装饰者模式能够动态地将责任附加到对象上,在扩展对象功能方面比继承更加灵活,具体来说,装饰者模式将行为委托给相应的包装对象,并添加上自己的对应逻辑来实现特定的功能。装饰者模式的UML图如下:
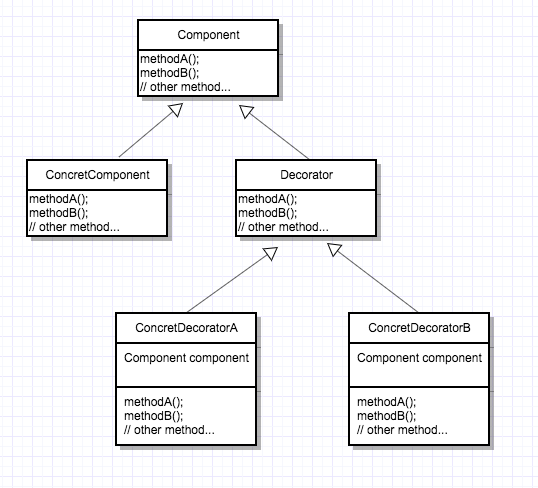
首先需要有被装饰的组件接口和具体组件,然后有装饰者对象,由于装饰者对象需要能够代替组件,所以要继承组件接口,并组合组件对象来完成委托任务。
下面以一个简单的快餐店为例子来介绍装饰者模式的用法。快餐店会有炒面、炒饭这些快餐,可以额外附加鸡蛋、火腿、培根这些配菜,当然加配菜需要额外加钱,每个配菜的价钱通常不太一样,那么计算总价就会显得比较麻烦。举个极端的例子,某个顾客一下子加了20中配菜,要计算总共需要多少钱估计还得拿个计算器出来算一会儿,这种情况下装饰者模式就有了用武之地。
按照上面的UML类图,先定义组件接口(快餐)和具体组件(炒饭、炒面)。
1 //快餐接口 2 public interface FastFood { 3 float getCost(); //获取价格 4 String getDescription(); //获取描述 5 } 6 7 //炒饭 8 public class FriedRice implements FastFood{ 9 private float price = 5; 10 String description = "炒饭"; 11 @Override 12 public float getCost() { 13 return this.price; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public String getDescription() { 18 return this.description; 19 } 20 } 21 22 //炒面 23 public class FriedNoodles implements FastFood{ 24 private float price = 5; 25 String description = "炒面"; 26 @Override 27 public float getCost() { 28 return this.price; 29 } 30 31 @Override 32 public String getDescription() { 33 return this.description; 34 } 35 }
接下来是配菜相关接口和类:
1 //配菜 2 public interface Garnish extends FastFood{ 3 String getDescription(); 4 } 5 6 //鸡蛋 7 public class Egg implements Garnish{ 8 float price = 1.5f; 9 String description = "鸡蛋"; 10 private FastFood fastFood; 11 12 public Egg(FastFood fastFood){ 13 this.fastFood = fastFood; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public float getCost() { 18 return this.price + fastFood.getCost(); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public String getDescription() { 23 return this.description + fastFood.getDescription(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 //培根 28 public class Bacon implements Garnish{ 29 private float price = 2f; 30 private String description = "培根"; 31 private FastFood fastFood; 32 33 public Bacon(FastFood fastFood){ 34 this.fastFood = fastFood; 35 } 36 37 @Override 38 public float getCost() { 39 return this.price + fastFood.getCost(); 40 } 41 42 @Override 43 public String getDescription() { 44 return this.description + fastFood.getDescription(); 45 } 46 } 47 48 //火腿 49 public class Ham implements Garnish{ 50 float price = 1f; 51 String description = "火腿"; 52 private FastFood fastFood; 53 54 public Ham(FastFood fastFood){ 55 this.fastFood = fastFood; 56 } 57 58 @Override 59 public float getCost() { 60 return this.price + fastFood.getCost(); 61 } 62 63 @Override 64 public String getDescription() { 65 return this.description + fastFood.getDescription(); 66 } 67 }
接下来就可以点几份快餐测试一下代码了:
1 public class DecoratorPatternTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 FastFood friedRice = new FriedRice(); 4 System.out.println(friedRice.getDescription() + " " + friedRice.getCost() + "元"); 5 FastFood friedNoodles = new FriedNoodles(); 6 friedNoodles = new Egg(friedNoodles); 7 friedNoodles = new Ham(friedNoodles); 8 System.out.println(friedNoodles.getDescription() + " " + friedNoodles.getCost() + "元"); 9 friedRice = new Bacon(friedRice); 10 System.out.println(friedRice.getDescription() + " " + friedRice.getCost() + "元"); 11 } 12 }
输出如下:
炒饭 5.0元 火腿鸡蛋炒面 7.5元 培根炒饭 7.0元
现在来回顾一下上面的类结构,我们在点培根炒饭时,先创建一个炒饭对象,然后用培根对象把炒饭包装了一下,当计算价格以及输出描述时,我们的做法是获取装饰者(培根)对象的价格和描述,同时需要获取组件(炒饭)的价格我描述,我们将这项任务委托给组件来完成,火腿鸡蛋炒面也是同样的道理。装饰者继承组件,使得装饰者可以包装任意的具体组件,同样也可以包装装饰者;同时,装饰者也可以加入自己的逻辑,给组件增添不一样的行为,例如这里在技术价格以及获取描述时,除了返回装饰者自己的属性,还增加了返回组件属性的逻辑。
其实装饰者模式在Java API中使用的很多,举个很简单的例子,当我们需要读取文件时,很可能会写出下面的代码:
1 BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("./test.txt")));
其中BufferedReader和FileReader就充当了装饰者的作用,而File则是被装饰的组件,还有一些其他的API也用到了装饰者模式,需要大家自己去摸索了。
参考文献:
<<Head First设计模式>>