解题思路
遗传算法步骤:
第一步:初始化 t←0进化代数计数器;T是最大进化代数(也可以没有);随机生成M个个体作为初始群体P(t);
第二步:个体评价 计算P(t)中各个个体的适应度;
第三步:选择运算 将选择算子作用于群体;
第四步:交叉运算 将交叉算子作用于群体;
第五步:变异运算 将变异算子作用于群体,并通过以上运算得到下一代群体P(t + 1);
第六步:终止条件判断 t≦T:t← t+1 转到步骤2;t>T:终止 输出解。
遗传算法求解的一般过程:
1)确定决策变量及各种约束条件,即个体的表现型X和问题的解空间;
2)建立优化模型 (目标函数最大OR 最小) 数学描述形式 量化方法;
3)染色体编码方法;
4)解码方法;
5)个体适应度的量化评价方法 F(x)
6)设计遗传算子;
7)确定有关运行参数。
方法实现
编码方式
应用于TSP问题,选用整数编码,每个整数代表一个城市,一整条路径就是整个染色体编码;如此显式的编码,可以不用解码;

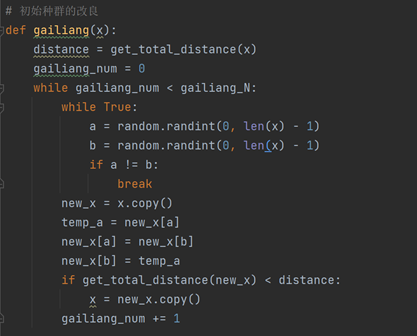
初始种群
随机生成初始种群,并计算这个初始种群的个体适应度。初始化种群时,采用改良版本,为了初始化一个较好的种群,如果随即交换两个城市的位置,如果总距离减小,那么就更新这个染色体。
选择算子
选择总距离作为适应度函数,距离越小适应度越高,(存活率与总距离的倒数成正比)

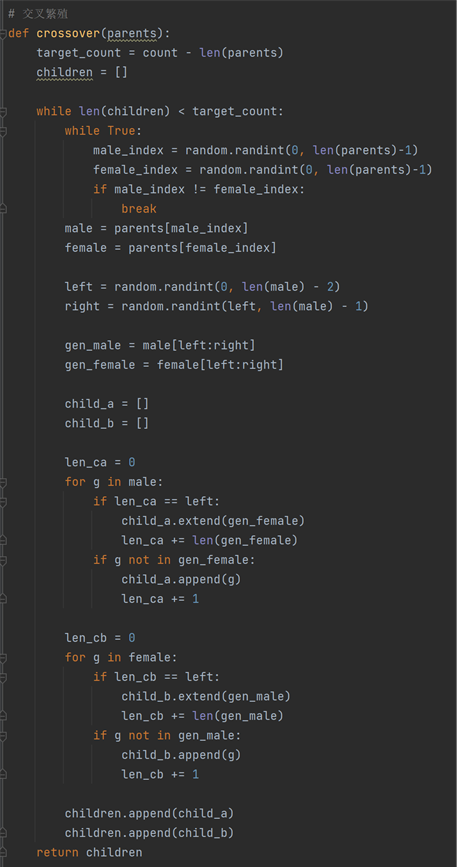
交叉算子
1 部分映射交叉
选择交换部分,交换父代个体基因产生子代,然后建立映射表,根据映射表来消除基因冲突。
2 顺序交叉
在父代样本1中选择交换部分,根据父代1的交叉部分先生成子代1的部分基因片段,然后将父代2中未被选中的基因按顺序复制到子代1的空余部分;然后根据父代2选择交叉部分生成子代2,并将父代1中未选择的部分复制到子代2的空余;
3 基于位置的交叉
在父代1选择时随机选择需要交换的基因,根据交叉部分生成子代1;将父代2中未被选择到的基因复制到子代1中;然后根据父代2随机选择交叉部分生成子代2,并将父代1中未选择的部分复制到子代2的空余;
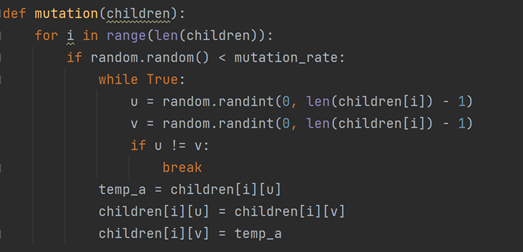
变异算子
根据变异算子的概率,变异时随机选择两个不同的位置的基因进行交换。也可以采用三点变异法,随机生成abc三点,将ac基因片段与bc做交换。
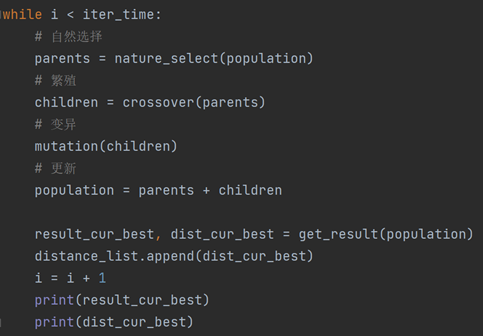
更新种群
采用杰出父代+子代的方式来更新种群。
我在求解时采用了在初始种群中进行改良的方法,收敛速度相对变快,求解与标准结果。完全正确
求解结果
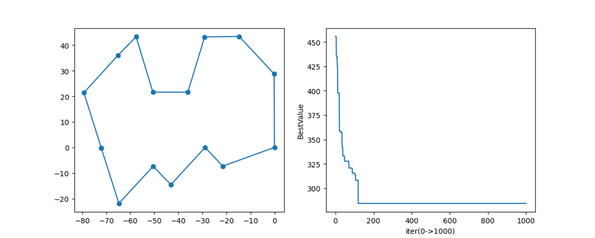
距离和城市序列

TSP图和Loss
实现代码
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
import math
import random
# 处理数据
coord = []
with open("p_xy.txt", "r") as lines:
lines = lines.readlines()
for line in lines:
xy = line.split()
coord.append(xy)
coord = np.array(coord)
w, h = coord.shape
coordinates = np.zeros((w, h), float)
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
coordinates[i, j] = float(coord[i, j])
# print(coordinates)
# 得到距离矩阵
distance = np.zeros((w, w))
for i in range(w):
for j in range(w):
distance[i, j] = distance[j, i] = np.linalg.norm(coordinates[i] - coordinates[j])
# 种群数
count = 300
# 进化次数
iter_time = 1000
# 最优选择概率
retain_rate = 0.3 # 适应度前30%可以活下来
# 弱者生存概率
random_select_rate = 0.5
# 变异
mutation_rate = 0.1
# 改良
gailiang_N = 3000
# 适应度
def get_total_distance(x):
dista = 0
for i in range(len(x)):
if i == len(x) - 1:
dista += distance[x[i]][x[0]]
else:
dista += distance[x[i]][x[i + 1]]
return dista
# 初始种群的改良
def gailiang(x):
distance = get_total_distance(x)
gailiang_num = 0
while gailiang_num < gailiang_N:
while True:
a = random.randint(0, len(x) - 1)
b = random.randint(0, len(x) - 1)
if a != b:
break
new_x = x.copy()
temp_a = new_x[a]
new_x[a] = new_x[b]
new_x[b] = temp_a
if get_total_distance(new_x) < distance:
x = new_x.copy()
gailiang_num += 1
# 自然选择
def nature_select(population):
grad = [[x, get_total_distance(x)] for x in population]
grad = [x[0] for x in sorted(grad, key=lambda x: x[1])]
# 强者
retain_length = int(retain_rate * len(grad))
parents = grad[: retain_length]
# 生存下来的弱者
for ruozhe in grad[retain_length:]:
if random.random() < random_select_rate:
parents.append(ruozhe)
return parents
# 交叉繁殖
def crossover(parents):
target_count = count - len(parents)
children = []
while len(children) < target_count:
while True:
male_index = random.randint(0, len(parents)-1)
female_index = random.randint(0, len(parents)-1)
if male_index != female_index:
break
male = parents[male_index]
female = parents[female_index]
left = random.randint(0, len(male) - 2)
right = random.randint(left, len(male) - 1)
gen_male = male[left:right]
gen_female = female[left:right]
child_a = []
child_b = []
len_ca = 0
for g in male:
if len_ca == left:
child_a.extend(gen_female)
len_ca += len(gen_female)
if g not in gen_female:
child_a.append(g)
len_ca += 1
len_cb = 0
for g in female:
if len_cb == left:
child_b.extend(gen_male)
len_cb += len(gen_male)
if g not in gen_male:
child_b.append(g)
len_cb += 1
children.append(child_a)
children.append(child_b)
return children
def mutation(children):
for i in range(len(children)):
if random.random() < mutation_rate:
while True:
u = random.randint(0, len(children[i]) - 1)
v = random.randint(0, len(children[i]) - 1)
if u != v:
break
temp_a = children[i][u]
children[i][u] = children[i][v]
children[i][v] = temp_a
def get_result(population):
grad = [[x, get_total_distance(x)] for x in population]
grad = sorted(grad, key=lambda x: x[1])
return grad[0][0], grad[0][1]
population = []
# 初始化种群
index = [i for i in range(w)]
for i in range(count):
x = index.copy()
random.shuffle(x)
gailiang(x)
population.append(x)
distance_list = []
result_cur_best, dist_cur_best = get_result(population)
distance_list.append(dist_cur_best)
i = 0
while i < iter_time:
# 自然选择
parents = nature_select(population)
# 繁殖
children = crossover(parents)
# 变异
mutation(children)
# 更新
population = parents + children
result_cur_best, dist_cur_best = get_result(population)
distance_list.append(dist_cur_best)
i = i + 1
print(result_cur_best)
print(dist_cur_best)
for i in range(len(result_cur_best)):
result_cur_best[i] += 1
result_path = result_cur_best
result_path.append(result_path[0])
print(result_path)
# 画图
X = []
Y = []
for index in result_path:
X.append(coordinates[index-1, 0])
Y.append(coordinates[index-1, 1])
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 20))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(X, Y, '-o')
# plt.set_title("GA_TSP")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(np.array(distance_list))
# plt.set_title("GA_TSPLoss")
plt.ylabel("BestValue")
plt.xlabel("iter({}->{})".format(0, iter_time))
plt.show()