MAC Address-Table Move Update
The MAC address-table move update feature allows the switch to provide rapid bidirectional convergence when a primary (forwarding) link goes down and the standby link begins forwarding traffic.
Figure 1. MAC Address-Table Move Update Example. In the following figure, switch A is an access switch, and ports 1 and 2 on switch A are connected to uplink switches B and D through a Flex Links pair. Port 1 is forwarding traffic, and port 2 is in the backup state. Traffic from the PC to the server is forwarded from port 1 to port 3. The MAC address of the PC has been learned on port 3 of switch C. Traffic from the server to the PC is forwarded from port 3 to port 1.
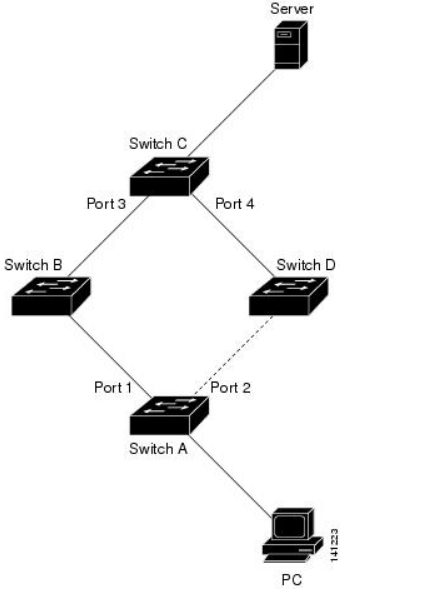
f the MAC address-table move update feature is not configured and port 1 goes down, port 2 starts forwarding traffic. However, for a short time, switch C keeps forwarding traffic from the server to the PC through port 3, and the PC does not get the traffic because port 1 is down. If switch C removes the MAC address of the PC on port 3 and relearns it on port 4, traffic can then be forwarded from the server to the PC through port 2.
If the MAC address-table move update feature is configured and enabled on the switches, and port 1 goes down, port 2 starts forwarding traffic from the PC to the server. The switch sends a MAC address-table move update packet from port 2. Switch C gets this packet on port 4 and immediately learns the MAC address of the PC on port 4, which reduces the reconvergence time.
You can configure the access switch, switch A, to send MAC address-table move update messages. You can also configure the uplink switches B, C, and D to get and process the MAC address-table move update messages. Whenswitch C gets a MAC address-table move update message from switch A, switch C learns the MAC address of the PC on port 4. Switch C updates the MAC address table, including the forwarding table entry for the PC.
Switch A does not need to wait for the MAC address-table update. The switch detects a failure on port 1 and immediately starts forwarding server traffic from port 2, the new forwarding port. This change occurs in less than 100 milliseconds (ms). The PC is directly connected to switch A, and the connection status does not change. Switch A does not need to update the PC entry in the MAC address table.
MAC Address-Table Move Update Configuration Guidelines
-
You can enable and configure this feature on the access switch to send the MAC address-table move updates.
-
You can enable and configure this feature on the uplink switches to get the MAC address-table move updates.
Configuring MAC Address-Table Move Update
SUMMARY STEPS
- configure terminal
- interface interface-id
- Use one of the following:
- switchport backup interface interface-id
- switchport backup interface interface-id mmu primary vlan vlan-id
- end
- mac address-table move update transmit
- end
| Step 3 |
Use one of the following:
Example: |
Configures a physical Layer 2 interface (or port channel), as part of a Flex Links pair with the interface. The MAC address-table move update VLAN is the lowest VLAN ID on the interface. Configure a physical Layer 2 interface (or port channel) and specifies the VLAN ID on the interface, which is used for sending the MAC address-table move update. When one link is forwarding traffic, the other interface is in standby mode. |
| Step 5 |
mac address-table move update transmit Example: |
Enables the access switch to send MAC address-table move updates to other switches in the network if the primary link goes down and the switch starts forwarding traffic through the standby link. |
Configuring a Switch to Obtain and Process MAC Address-Table Move Update Messages
SUMMARY STEPS
- configure terminal
- mac address-table move update receive
- end
Monitoring the MAC Address-Table Move Update
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
show mac address-table move update |
Displays the MAC address-table move update information on theswitch. |