前言
书接上文,本文造第三个轮子,也是asyncio包里面非常常用的一个函数gather
一、知识准备
● 相对于前两个函数,gather的使用频率更高,因为它支持多个协程任务“同时”执行
● 理解__await__ __iter__的使用
● 理解关键字async/await,async/await是3.5之后的语法,和yield/yield from异曲同工
● 今天的文章有点长,请大家耐心看完
二、环境准备
| 组件 | 版本 |
|---|---|
| python | 3.7.7 |
三、
gather的实现
先来看下官方gather的使用方法:
|># more main.py
import asyncio
async def hello():
print('enter hello ...')
return 'return hello ...'
async def world():
print('enter world ...')
return 'return world ...'
async def helloworld():
print('enter helloworld')
ret = await asyncio.gather(hello(), world())
print('exit helloworld')
return ret
if __name__ == "__main__":
ret = asyncio.run(helloworld())
print(ret)
|># python3 main.py
enter helloworld
enter hello ...
enter world ...
exit helloworld
['return hello ...', 'return world ...']
来看下造的轮子的使用方式:
▶ more main.py
import wilsonasyncio
async def hello():
print('enter hello ...')
return 'return hello ...'
async def world():
print('enter world ...')
return 'return world ...'
async def helloworld():
print('enter helloworld')
ret = await wilsonasyncio.gather(hello(), world())
print('exit helloworld')
return ret
if __name__ == "__main__":
ret = wilsonasyncio.run(helloworld())
print(ret)
▶ python3 main.py
enter helloworld
enter hello ...
enter world ...
exit helloworld
['return hello ...', 'return world ...']
自己造的轮子也很好的运行了,下面我们来看下轮子的代码
四、代码解析
1)代码组成
|># tree
.
├── eventloops.py
├── futures.py
├── main.py
├── tasks.py
├── wilsonasyncio.py
| 文件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| eventloops.py | 事件循环 |
| futures.py | futures对象 |
| tasks.py | tasks对象 |
| wilsonasyncio.py | 可调用方法集合 |
| main.py | 入口 |
2)代码概览:
eventloops.py
| 类/函数 | 方法 | 对象 | 作用 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eventloop | 事件循环,一个线程只有运行一个 | |||
__init__ |
初始化两个重要对象 self._ready 与 self._stopping |
|||
self._ready |
所有的待执行任务都是从这个队列取出来,非常重要 | |||
self._stopping |
事件循环完成的标志 | |||
call_soon |
调用该方法会立即将任务添加到待执行队列 | |||
run_once |
被run_forever调用,从self._ready队列里面取出任务执行 |
|||
run_forever |
死循环,若self._stopping则退出循环 |
|||
run_until_complete |
非常重要的函数,任务的起点和终点(后面详细介绍) | |||
create_task |
将传入的函数封装成task对象,这个操作会将task.__step添加到__ready队列 |
|||
Handle |
所有的任务进入待执行队列(Eventloop.call_soon)之前都会封装成Handle对象 |
|||
__init__ |
初始化两个重要对象 self._callback 与 self._args |
|||
self._callback |
待执行函数主体 | |||
self._args |
待执行函数参数 | |||
_run |
待执行函数执行 | |||
get_event_loop |
获取当前线程的事件循环 | |||
_complete_eventloop |
将事件循环的_stopping标志置位True |
|||
run |
入口函数 | |||
gather |
可以同时执行多个任务的入口函数 | 新增 | ||
_GatheringFuture |
将每一个任务组成列表,封装成一个新的类 | 新增 |
tasks.py
| 类/函数 | 方法 | 对象 | 作用 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task | 继承自Future,主要用于整个协程运行的周期 | |||
__init__ |
初始化对象 self._coro ,并且call_soon将self.__step加入self._ready队列 |
|||
self._coro |
用户定义的函数主体 | |||
__step |
Task类的核心函数 | |||
__wakeup |
唤醒任务 | 新增 | ||
ensure_future |
如果对象是一个Future对象,就返回,否则就会调用create_task返回,并且加入到_ready队列 |
futures.py
| 类/函数 | 方法 | 对象 | 作用 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Future | 主要负责与用户函数进行交互 | |||
__init__ |
初始化两个重要对象 self._loop 与 self._callbacks |
|||
self._loop |
事件循环 | |||
self._callbacks |
回调队列,任务暂存队列,等待时机成熟(状态不是PENDING),就会进入_ready队列 |
|||
add_done_callback |
添加任务回调函数,状态_PENDING,就虎进入_callbacks队列,否则进入_ready队列 |
|||
set_result |
获取任务执行结果并存储至_result,将状态置位_FINISH,调用__schedule_callbacks |
|||
__schedule_callbacks |
将回调函数放入_ready,等待执行 |
|||
result |
获取返回值 | |||
__await__ |
使用await就会进入这个方法 | 新增 | ||
__iter__ |
使用yield from就会进入这个方法 | 新增 |
3)执行过程
3.1)入口函数
main.py
if __name__ == "__main__":
ret = wilsonasyncio.run(helloworld())
print(ret)
ret = wilsonasyncio.run(helloworld())使用run,参数是用户函数helloworld(),进入run,run的流程可以参考上一小节run-->run_until_complete
3.2)事件循环启动,同之前
3.3)第一次循环run_forever --> run_once
- 将
_ready队列的内容(即:task.__step)取出来执行,这里的coro是helloworld()
def __step(self, exc=None):
coro = self._coro
try:
if exc is None:
result = coro.send(None)
else:
result = coro.throw(exc)
except StopIteration as exc:
super().set_result(exc.value)
else:
blocking = getattr(result, '_asyncio_future_blocking', None)
if blocking:
result._asyncio_future_blocking = False
result.add_done_callback(self.__wakeup, result)
finally:
self = None
__step较之前的代码有改动result = coro.send(None),进入用户定义函数
async def helloworld():
print('enter helloworld')
ret = await wilsonasyncio.gather(hello(), world())
print('exit helloworld')
return ret
ret = await wilsonasyncio.gather(hello(), world()),这里没啥可说的,进入gather函数
def gather(*coros_or_futures, loop=None):
loop = get_event_loop()
def _done_callback(fut):
nonlocal nfinished
nfinished += 1
if nfinished == nfuts:
results = []
for fut in children:
res = fut.result()
results.append(res)
outer.set_result(results)
children = []
nfuts = 0
nfinished = 0
for arg in coros_or_futures:
fut = tasks.ensure_future(arg, loop=loop)
nfuts += 1
fut.add_done_callback(_done_callback)
children.append(fut)
outer = _GatheringFuture(children, loop=loop)
return outer
loop = get_event_loop()获取事件循环def _done_callback(fut)这个函数是回调函数,细节后面分析,现在只需要知道任务(hello()与world())执行完之后就会回调就行for arg in coros_or_futuresfor循环确保每一个任务都是Future对象,并且add_done_callback将回调函数设置为_done_callback,还有将他们加入到_ready队列等待下一次循环调度- 3个重要的变量:
children里面存放的是每一个异步任务,在本例是hello()与world()
nfuts存放是异步任务的数量,在本例是2
nfinished存放的是异步任务完成的数量,目前是0,完成的时候是2 - 继续往下,来到了
_GatheringFuture,看看源码:
class _GatheringFuture(Future):
def __init__(self, children, *, loop=None):
super().__init__(loop=loop)
self._children = children
_GatheringFuture最主要的作用就是将多个异步任务放入self._children,然后用_GatheringFuture这个对象来管理。需要注意,这个对象继承了Future- 至此,
gather完成初始化,返回了outer,其实就是_GatheringFuture - 总结一下
gather,初始化了3个重要的变量,后面用来存放状态;给每一个异步任务添加回调函数;将多个异步子任务合并,并且使用一个Future对象去管理
3.3.1)gather完成,回到helloworld()
async def helloworld():
print('enter helloworld')
ret = await wilsonasyncio.gather(hello(), world())
print('exit helloworld')
return ret
ret = await wilsonasyncio.gather(hello(), world())gather返回_GatheringFuture,随后使用await,就会进入Future.__await__
def __await__(self):
if self._state == _PENDING:
self._asyncio_future_blocking = True
yield self
return self.result()
- 由于
_GatheringFuture的状态是_PENDING,所以进入if,遇到yield self,将self,也就是_GatheringFuture返回(这里注意yield的用法,流程控制的功能) - 那
yield回到哪儿去了呢?从哪儿send就回到哪儿去,所以,他又回到了task.__step函数里面去
def __step(self, exc=None):
coro = self._coro
try:
if exc is None:
result = coro.send(None)
else:
result = coro.throw(exc)
except StopIteration as exc:
super().set_result(exc.value)
else:
blocking = getattr(result, '_asyncio_future_blocking', None)
if blocking:
result._asyncio_future_blocking = False
result.add_done_callback(self.__wakeup, result)
finally:
self = None
- 这里是本函数的第一个核心点,流程控制/跳转,需要非常的清晰,如果搞不清楚的同学,再详细的去阅读有关
yield/yield from的文章 - 继续往下走,由于用户函数
helloworld()没有结束,所以不会抛异常,所以来到了else分支 blocking = getattr(result, '_asyncio_future_blocking', None)这里有一个重要的状态,那就是_asyncio_future_blocking,只有调用__await__,才会有这个参数,默认是true,这个参数主要的作用:一个异步函数,如果调用了多个子异步函数,那证明该异步函数没有结束(后面详细讲解),就需要添加“唤醒”回调result._asyncio_future_blocking = False将参数置位False,并且添加self.__wakeup回调等待唤醒__step函数完成
这里需要详细讲解一下_asyncio_future_blocking 的作用
- 如果在异步函数里面出现了await,调用其他异步函数的情况,就会走到
Future.__await__将_asyncio_future_blocking设置为true
async def helloworld():
print('enter helloworld')
ret = await wilsonasyncio.gather(hello(), world())
print('exit helloworld')
return ret
class Future:
def __await__(self):
if self._state == _PENDING:
self._asyncio_future_blocking = True
yield self
return self.result()
- 这样做了之后,在
task.__step中就会把该任务的回调函数设置为__wakeup - 为啥要
__wakeup,因为helloworld()并没有执行完成,所以需要再次__wakeup来唤醒helloworld()
这里揭示了,在Eventloop里面,只要使用await调用其他异步任务,就会挂起父任务,转而去执行子任务,直至子任务完成之后,回到父任务继续执行
先喝口水,休息一下,下面更复杂。。。
3.4)第二次循环run_forever --> run_once
eventloops.py
def run_once(self):
ntodo = len(self._ready)
for _ in range(ntodo):
handle = self._ready.popleft()
handle._run()
- 从队列中取出数据,此时
_ready队列有两个任务,hello()world(),在gather的for循环时添加的
async def hello():
print('enter hello ...')
return 'return hello ...'
async def world():
print('enter world ...')
return 'return world ...'
- 由于
hello()world()没有await调用其他异步任务,所以他们的执行比较简单,分别一次task.__step就结束了,到达set_result()处 set_result()将回调函数放入_ready队列,等待下次循环执行
3.5)第三次循环run_forever --> run_once
- 我们来看下回调函数
def _done_callback(fut):
nonlocal nfinished
nfinished += 1
if nfinished == nfuts:
results = []
for fut in children:
res = fut.result()
results.append(res)
outer.set_result(results)
- 没错,这是本文的第二个核心点,我们来仔细分析一下
- 这段代码最主要的逻辑,其实就是,只有当所有的子任务执行完之后,才会启动父任务的回调函数,本文中只有
hello()world()都执行完之后if nfinished == nfuts:,才会启动父任务_GatheringFuture的回调outer.set_result(results) results.append(res)将子任务的结果取出来,放进父任务的results里面- 子任务执行完成,终于到了唤醒父任务的时候了
task.__wakeup
def __wakeup(self, future):
try:
future.result()
except Exception as exc:
raise exc
else:
self.__step()
self = None
3.6)第四次循环run_forever --> run_once
future.result()从_GatheringFuture取出结果,然后进入task.__step
def __step(self, exc=None):
coro = self._coro
try:
if exc is None:
result = coro.send(None)
else:
result = coro.throw(exc)
except StopIteration as exc:
super().set_result(exc.value)
else:
blocking = getattr(result, '_asyncio_future_blocking', None)
if blocking:
result._asyncio_future_blocking = False
result.add_done_callback(self.__wakeup, result)
finally:
self = None
result = coro.send(None)其实就是helloworld() --> send又要跳回到当初yield的地方,那就是Future.__await__
def __await__(self):
if self._state == _PENDING:
self._asyncio_future_blocking = True
yield self
return self.result()
return self.result()终于返回到helloworld()函数里面去了
async def helloworld():
print('enter helloworld')
ret = await wilsonasyncio.gather(hello(), world())
print('exit helloworld')
return ret
helloworld终于也执行完了,返回了ret
3.7)第五次循环run_forever --> run_once
- 循环结束
- 回到
run
3.8)回到主函数,获取返回值
if __name__ == "__main__":
ret = wilsonasyncio.run(helloworld())
print(ret)
3.9)执行结果
▶ python3 main.py
enter helloworld
enter hello ...
enter world ...
exit helloworld
['return hello ...', 'return world ...']
五、流程总结
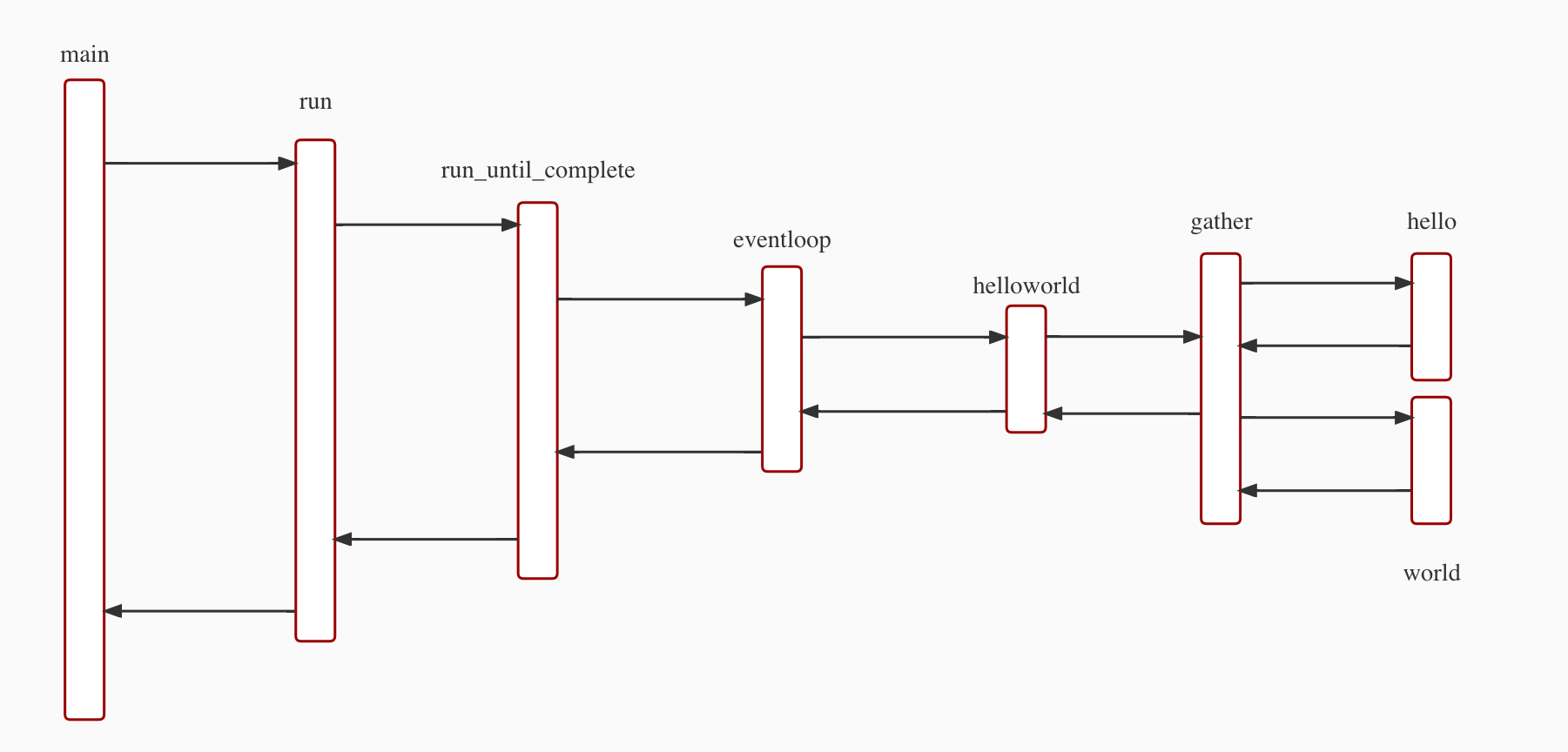
六、小结
● 终于结束了,这是一个非常长的小节了,但是我感觉很多细节还是没有说到,大家有问题请及时留言探讨
● _GatheringFuture一个非常重要的对象,它不但追踪了hello() world()的执行状态,唤醒helloworld(),并且将返回值传递给helloworld
● await async yield对流程的控制需要特别关注
● 本文中的代码,参考了python 3.7.7中asyncio的源代码,裁剪而来
● 本文中代码:代码
至此,本文结束
在下才疏学浅,有撒汤漏水的,请各位不吝赐教...
更多文章,请关注我:wilson.chai