图1 享元模式【点击查看图片】
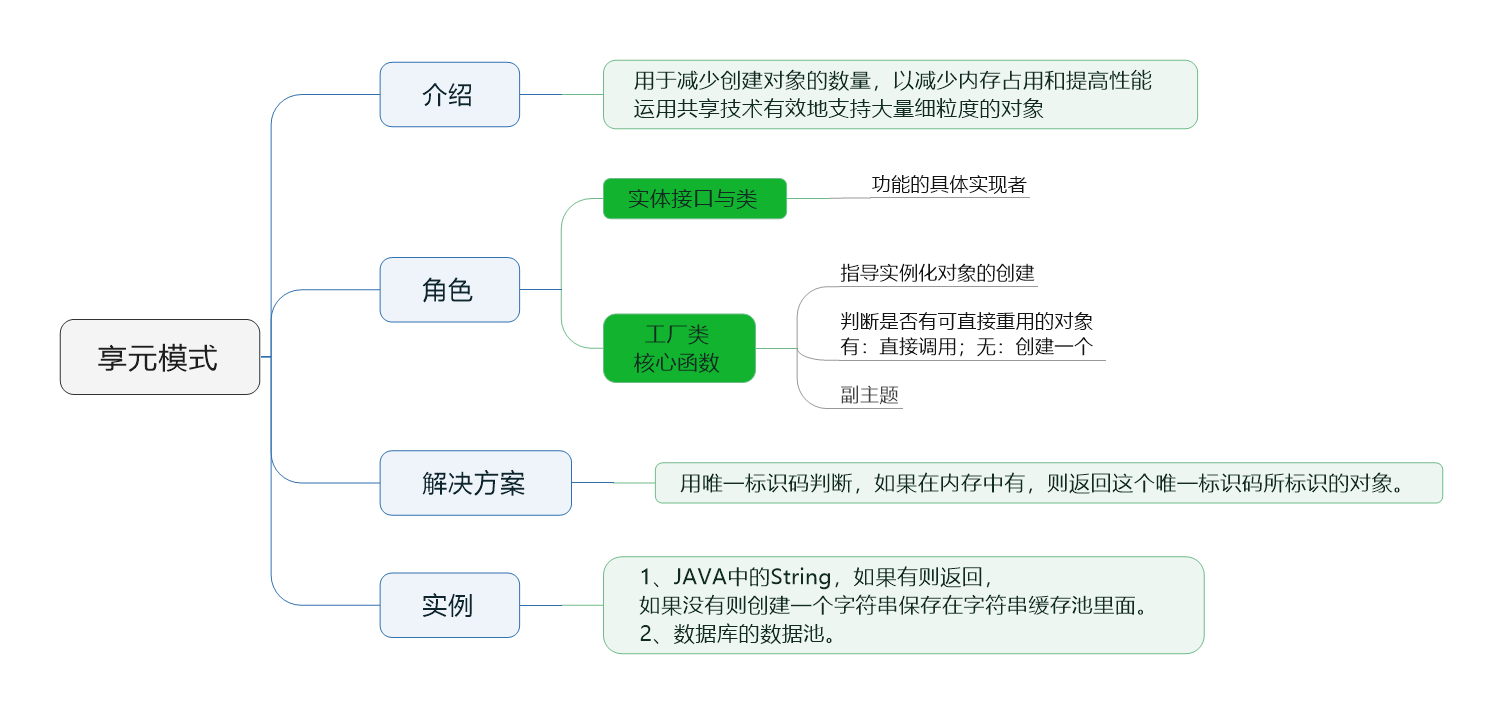
本质是为了使用类似常量池的这样一种缓存结构,用来防止大量的对象新建,耗费大量内存和CPU资源,我们可以直接使用已有的一些实例化对象,只用修改其中的字段属性就可以变身成为一个我们所需要的实例化对象!
后续可以使用ConcurrenHashMap来进行线程安全规范。
1,实体接口与类
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo2; public interface People { void say(); } class Person implements People{ private String country; private boolean gender; private int age; private final String[] StrGender={"Male","Female"}; public Person(String country) { this.country=country; } public String getCountry() { return country; } public void setCountry(String country) { this.country = country; } public boolean isGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(boolean gender) { this.gender = gender; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public void say() { System.out.println("I was "+age+" years old,a "+StrGender[(gender?0:1)]+",came from "+country); } }
2,工厂类
这个是享元模式的核心函数:①使用HashMap存储实例化对象!Spring中的Definition?!!一个套路;②与单例模式相识的,私有化构造函数;③单例模式中的懒汉加载模式;
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo2; import java.util.HashMap; public class PersonFactory { private static final HashMap<String, People> peopleHashMap = new HashMap<>();//和单例模式有点像 public static People getPerson(String country) { People people = (People) peopleHashMap.get(country); if(people==null){ people=new Person(country); peopleHashMap.put(country,people); System.out.println("Creating person of country : " + country); } return people; } }
3,享元类【改正:这里不应该叫做享元类,只应该叫做场景类】
享元模式的核心功能基本上都在工厂类中实现了!
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo2; public class FlyweightPatternDemo { private static final String[] COUNTRY={ "China", "Russia", "America", "England", "France" }; public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0; i < 20; ++i) { Person pr =(Person) PersonFactory.getPerson(getCountry()); pr.setAge(getAge()); pr.setGender(getGender()); pr.say(); } } private static String getCountry() {//获取国家信息 return COUNTRY[(int)(Math.random()*COUNTRY.length)]; } private static boolean getGender() { return ((int)(Math.random()*2 )==0? true : false); } private static int getAge() { return (int)(Math.random()*100); } }