1. 什么是会话跟踪技术
需要先了解什么是会话!可以把会话理解为客户端与服务器之间的一次会晤,在一次会晤中可能会包含多次请求和响应。例如你给10086打个电话,你就是客户端,而10086服务人员就是服务器了。从双方接通电话那一刻起,会话就开始了,到某一方挂断电话表示会话结束。在通话过程中,你会向10086发出多个请求,那么这多个请求都在一个会话中。
在JavaWeb中,客户向某一服务器发出第一个请求开始,会话就开始了,直到客户关闭了浏览器会话结束。
在一个会话的多个请求中共享数据,这就是会话跟踪技术。例如在一个会话中的请求如下: 请求银行主页;
- 请求登录(请求参数是用户名和密码);
- 请求转账(请求参数与转账相关的数据);
- 请求信誉卡还款(请求参数与还款相关的数据)。
在这上会话中当前用户信息必须在这个会话中共享的,因为登录的是张三,那么在转账和还款时一定是相对张三的转账和还款!这就说明我们必须在一个会话过程中有共享数据的能力。
2. 会话路径技术使用Cookie或session完成
我们知道HTTP协议是无状态协议,也就是说每个请求都是独立的!无法记录前一次请求的状态。但HTTP协议中可以使用Cookie来完成会话跟踪!在Web开发中,使用session来完成会话跟踪,session底层依赖Cookie技术。
3. Cookie概述
Cookie翻译成中文是小甜点,小饼干的意思。在HTTP中它表示服务器送给客户端浏览器的小甜点。其实Cookie是key-value结构,类似于一个python中的字典。随着服务器端的响应发送给客户端浏览器。然后客户端浏览器会把Cookie保存起来,当下一次再访问服务器时把Cookie再发送给服务器。 Cookie是由服务器创建,然后通过响应发送给客户端的一个键值对。客户端会保存Cookie,并会标注出Cookie的来源(哪个服务器的Cookie)。当客户端向服务器发出请求时会把所有这个服务器Cookie包含在请求中发送给服务器,这样服务器就可以识别客户端了!

3.1 Cookie规范
- Cookie大小上限为4KB;
- 一个服务器最多在客户端浏览器上保存20个Cookie;
- 一个浏览器最多保存300个Cookie;
上面的数据只是HTTP的Cookie规范,但在浏览器大战的今天,一些浏览器为了打败对手,为了展现自己的能力起见,可能对Cookie规范“扩展”了一些,例如每个Cookie的大小为8KB,最多可保存500个Cookie等!但也不会出现把你硬盘占满的可能!
注意,不同浏览器之间是不共享Cookie的。也就是说在你使用IE访问服务器时,服务器会把Cookie发给IE,然后由IE保存起来,当你在使用FireFox访问服务器时,不可能把IE保存的Cookie发送给服务器。
3.2 Cookie与HTTP头
Cookie是通过HTTP请求和响应头在客户端和服务器端传递的:
- Cookie:请求头,客户端发送给服务器端;
- 格式:Cookie: a=A; b=B; c=C。即多个Cookie用分号离开; Set-Cookie:响应头,服务器端发送给客户端;
- 一个Cookie对象一个Set-Cookie: Set-Cookie: a=A Set-Cookie: b=B Set-Cookie: c=C
3.3 Cookie的覆盖
如果服务器端发送重复的Cookie那么会覆盖原有的Cookie,例如客户端的第一个请求服务器端发送的Cookie是:Set-Cookie: a=A;第二请求服务器端发送的是:Set-Cookie: a=AA,那么客户端只留下一个Cookie,即:a=AA。
4. 案例配置cookie
4.1 代码目录结构
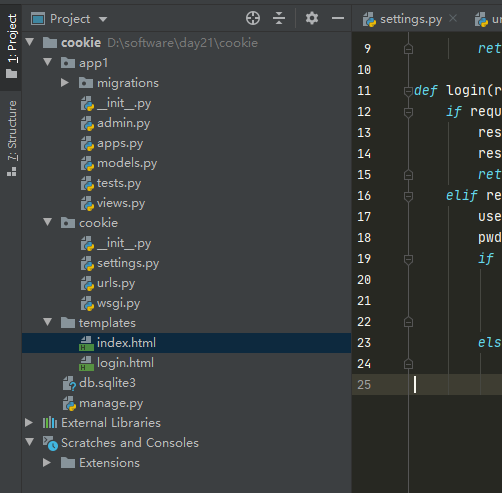
4.2 配置路由url
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from app1 import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('index/', views.index),
path('login/', views.login),
4.3 配置templates目录下的index.html、login.html
【login.html】
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello {{ user }}</h1>
<h2><a href="/login/">注销</a> </h2>
</body>
</html>
【index.html】
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>test</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/login/" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="user">
密码: <input type="text" name="pwd">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
4.4 配置views视图
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect,HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
is_login = request.COOKIES.get("is_login")
if is_login == "kyle":
return render(request, "index.html", {"user":"wangwen"})
else:
return redirect("/login/")
def login(request):
if request.method == "GET":
response = render(request, "login.html")
response.delete_cookie("is_login")
return response
elif request.method == "POST":
user = request.POST.get("user")
pwd = request.POST.get("pwd")
if user == "kyle" and pwd == "111":
response = HttpResponse("登陆成功")
response.set_cookie("is_login","kyle",10)
return response
else:
return HttpResponse("登录失败")
4.5 测试url
(1)网页首次登录页面,触发红色rediect("/login"),输入账户密码kyle/111
def index(request):
is_login = request.COOKIES.get("is_login")
if is_login == "kyle":
return render(request, "index.html", {"user":"wangwen"})
else:
return redirect("/login/")
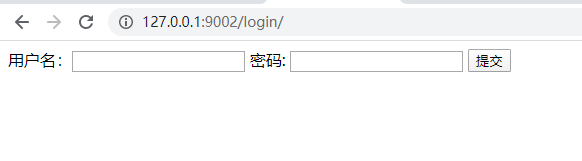
(2)跳转页面
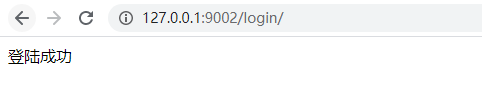
(3) 查看cookie

(4)再次登录首页,触发判断is_login =="kyle",显示页面如下,触发红色代码
def index(request):
is_login = request.COOKIES.get("is_login")
if is_login == "kyle":
return render(request, "index.html", {"user":"wangwen"})
else:
return redirect("/login/")
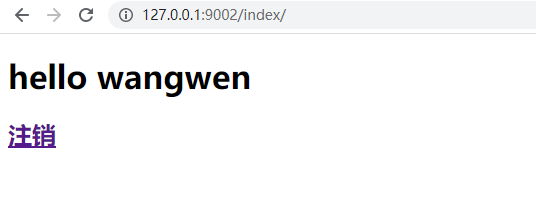
(5) 点击注销,触发红色代码,清理cookie,返回登录首页
def login(request):
if request.method == "GET":
response = render(request, "login.html")
response.delete_cookie("is_login")
return response
elif request.method == "POST":
user = request.POST.get("user")
pwd = request.POST.get("pwd")
if user == "kyle" and pwd == "111":
response = HttpResponse("登陆成功")
response.set_cookie("is_login","kyle",10)
return response
以上完成了set_cookie与delete_cookie模拟登录退出操作。