首先说明:如果没有进入调试模式的话,默认的调试窗口如下:
开始前的准备:
新建控制台程序DebugWindowDemo:
修改Program.cs 的代码为:
program.csusing System; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Diagnostics; class S { public static void Main() { pcount = Environment.ProcessorCount; Console.WriteLine("Proc count = " + pcount); ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(4, -1); ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(4, -1); t1 = new Task(A, 1); t2 = new Task(A, 2); t3 = new Task(A, 3); t4 = new Task(A, 4); Console.WriteLine("Starting t1 " + t1.Id.ToString()); t1.Start(); Console.WriteLine("Starting t2 " + t2.Id.ToString()); t2.Start(); Console.WriteLine("Starting t3 " + t3.Id.ToString()); t3.Start(); Console.WriteLine("Starting t4 " + t4.Id.ToString()); t4.Start(); Console.ReadLine(); } static void A(object o) { B(o); } static void B(object o) { C(o); } static void C(object o) { int temp = (int)o; Interlocked.Increment(ref aa); while (aa < 4) { ; } if (temp == 1) { // BP1 - all tasks in C Debugger.Break(); waitFor1 = false; } else { while (waitFor1) { ; } } switch (temp) { case 1: D(o); break; case 2: F(o); break; case 3: case 4: I(o); break; default: Debug.Assert(false, "fool"); break; } } static void D(object o) { E(o); } static void E(object o) { // break here at the same time as H and K while (bb < 2) { ; } //BP2 - 1 in E, 2 in H, 3 in J, 4 in K Debugger.Break(); Interlocked.Increment(ref bb); //after L(o); } static void F(object o) { G(o); } static void G(object o) { H(o); } static void H(object o) { // break here at the same time as E and K Interlocked.Increment(ref bb); Monitor.Enter(mylock); while (bb < 3) { ; } Monitor.Exit(mylock); //after L(o); } static void I(object o) { J(o); } static void J(object o) { int temp2 = (int)o; switch (temp2) { case 3: t4.Wait(); break; case 4: K(o); break; default: Debug.Assert(false, "fool2"); break; } } static void K(object o) { // break here at the same time as E and H Interlocked.Increment(ref bb); Monitor.Enter(mylock); while (bb < 3) { ; } Monitor.Exit(mylock); //after L(o); } static void L(object oo) { int temp3 = (int)oo; switch (temp3) { case 1: M(oo); break; case 2: N(oo); break; case 4: O(oo); break; default: Debug.Assert(false, "fool3"); break; } } static void M(object o) { // breaks here at the same time as N and Q Interlocked.Increment(ref cc); while (cc < 3) { ; } //BP3 - 1 in M, 2 in N, 3 still in J, 4 in O, 5 in Q Debugger.Break(); Interlocked.Increment(ref cc); while (true) Thread.Sleep(500); // for ever } static void N(object o) { // breaks here at the same time as M and Q Interlocked.Increment(ref cc); while (cc < 4) { ; } R(o); } static void O(object o) { Task t5 = Task.Factory.StartNew(P, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent); t5.Wait(); R(o); } static void P() { Console.WriteLine("t5 runs " + Task.CurrentId.ToString()); Q(); } static void Q() { // breaks here at the same time as N and M Interlocked.Increment(ref cc); while (cc < 4) { ; } // task 5 dies here freeing task 4 (its parent) Console.WriteLine("t5 dies " + Task.CurrentId.ToString()); waitFor5 = false; } static void R(object o) { if ((int)o == 2) { //wait for task5 to die while (waitFor5) { ;} int i; //spin up all procs for (i = 0; i < pcount - 4; i++) { Task t = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { while (true);}); Console.WriteLine("Started task " + t.Id.ToString()); } Task.Factory.StartNew(T, i + 1 + 5, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent); //scheduled Task.Factory.StartNew(T, i + 2 + 5, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent); //scheduled Task.Factory.StartNew(T, i + 3 + 5, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent); //scheduled Task.Factory.StartNew(T, i + 4 + 5, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent); //scheduled Task.Factory.StartNew(T, (i + 5 + 5).ToString(), TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent); //scheduled //BP4 - 1 in M, 2 in R, 3 in J, 4 in R, 5 died Debugger.Break(); } else { Debug.Assert((int)o == 4); t3.Wait(); } } static void T(object o) { Console.WriteLine("Scheduled run " + Task.CurrentId.ToString()); } static Task t1, t2, t3, t4; static int aa = 0; static int bb = 0; static int cc = 0; static bool waitFor1 = true; static bool waitFor5 = true; static int pcount; static S mylock = new S(); }
按F5,开始运行:
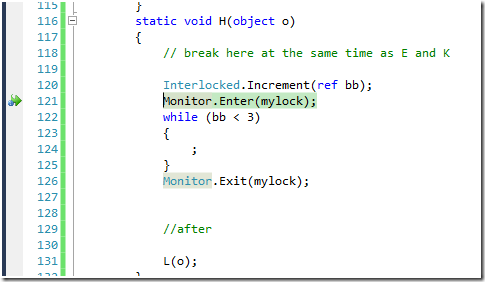
由于Debugger.Break();
所以当执行到这里的时候,Debugger会中断。
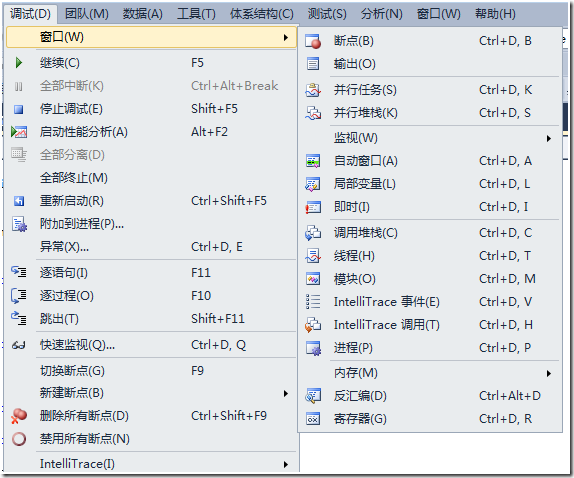
这个时候再看看调试窗口会发现多了几个窗口:
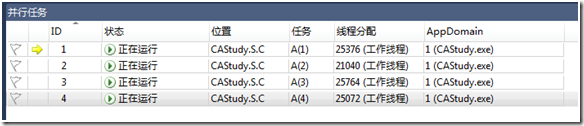
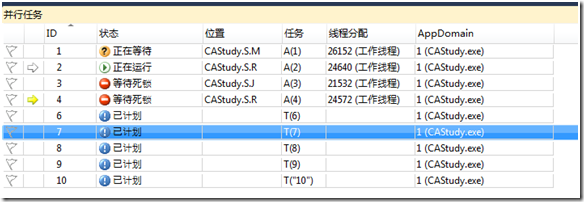
点击调试->窗口->并行任务,界面如下:
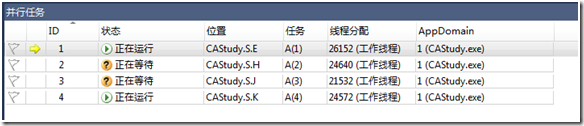
按下F5,继续运行:
双击查看相应等待的任务,就可以知道这个工作线程为什么等待了。
例如:
继续按F5,运行,你应该会看到:
总之关于当前运行的并行任务你都可以看的到。
关闭程序,重新F5,进入调试模式
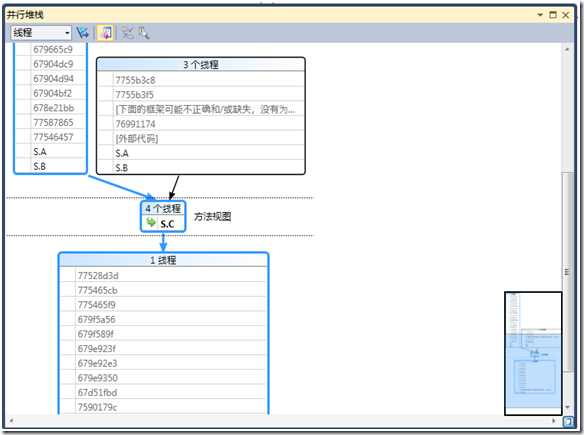
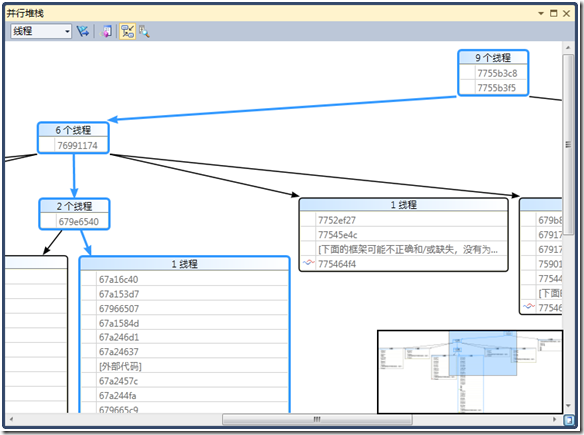
选择调试->窗口->并行堆栈
可以看到:
其中蓝线代表当前正在执行的线程。
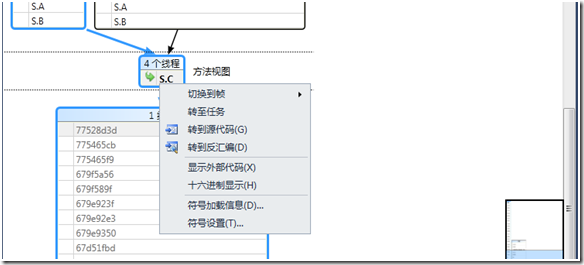
点击切换方法视图
可以看到:
关闭程序,重新F5,进入调试模式
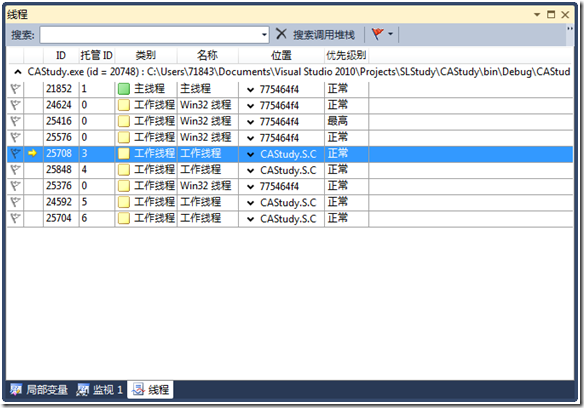
点击调试->窗口->线程:
可以看到:
当前控制台的所有线程都在这里。
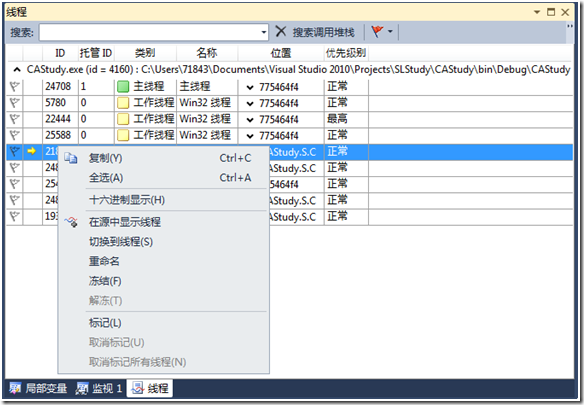
在线程上点击右键可以冻结线程:
冻结线程也就是Pause线程,
冻结的线程可以被解冻,也就是Resume。
其他的窗口:
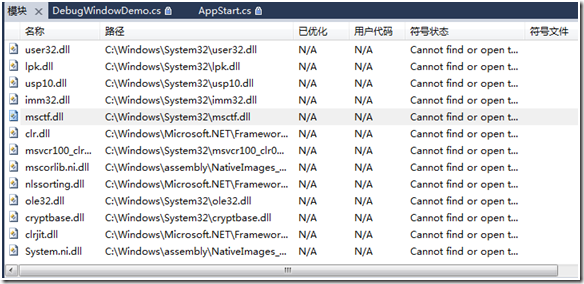
调试->窗口->模块:可以看到当前程序加载的所有模块。
调试->窗口->进程:
调试->窗口->反汇编:
调试->窗口->寄存器:
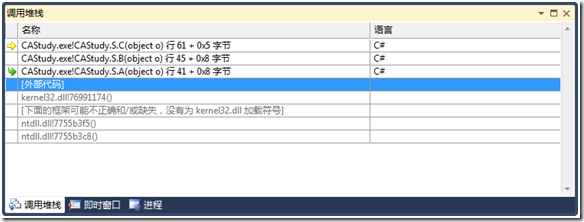
调试->窗口->调用堆栈:
调用堆栈窗口是比较常用的窗口:
上图表示先调用A方法,接着B方法,接着C方法。
也可以认为是C方法是B调用,而B方法是A调用的。
其他窗口比较常用,就不介绍了,是不是有一些你没用到的窗口呢?