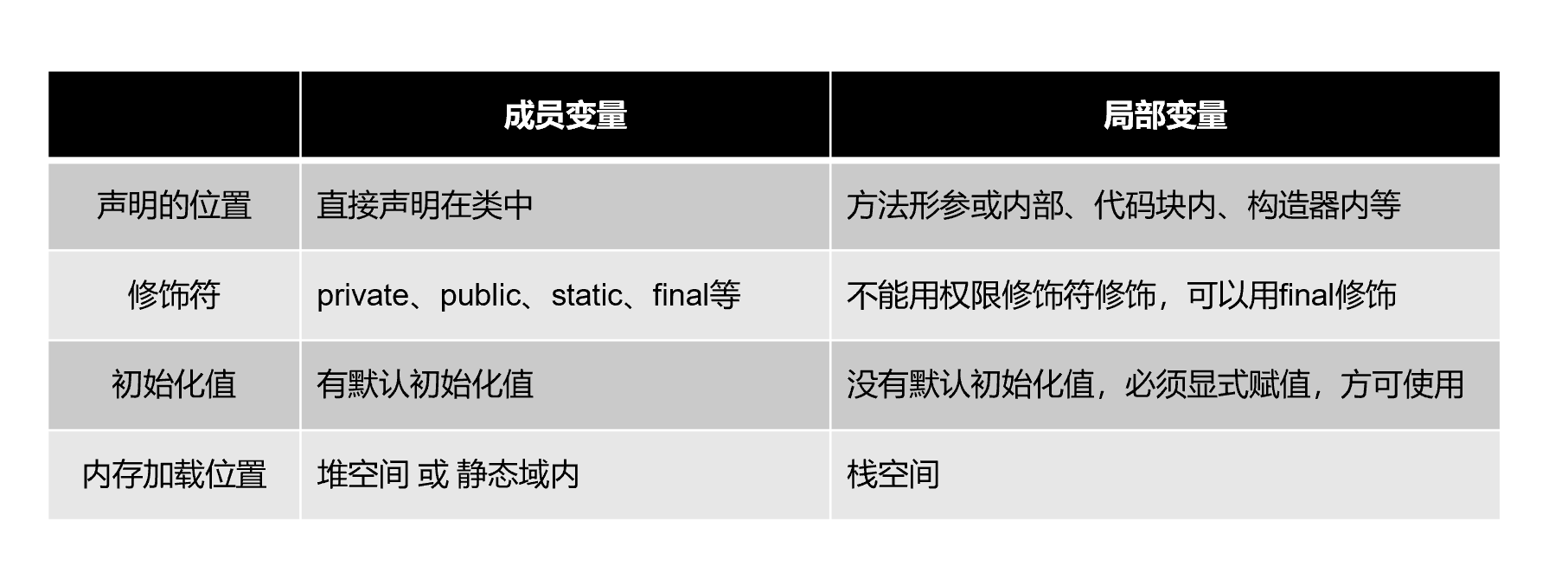
- 属性 = 成员变量 = field = 域、字段
- 方法 = 成员方法 = 函数 = method
- 创建类的对象 = 类的实例化 = 实例化类
- 二、类和对象的使用(面向对象思想落地的实现):
- 1.创建类,设计类的成员
- 2.创建类的对象
- 3.通过“对象.属性”或“对象.方法”调用对象的结构
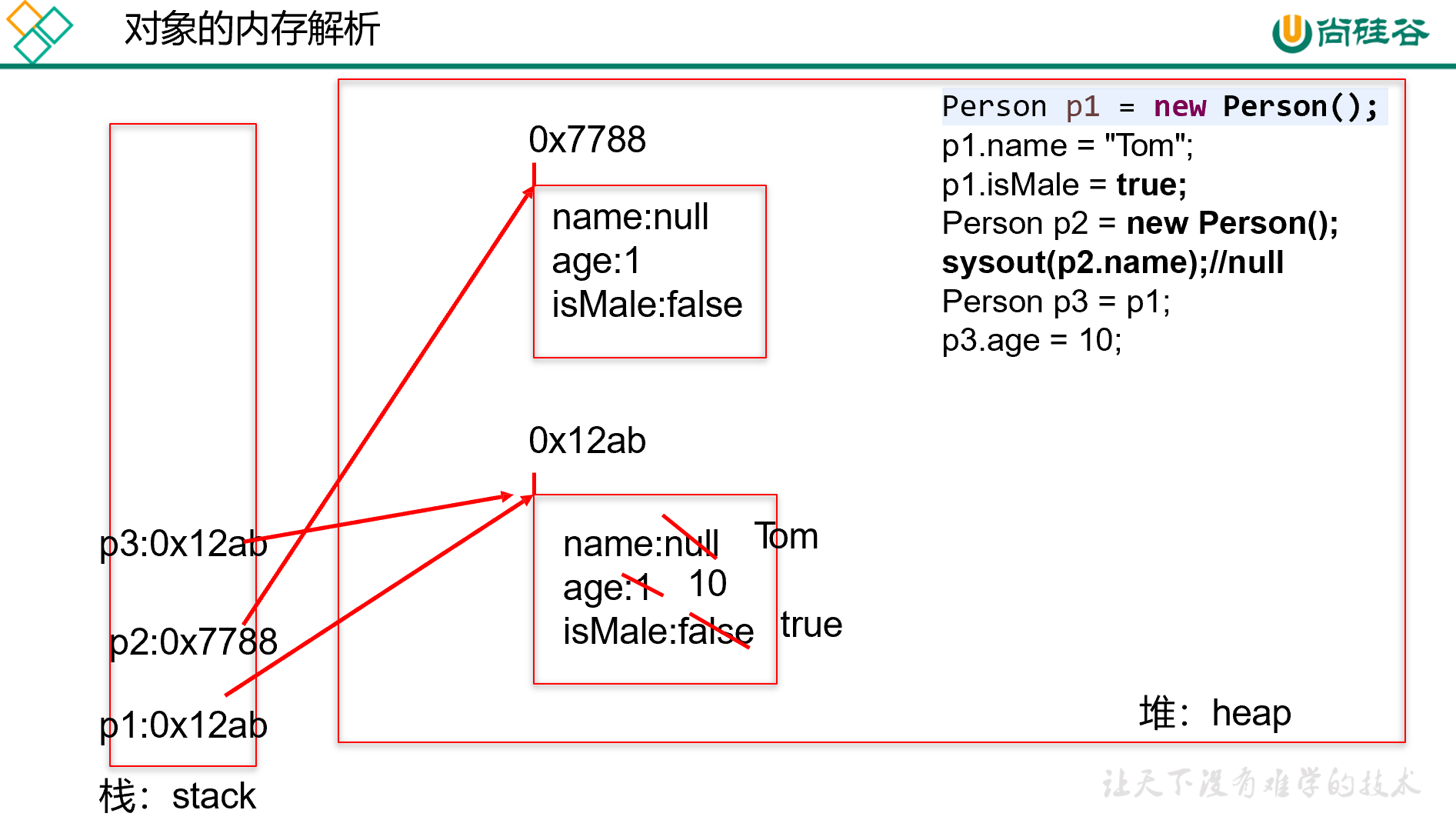
- 三、如果创建了一个类的多个对象,则每个对象都独立的拥有一套类的属性。(非static的)
- 意味着:如果我们修改一个对象的属性a,则不影响另外一个对象属性a的值。

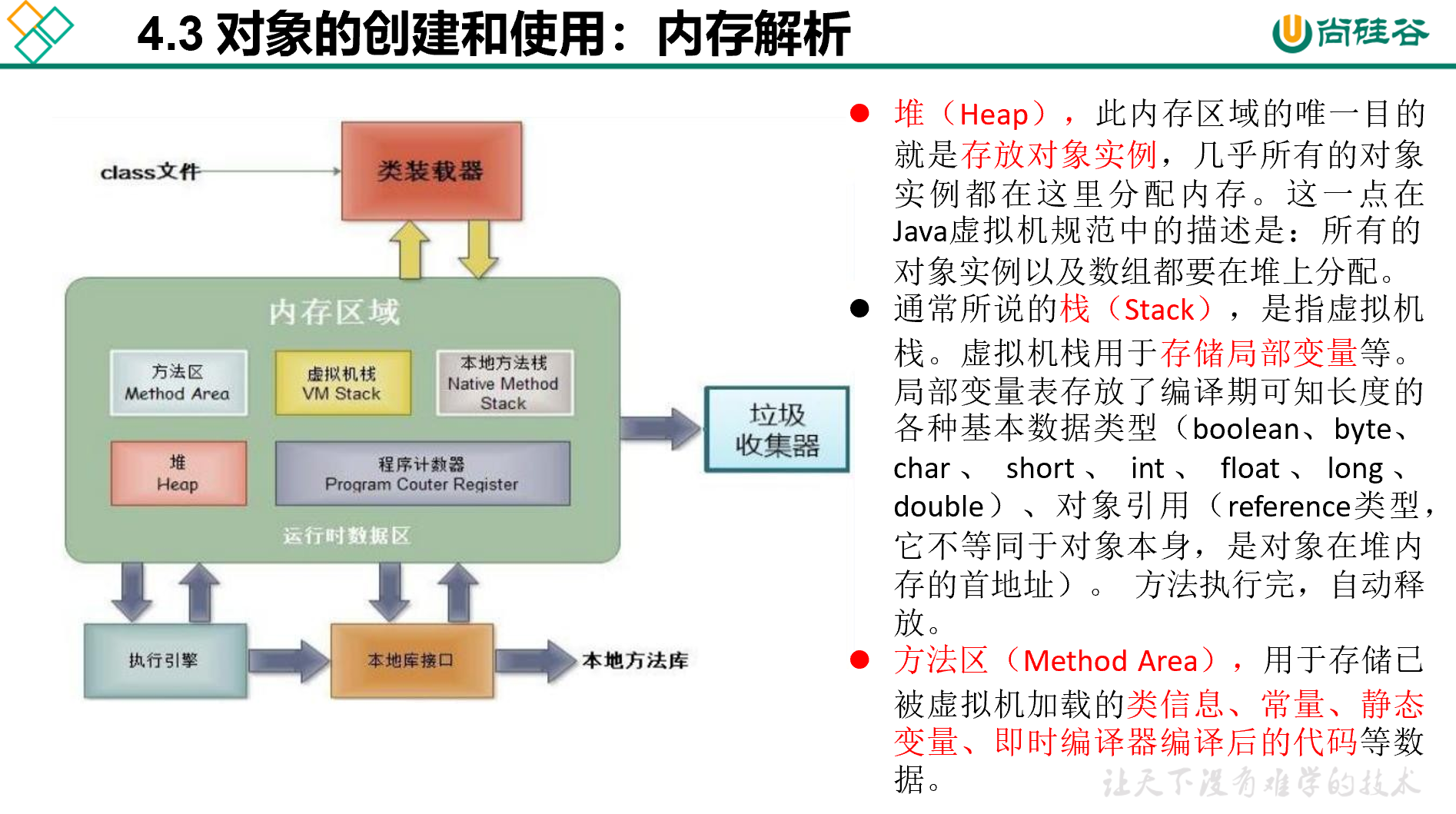

属性

方法

生成随机数:Math.random(),返回值类型double; (a,b) = Math.random() * (b - a + 1) + a;
四舍五入取整:Math.round(double d),返回值类型long。
练习1:对象数组
方式一:
package com.atguigu.exer;
/*
* . 对象数组题目:
定义类Student,包含三个属性:学号number(int),年级state(int),成绩 score(int)。
创建20个学生对象,学号为1到20,年级和成绩都由随机数确定。
问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。
问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息
提示:
生成随机数:Math.random(),返回值类型double;
四舍五入取整:Math.round(double d),返回值类型long。
*
*/
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建20个学生对象,可以使用数组方式存储
//要想存储对象的地址值,数组创建时类型需要使用类名
Student[] stud = new Student[20];
//2.循环创建对象
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
//上面创建了类类型的数组,直接将new出的类存储到数组元素中即可
stud[i] = new Student();
stud[i].number = i + 1;
stud[i].state = (int)(Math.random() * (6 - 1 + 1) + 1);
stud[i].score = (int)(Math.random() * (100 - 0 + 1));
}
//3.输出测试
for(int i = 0; i < stud.length; i++){
System.out.println(stud[i].info());
}
System.out.println("===============搜索指定年级===============");
//4.打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。
for(int i = 0; i < stud.length; i++){
if(stud[i].state == 3){
System.out.println(stud[i].info());
}
}
System.out.println("==============排序================");
//5.使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息
for(int i = 0; i < stud.length - 1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < stud.length - 1 - i; j++){
if(stud[j].score < stud[j+1].score){
//调换的是存储在数组中的地址值
Student temp = stud[j];
stud[j] = stud[j+1];
stud[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
//6.打印测试
for(int i = 0; i < stud.length; i++){
System.out.println(stud[i].info());
}
}
}
class Student{
int number;//学号
int state;//年级
int score;//成绩
public String info(){
return "学号:" + number + "年级:" + state + "成绩:" + score;
}
}
方式二:
package com.atguigu.exer;
/*
* . 对象数组题目:
定义类Student,包含三个属性:学号number(int),年级state(int),成绩 score(int)。
创建20个学生对象,学号为1到20,年级和成绩都由随机数确定。
问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。
问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息
提示:
生成随机数:Math.random(),返回值类型double;
四舍五入取整:Math.round(double d),返回值类型long。
*
*/
public class StudentTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建20个学生对象,可以使用数组方式存储
//要想存储对象的地址值,数组创建时类型需要使用类名
Pupil[] stud = new Pupil[20];
//2.循环创建对象
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
//上面创建了类类型的数组,直接将new出的类存储到数组元素中即可
stud[i] = new Pupil();
stud[i].number = i + 1;
stud[i].state = (int)(Math.random() * (6 - 1 + 1) + 1);
stud[i].score = (int)(Math.random() * (100 - 0 + 1));
}
StudentTest1 student = new StudentTest1();
//3.输出测试
student.print(stud);
System.out.println("===============搜索指定年级===============");
//4.打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。
student.search(stud, 3);
System.out.println("==============排序================");
//5.使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息
student.order(stud);
//6.打印测试
student.print(stud);
}
/**
*
* @Description 输出全部信息
* @author xiaojie
* @date 2021年1月20日上午10:16:48
* @param stud 传入Pupil类型数组
*/
public void print(Pupil[] stud){
for(int i = 0; i < stud.length; i++){
System.out.println(stud[i].info());
}
}
/**
*
* @Description 搜索指定班级
* @author xiaojie
* @date 2021年1月20日上午10:18:43
* @param stud 传入数组
* @param dest 要搜索的年级
*/
public void search(Pupil[] stud, int dest){
for(int i = 0; i < stud.length; i++){
if(stud[i].state == dest){
System.out.println("学号:" + stud[i].number + " " +
"年级:" + stud[i].state + " " + "成绩:" + stud[i].score );
}
}
}
/**
*
* @Description 使用冒泡排序方法将数组进行从大到小的排序
* @author xiaojie
* @date 2021年1月20日上午10:22:40
* @param stud 传入Pupil类型数组
*/
public void order(Pupil[] stud){
for(int i = 0; i < stud.length - 1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < stud.length - 1 - i; j++){
if(stud[j].score < stud[j+1].score){
//调换的是存储在数组中的地址值
Pupil temp = stud[j];
stud[j] = stud[j+1];
stud[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
class Pupil{
int number;//学号
int state;//年纪
int score;//成绩
public String info(){
String result = "学号:" + number + " " + "年级:" + state + " " + "成绩:" + score;
return result;
}
}
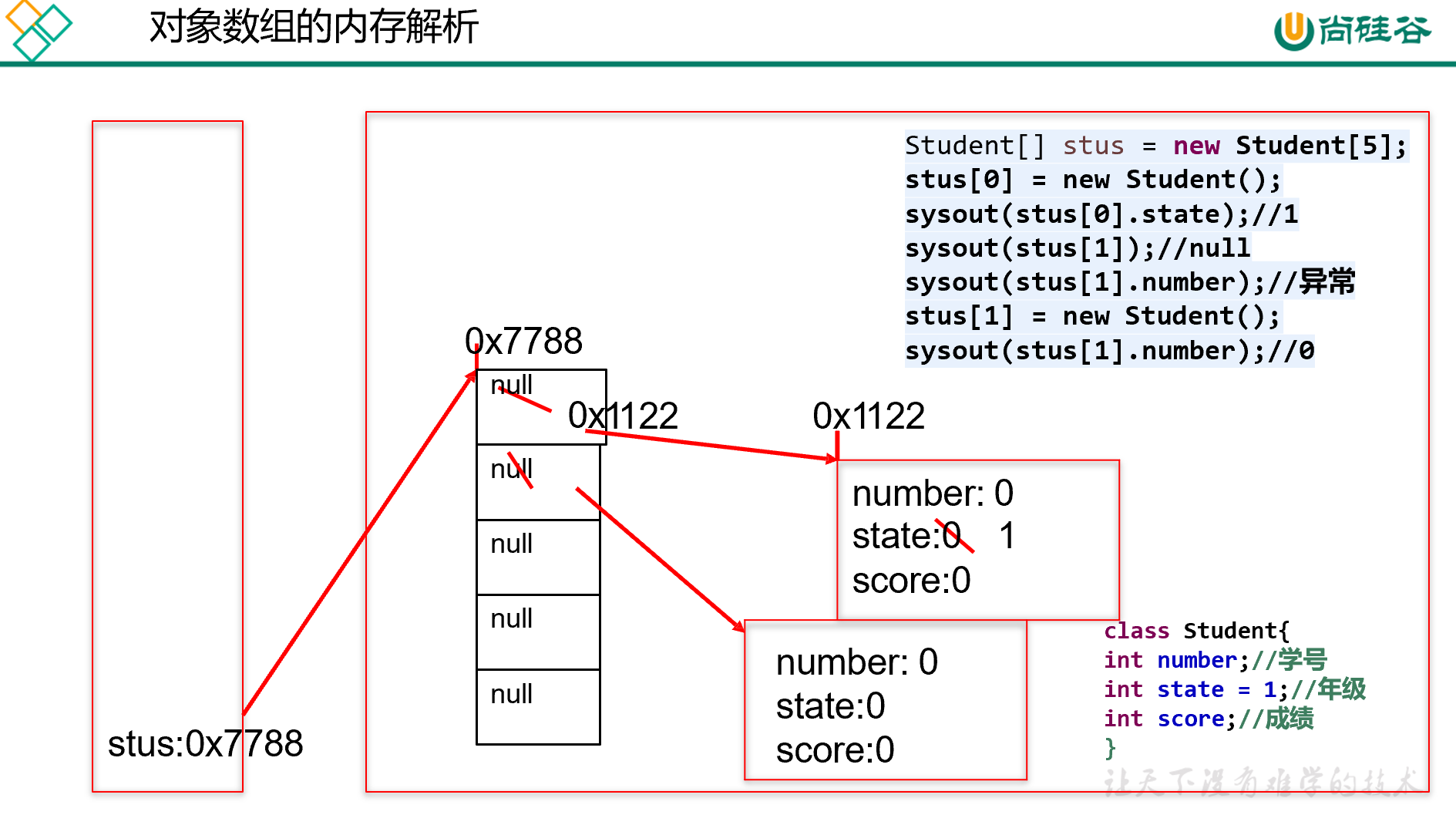
练习2:类与对象
package com.atguigu.java;
/*
定义银行账户类Account,有属性:卡号cid,余额balance,所属用户Customer
银行账户类Account有方法:
(1)getInfo(),返回String类型,返回卡的详细信息
(2)取钱方法withdraw(),参数自行设计,如果取钱成功返回true,失败返回false
(3)存钱方法save(),参数自行设计,如果存钱成功返回true,失败返回false
其中Customer类有姓名、身份证号、联系电话、家庭地址等属性
Customer类有方法say(),返回String类型,返回他的个人信息。
在测试类Bank中创建银行账户类对象和用户类对象,并设置信息,与显示信息
*/
public class Bank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account();
Customer customer = new Customer();
account.cid = 888888;
System.out.println(account.getInfo(customer));
System.out.println(account.withdraw(1000));
System.out.println(account.getInfo(customer));
System.out.println(account.save(500));
System.out.println(account.getInfo(customer));
}
}
class Account{
int cid;
double balance = 1000;
//所属用户Customer
/**
*
* @Description 显示客户银行卡信息
* @author xiaojie
* @date 2021年1月24日下午8:12:15
* @return 返回账户信息
*/
public String getInfo(Customer customer){
customer.name = "jerry";
customer.identityCard = "130111222233334444";
customer.contactPhone = "13511112222";
customer.homeAddress = "大屯路东";
String info = "cid: " + cid + "
" + "balance: " + balance + "
"
+ customer.say();
return info;
}
/**
*
* @Description 客户取钱功能
* @author xiaojie
* @date 2021年1月24日下午8:13:30
* @param money 取走金额
* @return
*/
public boolean withdraw(double money){
if(money > 0.0 && balance >= money){
balance -= money;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
/**
*
* @Description 客户存钱功能
* @author xiaojie
* @date 2021年1月24日下午8:18:12
* @param money 存入金额
* @return
*/
public boolean save(double money){
if(money > 0.0){
balance += money;
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
class Customer{
String name;
String identityCard;
String contactPhone;
String homeAddress;
public String say(){
String info = "name: " + name + "
" + "identityCard: " + identityCard + "
"
+ "contactPhone: " + contactPhone + "
" + "homeAddress: " + homeAddress;
return info;
}
}
练习3:计算圆柱体
package com.atguigu.java;
/*
* (1)声明一个圆柱体类型,
(2)声明属性:底边的半径,和高
(3)声明方法:
A:方法的功能:在方法中打印圆柱体的详细信息
圆柱体的底边的半径是xxx,高是xxx,底面积是xxx,体积是xxx。
B:方法的功能:返回底面积
C:方法的功能:返回体积
D:方法的功能:为圆柱体的底边的半径,和高赋值
E:方法的功能:为圆柱体的底边的半径,和高赋值,并返回赋值的结果
如果底边的半径或高为<=0,赋值失败,返回false,否则返回true
*/
class Cylinder{
//声明属性:底边的半径,和高
double redius;
double height;
//在方法中打印圆柱体的详细信息
//A 圆柱体的底边的半径是xxx,高是xxx,底面积是xxx,体积是xxx。
public void getInfo(){
System.out.println("圆柱体的底边的半径是: " + redius + ", " + "高是: " + height
+ ", " + "底面积是: " + bottom() + ", " + "体积是: " + area());
}
//B 返回底面积
public double bottom(){
return Math.PI * redius * redius;
}
//C 返回体积
public double area(){
return bottom() * height;
}
//D 为圆柱体的底边的半径,和高赋值
public void assign(double r, double h){
redius = r;
height = h;
}
//E 为圆柱体的底边的半径,和高赋值,并返回赋值的结果
//如果底边的半径或高为<=0,赋值失败,返回false,否则返回true
public boolean assignIf(double r,double h){
if(r <= 0 || h <=0){
return false;
}else{
assign(r,h);
//System.out.println("redius: " + redius + " " + "height: " + height);
return true;
}
}
}
public class CylinderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cylinder cylinder = new Cylinder();
boolean flag = cylinder.assignIf(5, 0);
if(!flag){
System.out.println("赋值失败");
}else{
cylinder.getInfo();
}
}
}
练习4:写出运行结果
class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args){
show(0);
show(1);
}
public static void show(int i){
switch(i){
default:
i+=2;
case 1:
i+=1;
case 4:
i+=8;
case 2:
i+=4;
}
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
}
class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args){
int x = 1;
for(show('a'); show('b') && x<3; show('c')){
show('d');
x++;
}
}
public static boolean show(char ch){
System.out.print(ch);
return true;
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static boolean foo(char c) {
System.out.print(c);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
for (foo('A'); foo('B') && (i < 2); foo('C')) {
i++;// 1 2
foo('D');
}
}
}