JavaScript类的相关知识
1.例子
/* 例1 */
// 定义一个构造函数
function Range(from, to){
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
// 所有Range类的实例化对象都会继承构造函数Range的prototype属性
Range.prototype = {
toString: function(){
return this.from + '....' + this.to;
},
includes: function(x){
return x >= this.from && x <= this.to;
}
};
// 实例化一个对象
var r = new Range(1, 3);
// 因为r继承了Range.prototype, 所以可以直接调用里面的方法
r.toString()
2.constructor属性
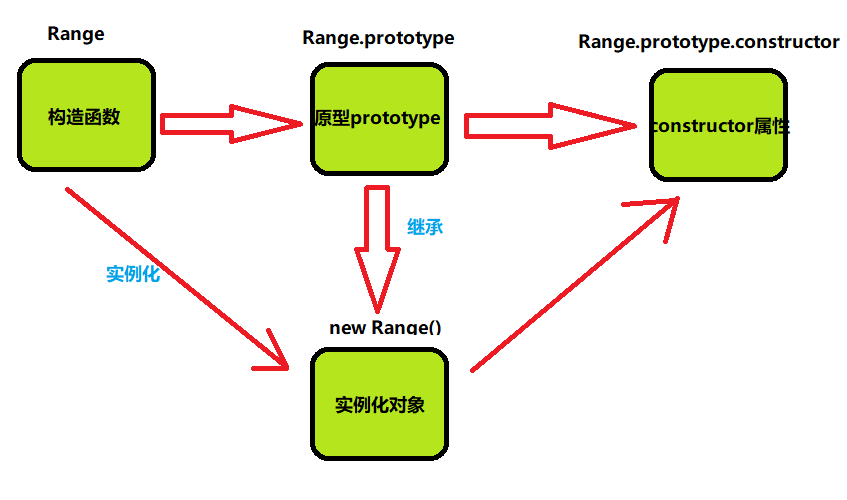
/* 例2 */
// 由上图可知
var F = function(){}; // F表示一个函数对象
var P = F.prototype; // P表示函数的原型对象
var C = P.constructor; // C表示原型对象下面的constructor属性
// 则有
C === F;
var O = new F(); // 创建类F的实例化对象
o.constructor === F;
/*
也就是说 F.prototype.constructor 就等于构造函数本身
而 F 实例化出来的对象 O 继承了 F.prototype 所以就
有 o.constructor === F
*/
// 在例1中,因为重写了Range预定义的原型对象,所以Range.prototype中便不存在constructor属性了,解决这一问题的方法有两种
// 法一:显示的给原型添加一个构造函数
Range.prototype = {
constructor: Range, // 显示的设置构造函数的反向引用
toString: function(){
return this.from + '....' + this.to;
},
includes: function(x){
return x >= this.from && x <= this.to;
}
};
// 法二:使用预定义的原型对象,因为预定义的原型对象中已经包含了constructor属性了
Range.prototype.toString = function(){
return this.from + '....' + this.to;
};
Range.prototype.includes = function(x){
return x >= this.from && x <= this.to;
};
由例1和例2可以总结出javascript中定义类的步骤:
第一步:先定义一个构造函数,并设置初始化新对象的实例属性
第二步:给构造函数的prototype对象定义实例方法
第三步:给构造函数定义类字段和类属性
3.继承

/* 例3 */ function Parent(name, age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; }; Parent.prototype.say = function(){ console.log(this.name, this.age); }; // 继承Parent类 function Child(name, age, sex){ Parent.call(this, name, age); this.sex = sex; }; // Child继承了来自父类Parent的方法,可以继续在自己的原型上扩展方法 Child.prototye.ask = function(){ console.log(this.name + '-----' + this.age + '-----' + this.sex); }; // child类为继承了Parent类属性及方法的类 var c = new Child('javascript', 18, 'male'); c.say(); c.ask();
4.新语法定义类以及及继承类
/* 例4 */
// 定义一个Parent类
class Parent{
constructor(name, age){ // 相当于Parent.prototype.constructor
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
say (){ // 相当于Parent.prototype.say = function(){}
console.log(this.name, this.age);
}
};
// 定义一个Child类继承Parent类
class Child extends Parent{
constructor(name, age, sex){
super(name, age);
this.sex = sex;
}
ask (){
super.say(); // 通过super关键字调用父类中的方法
}
};
