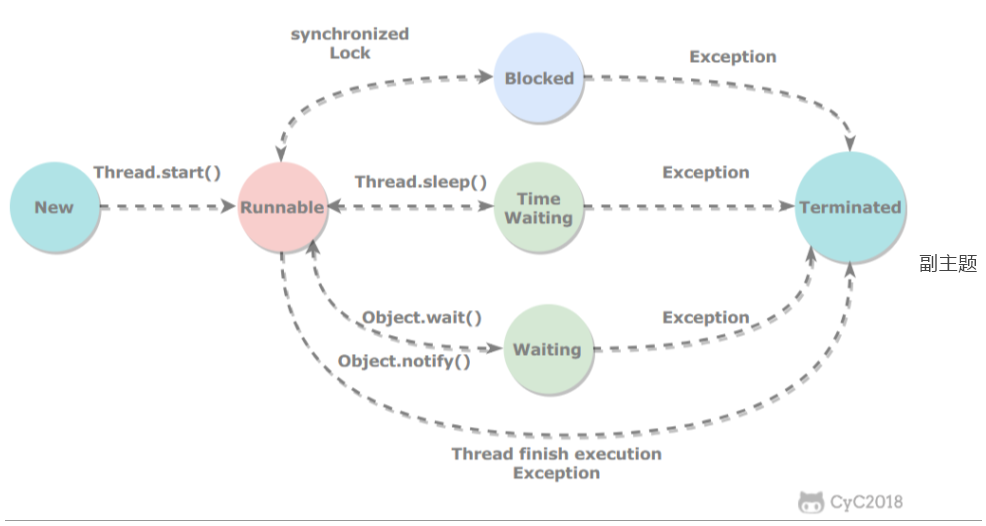
1,线程状态转换
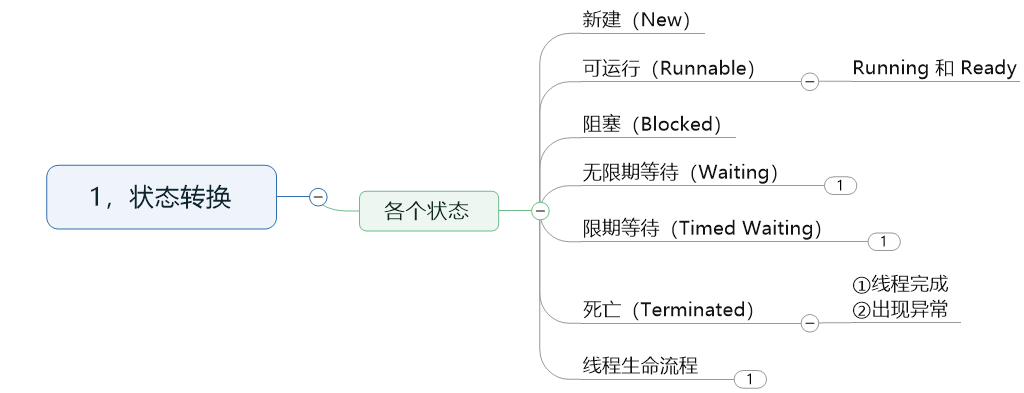
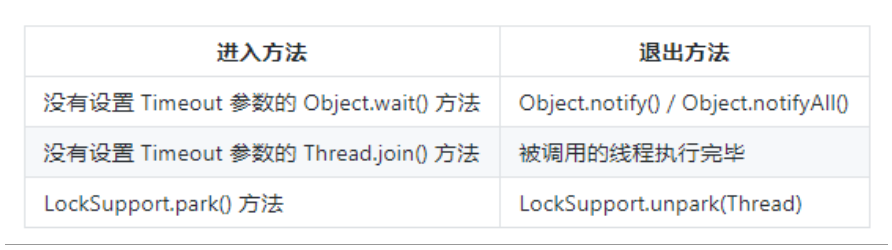
无限期等待:
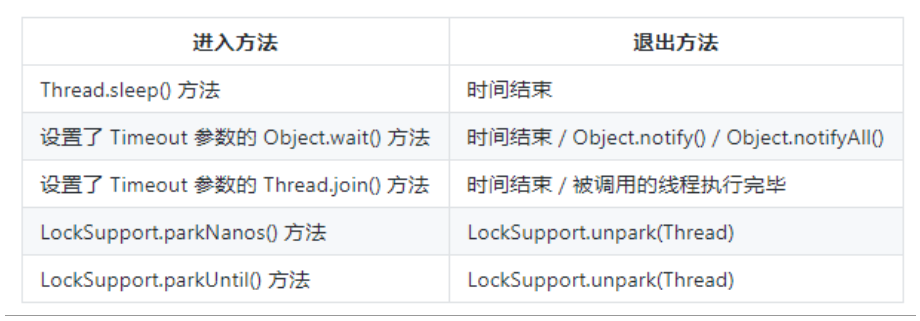
限期等待:
线程生命流程:
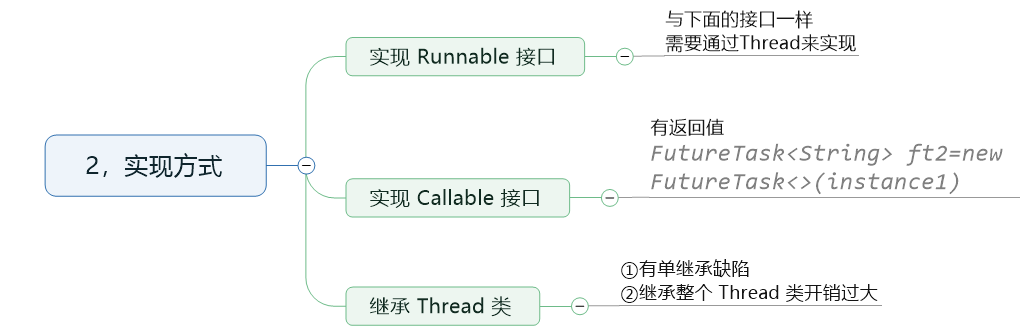
2,实现方式
代码实现样例【三种方式】:

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo2; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; public class test1_Runnable implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<50;i++){ System.out.println("当前线程:"+i); } } } class test2_Callable implements Callable<String> { private int num; public test2_Callable(){} public test2_Callable(int num){ this.num=num; } @Override public String call() throws Exception { for(int i=0;i<50;i++){ System.out.println(this.num+"线程:"+i); } return num+"线程已完成"; } } class test3_Thread extends Thread { private int num; public test3_Thread(){} public test3_Thread(int num){ this.num=num; } @Override public void run() { for(int i=0;i<50;i++){ System.out.println(this.num+"线程:"+i); } } }

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo2; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { //实现 Runnable 接口 // test1_Runnable instance=new test1_Runnable(); // Thread thread=new Thread(instance); // Thread thread1=new Thread(instance); // thread.start(); // thread1.start(); //实现 Callable 接口 // test2_Callable instance=new test2_Callable(1); // FutureTask<String> ft=new FutureTask<>(instance); // Thread thread = new Thread(ft); // test2_Callable instance1=new test2_Callable(2); // FutureTask<String> ft2=new FutureTask<>(instance1); // Thread thread1 = new Thread(ft2); // // thread.start(); // thread1.start(); // System.out.println(ft.get()); // System.out.println(ft2.get()); //继承 Thread 类 test3_Thread thread1=new test3_Thread(1); test3_Thread thread2=new test3_Thread(2); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }
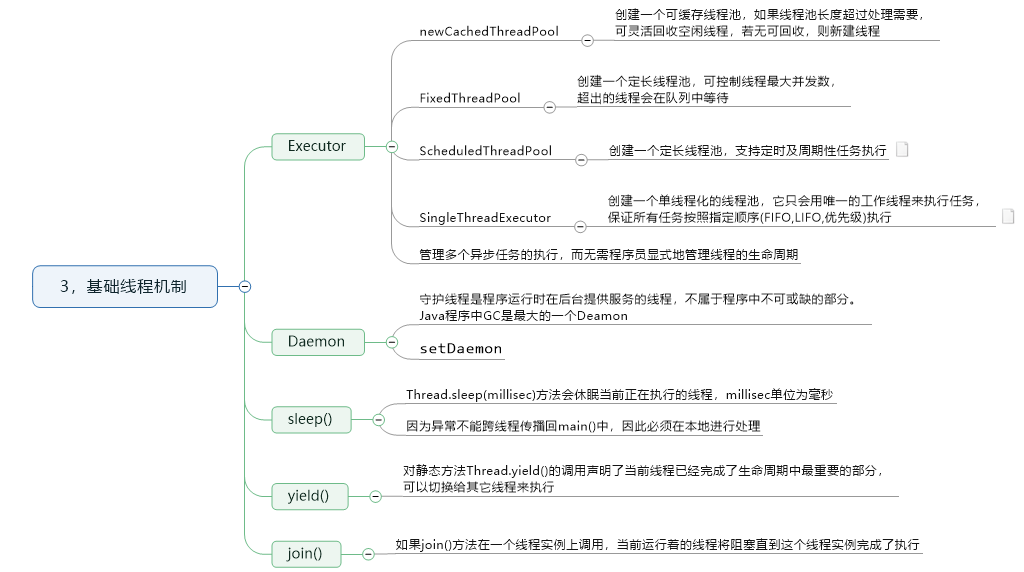
3,基础线程机制
代码实现样例:

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo3; public class Client1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //设置守护线程 setDaemon 伴随线程而运行 // Thread thread1 = new Thread(new test1_Runnable(1)); // Thread thread2 = new Thread(new test3_Thread(2)); // thread1.setDaemon(true); // thread1.start(); // thread2.start(); //sleep Thread.sleep(millisec) 方法会休眠当前正在执行的线程,millisec 单位为毫秒 // sleep() 可能会抛出 InterruptedException,因为异常不能跨线程传播回 main() 中,因此必须在本地进行处理 // Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{ // try { // System.out.println("延迟2s"); // Thread.sleep(2000); // System.out.println("延迟结束"); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // }); // thread1.start(); // new Thread(new Runnable() { // @Override // public void run() { // System.out.println("延迟2s"); // try { // Thread.sleep(2000); // System.out.println("延迟结束"); // Thread.yield();//可以让出资源 // Thread.sleep(2000); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // }finally { // System.out.println("线程1运行结束"); // } // } // }).start(); // // new Thread(()->{ // try { // Thread.sleep(2000); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // }finally { // System.out.println("线程2延迟结束"); // } // }).start(); Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable(){ public void run(){ System.out.println("First task started"); System.out.println("Sleeping for 2 seconds"); try{ Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("First task completed"); } }); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable(){ public void run(){ System.out.println("Second task completed"); } }); //在t执行完毕后t1执行 t.start(); // Line 15 t.join(); // Line 16 t1.start(); } }
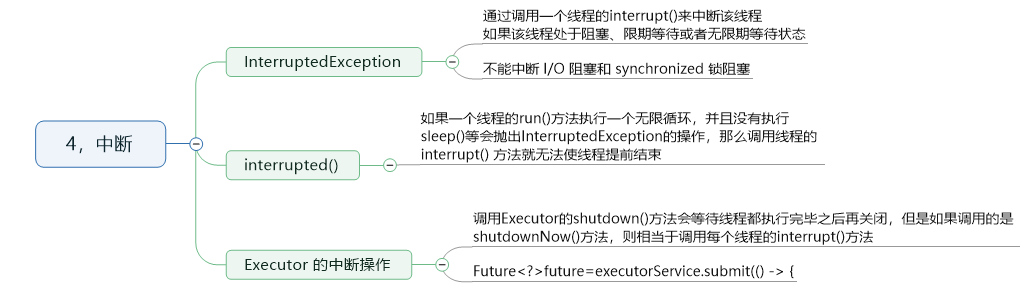
4,中断

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo4; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import static java.lang.Thread.interrupted; class InterruptExample extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("sleep 2s"); try { Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("Thread run"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("休眠中断"); e.printStackTrace(); } } } class InterruptExample1 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { while (!interrupted()) { // .. } System.out.println("Thread end"); } } public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { // InterruptExample thread1 = new InterruptExample(); // thread1.start(); // thread1.interrupt(); // System.out.println("Main run"); // InterruptExample1 thread2 = new InterruptExample1(); // thread2.start(); // thread2.interrupt(); // ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // executorService.execute(() -> { // try { // Thread.sleep(2000); // System.out.println("Thread run"); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // System.out.println("线程程序池全体中断"); // e.printStackTrace(); // } // }); // executorService.shutdownNow(); // System.out.println("Main run"); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); Future<?> future=executorService.submit(()->{ System.out.println("3"); while (!interrupted()){ System.out.println("2"); } System.out.println("1"); }); future.cancel(true);//强制中断 } }
5,互斥同步
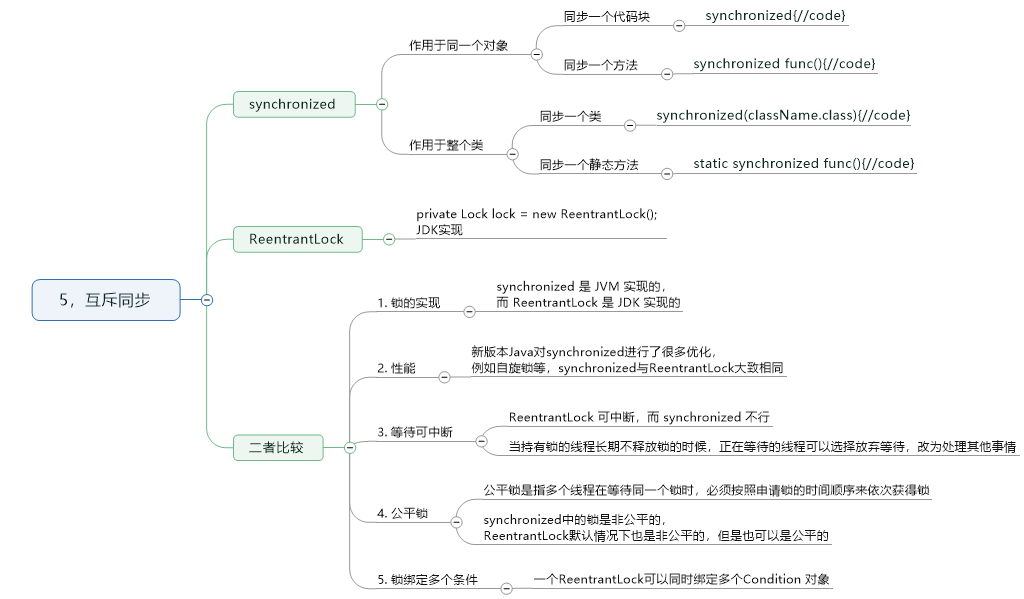
代码实现:

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo5; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; class SynchronizedExample {//同步代码块,作用于同一个对象 public void func1() { synchronized (this) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.print(i + " "); } } } } class SynchronizedExample1 {//同步方法,作用于同一个对象 public synchronized void func1() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.print(i + " "); } } } class SynchronizedExample2 {//同步类,作用于整个类。 public void func1() { synchronized(SynchronizedExample2.class){ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.print(i + " "); } } } } class SynchronizedExample3 {//同步静态方法,作用于整个类。 public static synchronized void func1() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.print(i + " "); } } } class LockExample {//ReentrantLock 是 java.util.concurrent(J.U.C)包中的锁。 private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); public void func() { lock.lock(); try { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.print(i + " "); } }finally { lock.unlock();//确保解锁,防止死锁 } } } public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { //synchronized-代码块 相同对象-同步代码块 // SynchronizedExample e1=new SynchronizedExample(); // ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // executorService.execute(()->e1.func1()); // executorService.execute(()->e1.func1()); //synchronized-代码块 不同对象-同步代码块,没有同步!!! // SynchronizedExample e1 = new SynchronizedExample(); // SynchronizedExample e2 = new SynchronizedExample(); // ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // executorService.execute(()->e1.func1()); // executorService.execute(()->e2.func1()); //synchronized-方法 不同对象,没有同步!!! // SynchronizedExample1 e1 = new SynchronizedExample1(); // SynchronizedExample1 e2 = new SynchronizedExample1(); // ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // executorService.execute(()->e1.func1()); // executorService.execute(()->e2.func1()); //synchronized-类 不同对象,有同步 // SynchronizedExample2 e1 = new SynchronizedExample2(); // SynchronizedExample2 e2 = new SynchronizedExample2(); // ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // executorService.execute(()->e1.func1()); // executorService.execute(()->e2.func1()); //synchronized-静态方法 不同对象,有同步 // SynchronizedExample3 e1 = new SynchronizedExample3(); // SynchronizedExample3 e2 = new SynchronizedExample3(); // ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // executorService.execute(()->e1.func1()); // executorService.execute(()->e2.func1()); //JDK实现的锁,作用一个对象 LockExample lockExample = new LockExample(); LockExample lockExample1 = new LockExample(); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); executorService.execute(() -> lockExample.func()); // executorService.execute(() -> lockExample1.func()); executorService.execute(() -> lockExample.func()); } }
6,线程协作
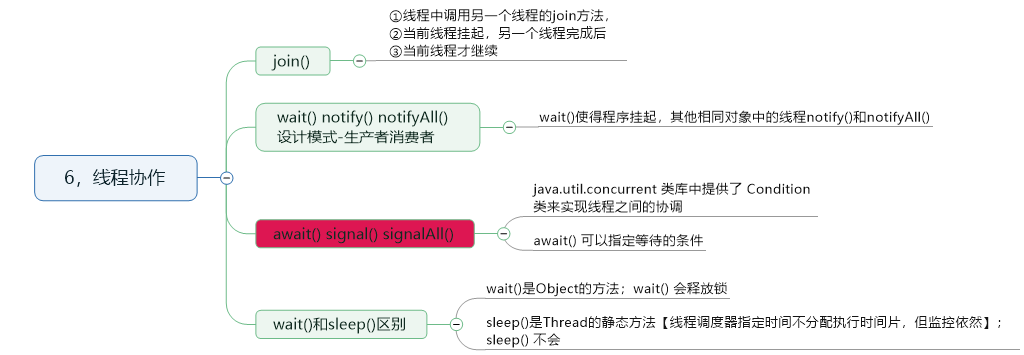
样例代码:

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo6; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; class JoinExample{ private class A extends Thread{ @Override public void run(){ for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ System.out.println("A:"+i); } } } private class B extends Thread { private A a; B(A a) { this.a = a; } @Override public void run() { try { a.join();//先完成A线程,继续B线程 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("B"); } } public void test() { A a = new A(); B b = new B(a); b.start(); a.start(); } } class WaitNotifyExample{ public synchronized void before(){ System.out.println("before"); notifyAll();//通知等待的线程 } public synchronized void after(){ try { wait();//先进行等待 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ System.out.print(i); } System.out.println("after"); } } class AwaitSingalExample{ private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); private Condition condition=lock.newCondition(); public void before(){ lock.lock(); try { System.out.println("before"); condition.signalAll(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void after(){ lock.lock(); try { condition.await(); System.out.println("after"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } } public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { // JoinExample example=new JoinExample(); // example.test(); // ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // WaitNotifyExample example = new WaitNotifyExample(); // WaitNotifyExample example1 = new WaitNotifyExample(); // executorService.execute(() -> example.after()); // executorService.execute(() -> example1.after()); // executorService.execute(() -> example.before()); // executorService.execute(() -> example1.before()); ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); AwaitSingalExample example=new AwaitSingalExample(); executorService.execute(()->example.after()); executorService.execute(()->example.before()); } }
7,J.U.C-AQS【java.util.concurrent】
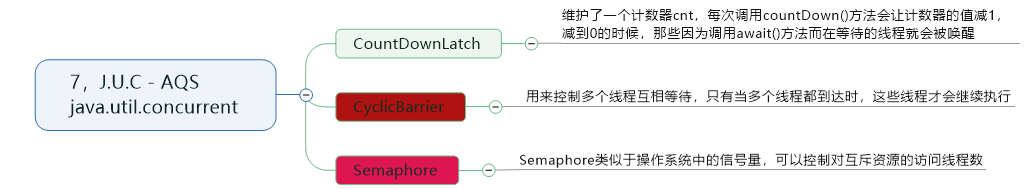
样例代码:

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo7; import java.util.concurrent.*; class CyclicBarrier { private int parties; private int count; private Runnable barrierCommand; public CyclicBarrier(int parties,Runnable barrierAction){ if (parties <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.parties = parties; this.count = parties; this.barrierCommand = barrierAction; } public CyclicBarrier(int parties) { this(parties, null); } } public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { final int clientCount=5; final int totalRequestCount=10; Semaphore semaphore=new Semaphore(clientCount); ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<totalRequestCount;i++){ executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); System.out.print(semaphore.availablePermits()+" "); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { semaphore.release(); } }); } executorService.shutdown(); //Semaphore // final int totalThread =10; // CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier=new CyclicBarrier(totalThread); // ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // for(int i=0;i<totalThread;i++){ // executorService.execute(()->{ // System.out.println("before..."); // try{ // cyclicBarrier.wait();//源程序是await,这里只能使用wait // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // System.out.print("after.."); // }); // executorService.shutdown(); // } //CountDownLatch实例 // final int totalThread=10; // CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(3); // ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // for(int i=0;i<6;i++){ // int finalI = i; // Thread.sleep(1000); // executorService.execute(()->{ // System.out.print(finalI +"run-"); // countDownLatch.countDown(); // }); // } // new Thread(()->{ // try { // countDownLatch.await(); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // System.out.println("await等待线程"); // }).start(); // // System.out.println("end"); // executorService.shutdown(); } }

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo7; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; public class SemaphoreExample { public static void main(String[] args) { final int clientCount = 3; final int totalRequestCount = 10; Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(clientCount); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for (int i = 0; i < totalRequestCount; i++) { executorService.execute(()->{ try { semaphore.acquire(); System.out.print(semaphore.availablePermits() + " "); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { semaphore.release(); } }); } executorService.shutdown(); } }
8.J.U.C-其他组件
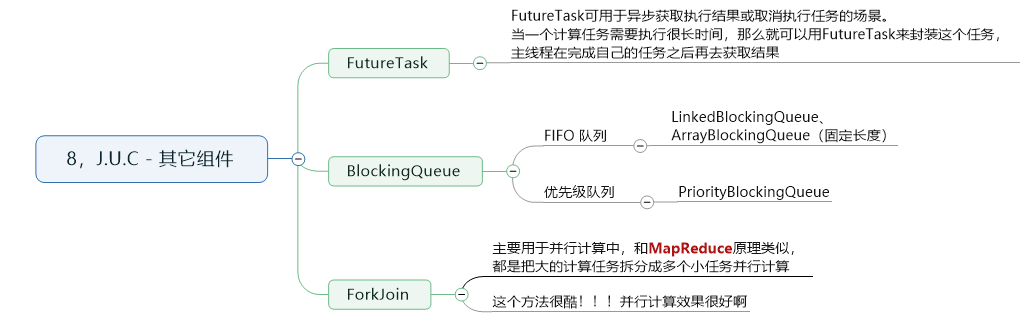
样例代码:

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo8; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask; public class ForkJoinExample extends RecursiveTask<Integer> { private final int threshold=5; private int first; private int last; public ForkJoinExample(int first,int last){ this.first=first; this.last=last; } @Override protected Integer compute() { int result=0; if(last-first<=threshold){ //运算量足够小直接计算 for(int i=first;i<=last;i++){ result +=i; } }else { //拆分成小任务 int middle=first+(last-first)/2; ForkJoinExample leftTask=new ForkJoinExample(first,middle); ForkJoinExample rightTask=new ForkJoinExample(middle+1,last); leftTask.fork(); rightTask.fork(); result =leftTask.join()+rightTask.join(); } return result; } public static int sum(int first,int last){ int sum=0; for(int i=first;i<=last;i++){ sum+=i; } return sum; } public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { //普通方法计算 // System.out.println(sum(1, 1000000000)); //并行计算方法 // ForkJoinExample example = new ForkJoinExample(1, 1000000000); // ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(); // Future result=forkJoinPool.submit(example); // System.out.println(result.get()); } }

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo8; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; public class FutureTaskExample{ public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { FutureTask<Integer> futureTask=new FutureTask<>(new Callable<Integer>() { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { int result=0; for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Thread.sleep(500); System.out.println("thread-A:"+i); result +=i; } return result; } }); Thread computeThread=new Thread(futureTask); computeThread.start(); Thread otherThread=new Thread(()->{ System.out.println("other task is running..."); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); otherThread.start(); System.out.println("运行正常"); System.out.println(futureTask.get()); } }

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo8; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; public class ProducerConsumer { private static BlockingQueue<String> queue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5); private static class Producer extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { try { queue.put("product"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(queue.size()+"produce.."); } } private static class Consumer extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { try { String product=queue.take(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(queue.size()+"consume.."); } } public static void main(String[] args) {//类似缓存,协调速率 for(int i=0;i<2;i++){ Producer producer=new Producer(); producer.start(); } for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ Consumer consumer=new Consumer(); consumer.start(); } for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { Producer producer = new Producer(); producer.start(); } } }
9.线程不安全


package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo9; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; class ThreadUnsafeExample{ private int cnt=0; // public synchronized void add(){//输出为1000,同步后输出正常 public void add(){//不同步后,输出不正常 cnt++; } public int get(){ return cnt; } } public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { final int threadSize=1000; ThreadUnsafeExample example=new ThreadUnsafeExample(); final CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(threadSize); ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<threadSize;i++){ executorService.execute(()->{ example.add(); countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); System.out.println(example.get()); } }
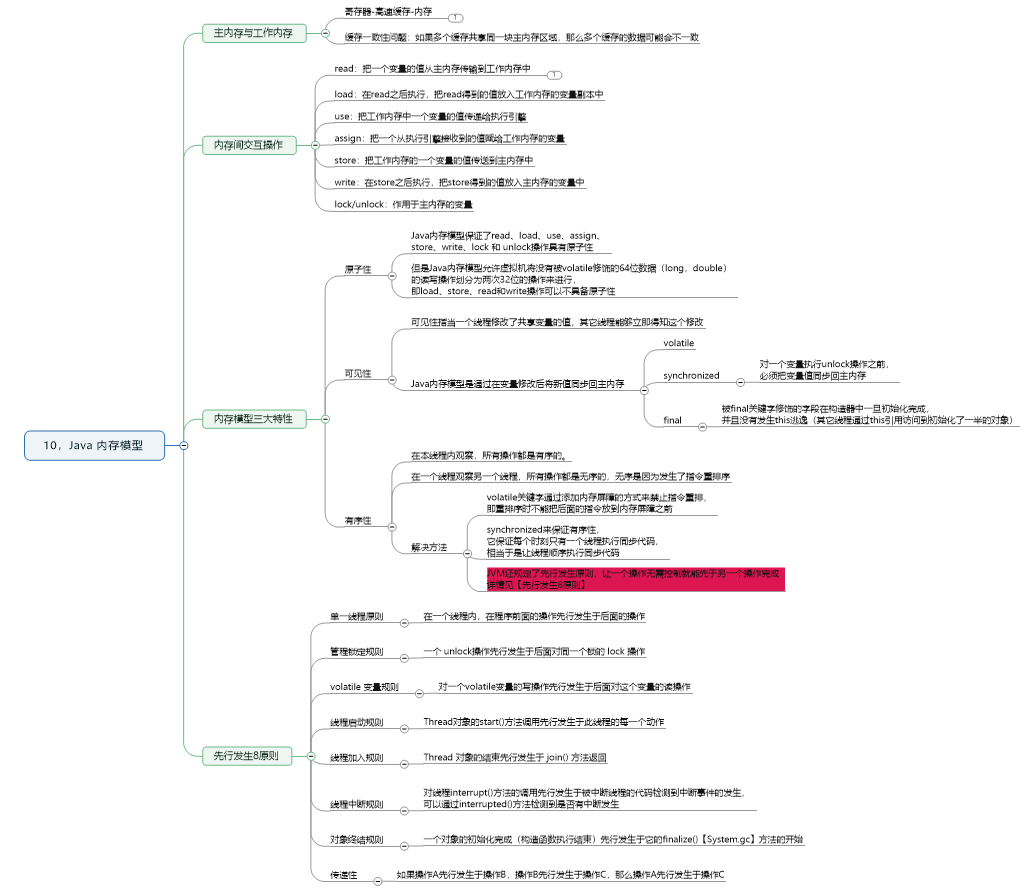
10.Java内存模式

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo10; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class AtomicExample { private AtomicInteger cnt=new AtomicInteger(); public void add(){ cnt.incrementAndGet();//原子自增 } public int get(){ return cnt.get(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { final int threadSize=1000; AtomicExample example=new AtomicExample(); final CountDownLatch countDownLatch=new CountDownLatch(threadSize); ExecutorService excutorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<threadSize;i++){ excutorService.execute(()->{ example.add(); countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); excutorService.shutdown(); System.out.println(example.get()); } }

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo10; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class AtomicSynchronizedExample { private int cnt=0; public synchronized void add(){ cnt++; } public synchronized int get(){ return cnt; } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { final int threadSize = 1000; AtomicSynchronizedExample example=new AtomicSynchronizedExample(); final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadSize); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<threadSize;i++){ executorService.execute(()->{ example.add(); countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } countDownLatch.await(); executorService.shutdown(); System.out.println(example.get()); } }
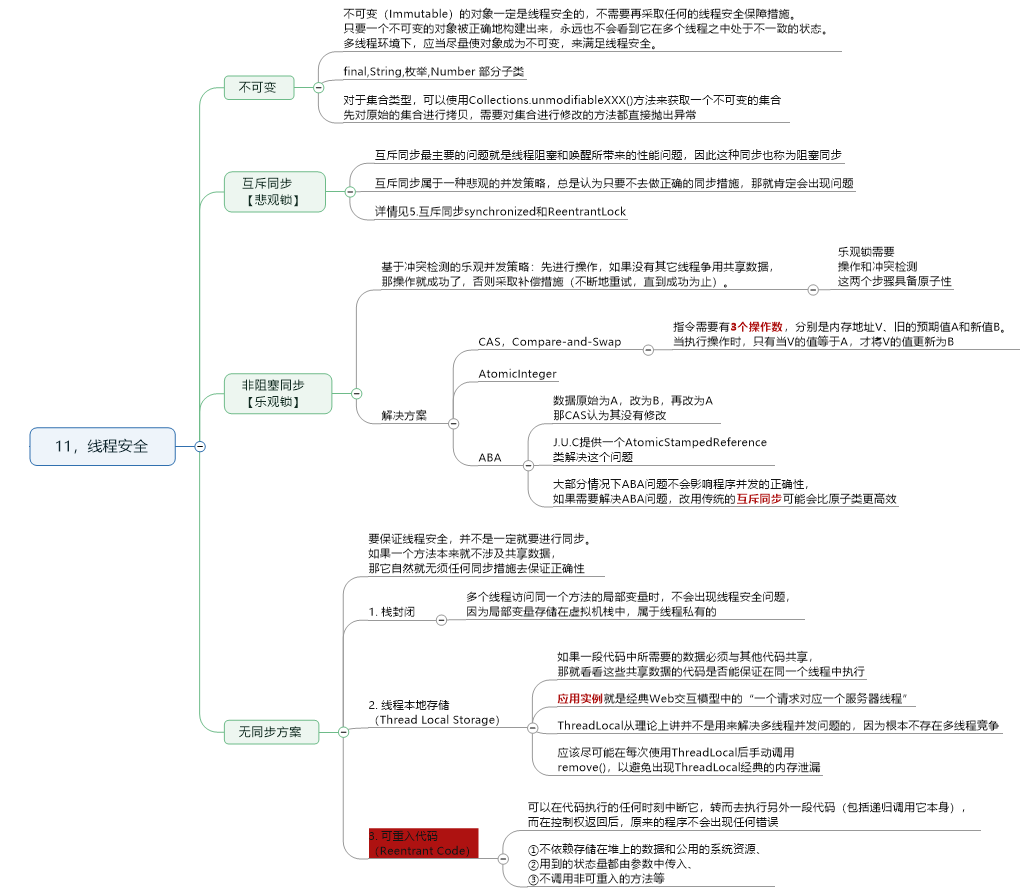
11.线程安全

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo11; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class AtomicIntegerExample { private AtomicInteger cnt=new AtomicInteger(); public void add(){ cnt.incrementAndGet(); } public int get(){ return cnt.get(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { AtomicIntegerExample example=new AtomicIntegerExample(); ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ executorService.execute(()->example.add()); } Thread.sleep(100); example.add(); System.out.println(example.get()); executorService.shutdown(); } }

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo11; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class ImmutableExample { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("b",2); System.out.println(map.get("b")); Map<String,Integer> unmodifiableMap= Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);//相当于设置一下 System.out.println(unmodifiableMap.get("b")); unmodifiableMap.put("a",1); } }

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo11; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Stack_closedExample { public void add100() { int cnt=0; for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ cnt++; } System.out.println(cnt); } public static void main(String[] args) { Stack_closedExample example=new Stack_closedExample(); ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); executorService.execute(()->example.add100()); executorService.execute(()->example.add100()); executorService.shutdown(); } }

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo11; public class ThreadLocalExample { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadLocal threadLocal=new ThreadLocal(); Thread thread1=new Thread(()->{ threadLocal.set(1); try{ Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(threadLocal.get()); threadLocal.remove(); }); Thread thread2=new Thread(()->{ threadLocal.set(2); threadLocal.remove(); }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo11; public class ThreadLocalExample1 { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadLocal threadLocal1=new ThreadLocal(); ThreadLocal threadLocal2=new ThreadLocal(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> { threadLocal1.set(1); threadLocal2.set(1); }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { threadLocal1.set(2); threadLocal2.set(2); }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }
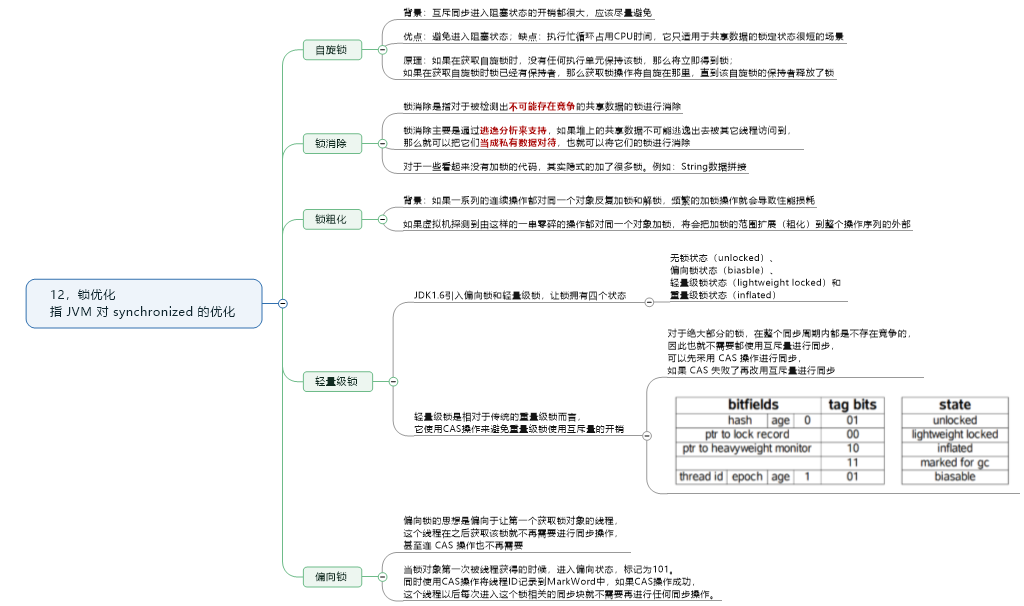
12.锁优化

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo12; public class StringExample { public static String concatString(String s1, String s2, String s3) { return s1 + s2 + s3; } public static String concatString1(String s1, String s2, String s3) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); sb.append(s1); sb.append(s2); sb.append(s3); return sb.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(concatString("12","34","56")); System.out.println(concatString1("12","34","56")); } }
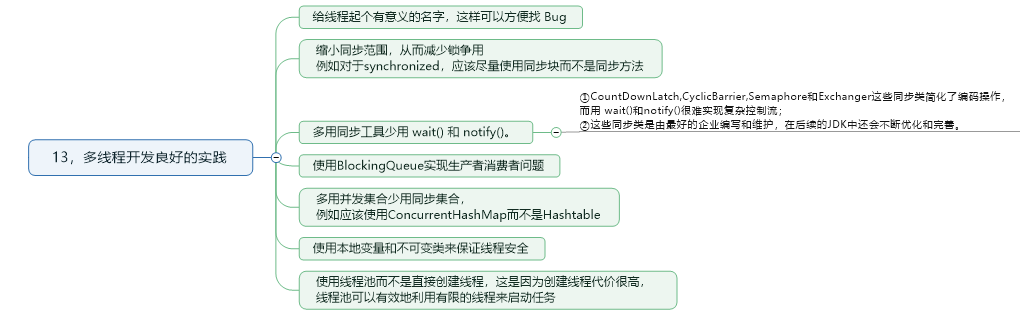
13.多线程开发良好的实践
https://blog.csdn.net/StefanTimber/article/details/73823689
https://github.com/CyC2018/CS-Notes/blob/master/notes/Java%20%E5%B9%B6%E5%8F%91.md
