简化模型:
- 假设1:影响房价的关键因素是卧室个数,卫生间个数和居住面积,记为
x1,x2,x3 - 假设2:成交价是关键因素的加权和。
y = w1x1+w2x2+w3x3
权重和偏差的实际值在后面决定
线性模型
- 给定n维输入
x = [x1,x2,...,xn]^T - 线性模型有一个n维权重和一个标量偏差
w = [w1,w2,...,wn]^T,b - 输出是输入的加权和
y = w1x1+w2x2+...+wnxn+b - 向量版本
y = <w,x>+b
平方损失

训练数据
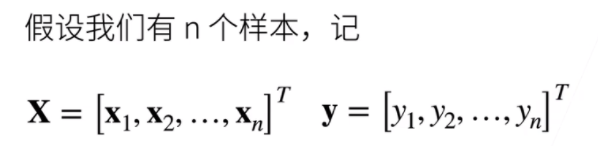
参数学习
- 训练损失
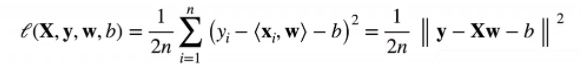
- 最小化损失学习参数
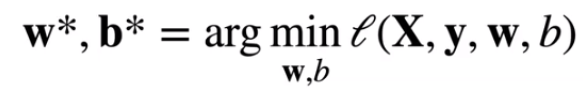
总结
- 线性回归是对n维输入的加权,外加偏差
- 使用平方损失来衡量预测值和真实值的差异
- 线性回归有显示解
- 线性回归可以看做是单层神经网络
基础优化算法
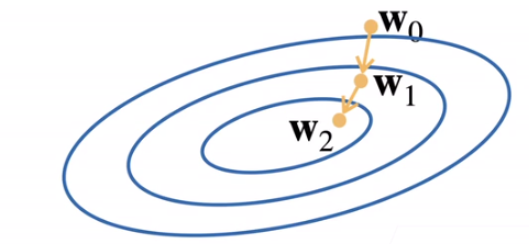
梯度下降
- 挑选一个初始值
w0 - 重复迭代参数t = 1,2,3
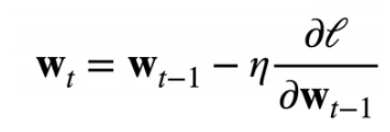
- 沿梯度方向将增加损失函数值
- 学习率:步长的超参数
小批量随机梯度下降
- 在整个训练集上算梯度太贵
一个深度神经网络模型可能需要数分钟至数小时 - 我们可以随机采样b个样本
i1,i2,...,ib来近似损失
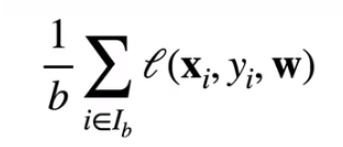
b是批量大小,另一个重要的超参数
线性回归从零开始实现
从零开始实现整个方法,包括数据流水线、模型、损失函数和小批量随机梯度下降优化器。
%matplotlib inline
import random #随机梯度权重
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
根据带有噪声的线性模型构造一个人造数据集。我们使用线性模型参数w = [2,-3.4]^T、b = 4.2和噪声项ε生成数据集及其标签:
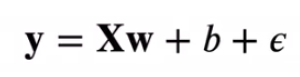
def synthetic_data(w,b,num_examples):
'''生成y = Xw + b + 噪声。'''
X = torch.normal(0,1,(num_examples,len(w)))#均值为零,方差为1的随机数
y = torch.matmul(X,w)+ b
y += torch.normal(0,0.01,y.shape)#均值为零,方差为0.01的随机噪音
return X,y.reshape((-1,1))#-1表示由pytorch自动推导,1表示固定,即列向量为1
true_w = torch.tensor([2,-3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features,labels = synthetic_data(true_w,true_b,1000)
features中的每一行都包含一个二维数据样本,labels中每一行都包含一维标签值(一个标量)
print('features:',features,'
label:',labels[0])
features: tensor([[ 0.7857, 0.0540],
[ 1.4230, 1.9870],
[-0.2214, 1.6215],
...,
[-1.2081, -0.4113],
[ 1.7863, 3.8525],
[ 0.8111, 0.7033]])
label: tensor([5.5789])
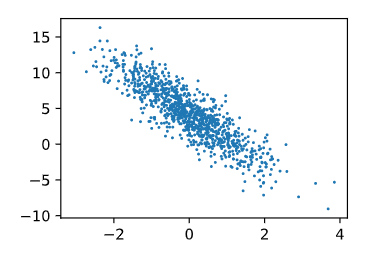
d2l.set_figsize()
# detach()表示分离出数值,不再含有梯度
d2l.plt.scatter(features[:,(1)].detach().numpy(),labels.detach().numpy(),1)
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x20c603fcc70>
定义一个data_iter函数,该函数接收批量大小、特征矩阵和标签向量作为输入,生成大小为batch_size的小批量
def data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
num_examples = len(features)
#设置索引
indices = list(range(num_examples))
#这些样本都是随机读取的,没有特定的顺序,需要打乱下标
random.shuffle(indices)
for i in range(0,num_examples,batch_size):
batch_indices = torch.tensor(indices[i:min(i+
batch_size,num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices],labels[batch_indices]
batch_size = 10
for X,y in data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
print(X,'
',y)
break
tensor([[-0.5396, 1.0611],
[-0.3577, -0.4951],
[-2.3002, 1.9732],
[-0.7790, -0.1243],
[ 1.4211, -2.1745],
[-0.3561, -0.2842],
[-0.8443, -0.0471],
[ 0.0722, -0.3774],
[-1.7615, 0.2300],
[-0.9065, -3.0624]])
tensor([[-0.4882],
[ 5.1640],
[-7.1245],
[ 3.0805],
[14.4374],
[ 4.4567],
[ 2.6782],
[ 5.6375],
[-0.1057],
[12.8029]])
定义初始化模型参数
w = torch.normal(0,0.01,size=(2,1),requires_grad = True)
b = torch.zeros(1,requires_grad = True)
定义模型
def linreg(X,w,b):
'''线性回归模型。'''
return torch.matmul(X,w) + b
定义损失函数
def squared_loss(y_hat,y):
'''均方损失。'''
return (y_hat-y.reshape(y_hat.shape))**2/2
定义优化算法
def sgd(params,lr,batch_size):
'''小批量随机梯度下降'''
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
param.grad.zero_()
训练过程
lr = 0.03 #学习率
num_epochs = 3 #扫描次数
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X,y in data_iter(batch_size,features,labels):
l = loss(net(X,w,b),y) # X和y的小批量损失
# 因为l形状是(batch_size,1),而不是一个标量,l中的所有元素被加到
#并以此计算关于[ w,b ]的梯度
l.sum().backward()
sgd([w,b],lr,batch_size)
with torch.no_grad():
train_l = loss(net(features,w,b),labels)
print(f'epoch{epoch+1},loss{float(train_l.mean()):f}')
epoch1,loss0.038016
epoch2,loss0.000143
epoch3,loss0.000050
比较真实参数和通过训练学到的参数来评估训练的成功程度
print(f'w的估计误差:{true_w - w.reshape(true_w.shape)}')
print(f'b的估计误差:{true_b - b}')
w的估计误差:tensor([ 0.0007, -0.0002], grad_fn=<SubBackward0>)
b的估计误差:tensor([0.0008], grad_fn=<RsubBackward1>)
线性回归的简洁实现
通过使用深度学习框架简介实现线性回归模型生成数据集
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch.utils import data
from d2l import torch as d2l
true_w = torch.tensor([2,-3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features,labels = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w,true_b,batch_size)
def load_array(data_arrays,batch_size,is_train = True):
'''构造一个PyTorch数据迭代器'''
dataset = data.TensorDataset(*data_arrays)#将两类数据一一对应
return data.DataLoader(dataset,batch_size,shuffle = is_train)#重新排序
batch_size = 10
data_iter = load_array((features,labels),batch_size)
next(iter(data_iter))
[tensor([[ 1.3788, -1.2938],
[-0.5648, 0.3607],
[-1.4867, -0.7318],
[-1.3304, 0.0436],
[-1.0882, -0.6597],
[ 2.4002, 1.1828],
[ 0.7691, -0.8790],
[-0.2221, -1.0182],
[-0.5332, -0.6340],
[-0.2190, -0.0083]]),
tensor([[11.3507],
[ 1.8421],
[ 3.7258],
[ 1.3721],
[ 4.2723],
[ 4.9844],
[ 8.7432],
[ 7.2262],
[ 5.2892],
[ 3.7768]])]
使用框架的预定好的层
# `nn`是神经网络的缩写
from torch import nn
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(2,1))
初始化模型参数
net[0].weight.data.normal_(0,0.01)
net[0].bias.data.fill_(0)
tensor([0.])
均方误差
loss = nn.MSELoss()
实例化sgd
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr = 0.03)#至少传入两个参数
训练过程
num_epochs = 3
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X,y in data_iter:
l = loss(net(X),y)
trainer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
trainer.step()
l = loss(net(features),labels)
print(f'epoch {epoch+1},loss {1:f}')
epoch 1,loss 1.000000
epoch 2,loss 1.000000
epoch 3,loss 1.000000