kotlin中range使用
fun main() {
for (i in 1.rangeTo(10).step(3)) { //类似于 1..10 step 3 写法
print(i.toString() + " ")
}
println()
for (i in 1.rangeTo(10)) { //类似于 1..10 写法 默认step为1
print(i.toString() + " ")
}
println()
for (i in 7.downTo(1).step(3)) { //类似于7 downTo 1 step 3 写法
print(i.toString() + " ")
}
println()
println(4 in 1..10 step 3) // true
println(5 in 1..10 step 3) // false
println((1..10).isEmpty()) // false
println((11..10 step 3).isEmpty()) // true
}
输出为
1 4 7 10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
7 4 1
true
false
false
true
java实现range功能
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
public class MyIntProgression implements Iterable<Integer> {
protected int first;
protected int last;
private int step;
protected MyIntProgression(int start, int endInclusive, int step) {
if (step == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Step must be non-zero.");
}
if (step == Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Step must be greater than Integer.MIN_VALUE to avoid overflow on negation.");
}
this.first = start;
this.last = getProgressionLastElement(start, endInclusive, step);
this.step = step;
}
public static MyIntProgression rangeTo(int start, int endInclusive) {
return new MyIntProgression(start, endInclusive, 1);
}
public static MyIntProgression downTo(int start, int endInclusive) {
return new MyIntProgression(start, endInclusive, -1);
}
public MyIntProgression step(int step) {
if (step <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("Step must be positive, was: %s.", step));
}
return new MyIntProgression(this.first, this.last, this.step > 0 ? step : -step);
}
public boolean contains(int value) {
for (Integer item : this) {
if (item == value) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public int getItem(int index) {
if (index < 0) {
throw indexOutOfBoundsException();
}
int item = first + index * step;
if (step > 0) {
if (item > last) {
throw indexOutOfBoundsException();
}
} else {
if (item < last) {
throw indexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
return item;
}
@Override
public Iterator<Integer> iterator() {
return new IntProgressionIterator(first, last, step);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return step > 0 ? (first > last) : (first < last);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if (step > 0) {
return String.format("%s..%s step %s", first, last, step);
} else {
return String.format("%s downTo %s step %s", first, last, -step);
}
}
private IndexOutOfBoundsException indexOutOfBoundsException() {
return new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index out of range.");
}
private static int getProgressionLastElement(int start, int endInclusive, int step) {
if (step == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Step is zero.");
}
if (step > 0) {
if (start >= endInclusive) {
return endInclusive;
} else {
return endInclusive - differenceModulo(endInclusive, start, step);
}
} else {
if (start <= endInclusive) {
return endInclusive;
} else {
return endInclusive + differenceModulo(start, endInclusive, -step);
}
}
}
//算数意义上的取模,a%b为取余,和取模有区别
private static int mod(int a, int b) {
int mod = a % b;
if (mod >= 0) {
return mod;
} else {
return mod + b;
}
}
//(a - b) mod c
private static int differenceModulo(int a, int b, int c) {
return mod(mod(a, c) - mod(b, c), c);
}
private static class IntProgressionIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {
private int last;
private int step;
private int next;
IntProgressionIterator(int first, int last, int step) {
this.last = last;
this.step = step;
this.next = first;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return step > 0 ? (next <= last) : (next >= last);
}
@Override
public Integer next() {
int value = next;
if (!hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
next += step;
return value;
}
}
}
带步长的范围
public class MyIntRange extends MyIntProgression {
protected MyIntRange(int start, int endInclusive) {
super(start, endInclusive, 1);
}
public static MyIntRange rangeTo(int start, int endInclusive) {
return new MyIntRange(start, endInclusive);
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int value) {
return value >= first && value <= last;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first > last;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("%s..%s", first, last);
}
}
默认步长为1的范围,上述两个类都是完全模仿kotlin源码实现的
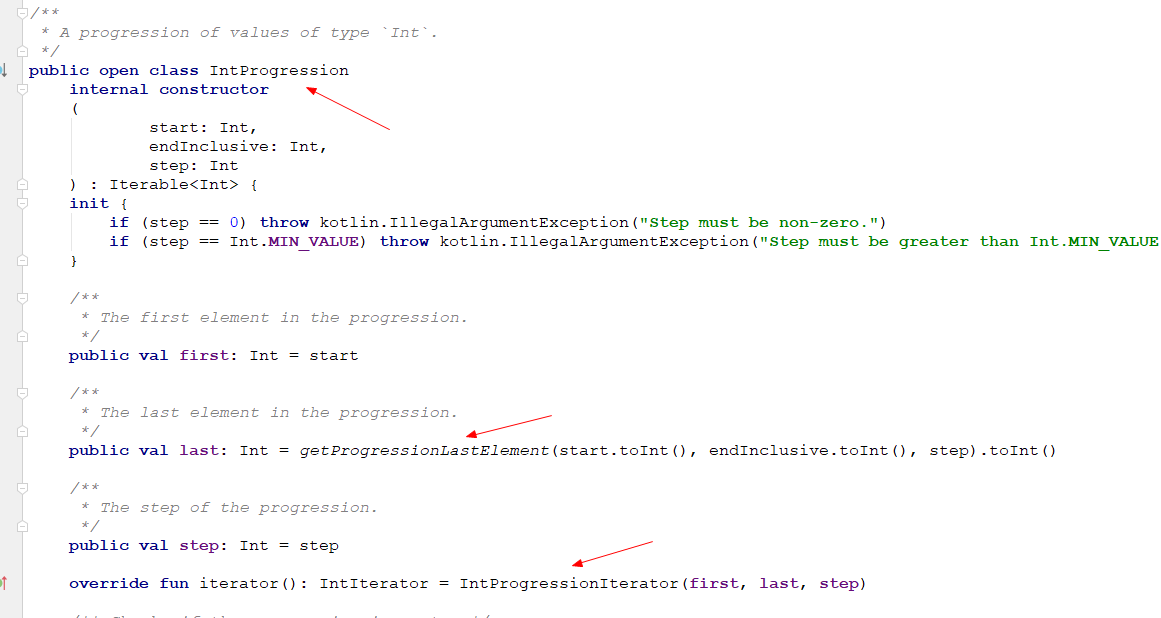
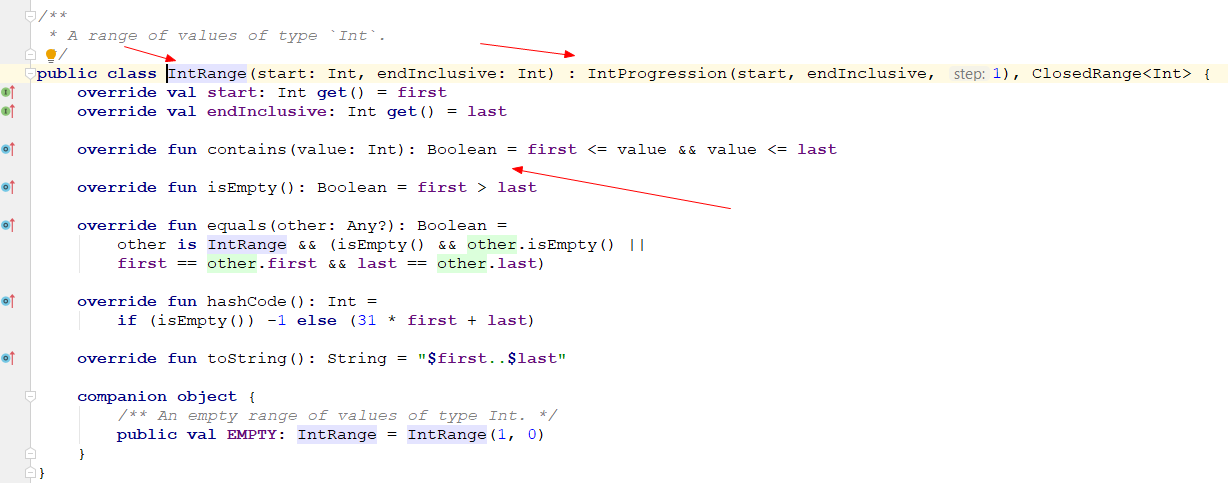
使用及测试
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testIntRange();
testIntProgression();
}
private static void testIntRange() {
testIterator(MyIntRange.rangeTo(1, 4));//1,2,3,4
testIterator(MyIntRange.rangeTo(11, 10));//empty
testIterator(MyIntRange.downTo(3, 1));//3,2,1
testIterator(MyIntRange.downTo(1, 10));//empty
testIsEmpty(MyIntRange.rangeTo(1, 3));//false
testIsEmpty(MyIntRange.downTo(1, 10));//true
testContains(MyIntRange.rangeTo(1, 10), 5);//true
testContains(MyIntRange.rangeTo(1, 10), 11);//false
testGetItem(MyIntRange.rangeTo(1, 10), 1);//2
testGetItem(MyIntRange.rangeTo(1, 10), 11);//throw exception
testGetItem(MyIntRange.downTo(10, 1), 1);//9
testGetItem(MyIntRange.downTo(10, 1), 11);//throw exception
}
private static void testIntProgression() {
testIterator(MyIntProgression.rangeTo(1, 10).step(4));//1,5,9
testIterator(MyIntProgression.rangeTo(11, 10).step(4));//empty
testIterator(MyIntProgression.downTo(10, 1).step(4));//10 6 2
testIterator(MyIntProgression.downTo(1, 10).step(4));//empty
testIsEmpty(MyIntProgression.rangeTo(1, 10).step(4));//false
testIsEmpty(MyIntProgression.downTo(1, 10).step(4));//true
testContains(MyIntProgression.rangeTo(1, 10).step(4), 5);//true
testContains(MyIntProgression.rangeTo(1, 10).step(4), 4);//false
testGetItem(MyIntProgression.rangeTo(1, 10).step(4), 1);//5
testGetItem(MyIntProgression.rangeTo(1, 10).step(4), 4);//throw exception
testGetItem(MyIntProgression.downTo(10, 1).step(4), 1);//6
testGetItem(MyIntProgression.downTo(10, 1).step(4), 3);//throw exception
}
private static void testIterator(MyIntProgression myIntProgression) {
System.out.println("=======" + myIntProgression);
for (Integer item : myIntProgression) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
private static void testIsEmpty(MyIntProgression myIntProgression) {
System.out.println("=======" + myIntProgression);
System.out.println(myIntProgression.isEmpty());
}
private static void testContains(MyIntProgression myIntProgression, int value) {
System.out.println("=======" + myIntProgression);
System.out.println(myIntProgression.contains(value));
}
private static void testGetItem(MyIntProgression myIntProgression, int index) {
System.out.println("=======" + myIntProgression);
try {
System.out.println(myIntProgression.getItem(index));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
参考
kotlin源码