iOS 屏幕适配:autoResizing autoLayout和sizeClass
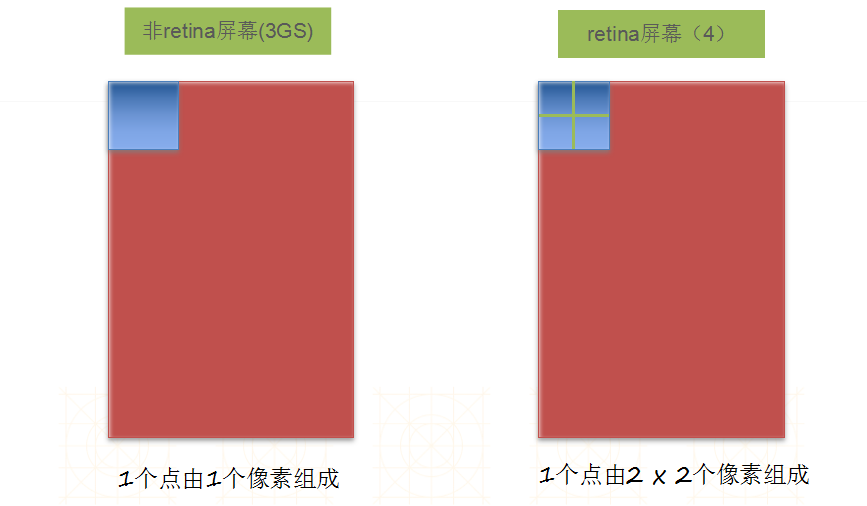
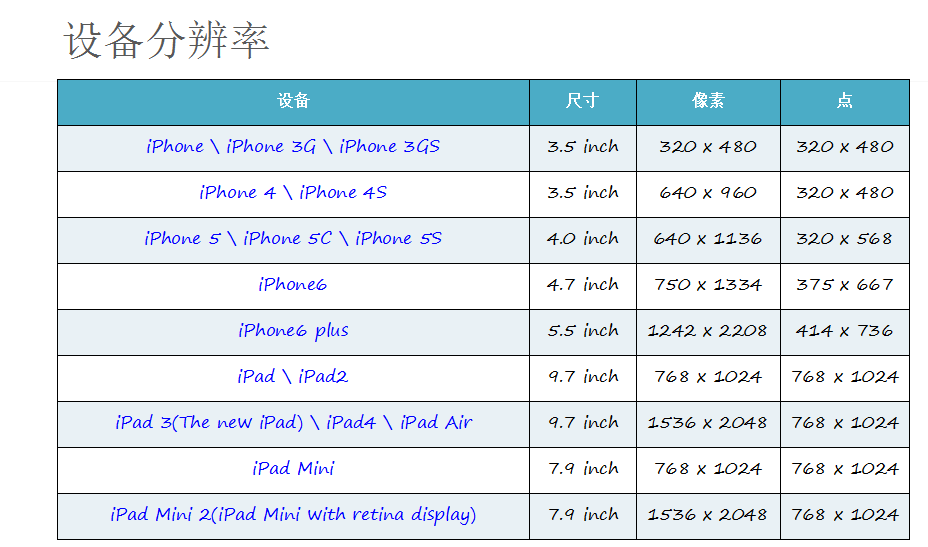
一.图片解说




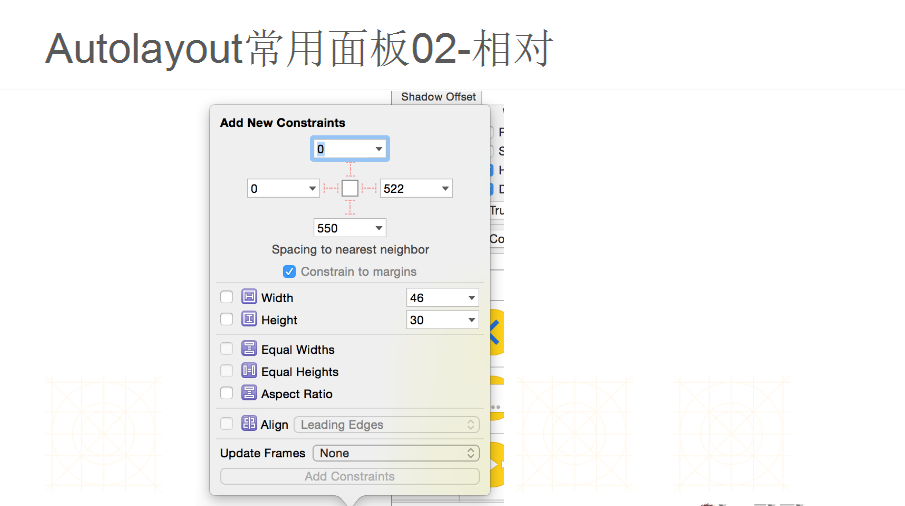
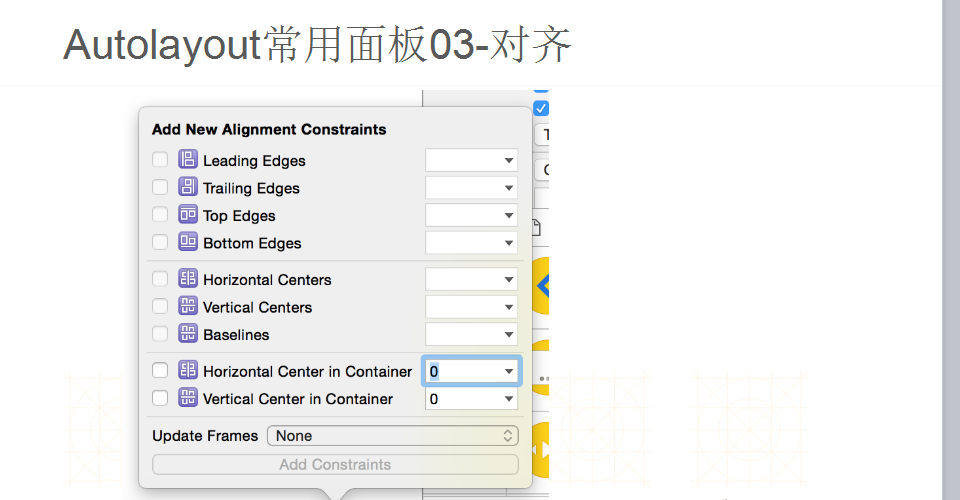





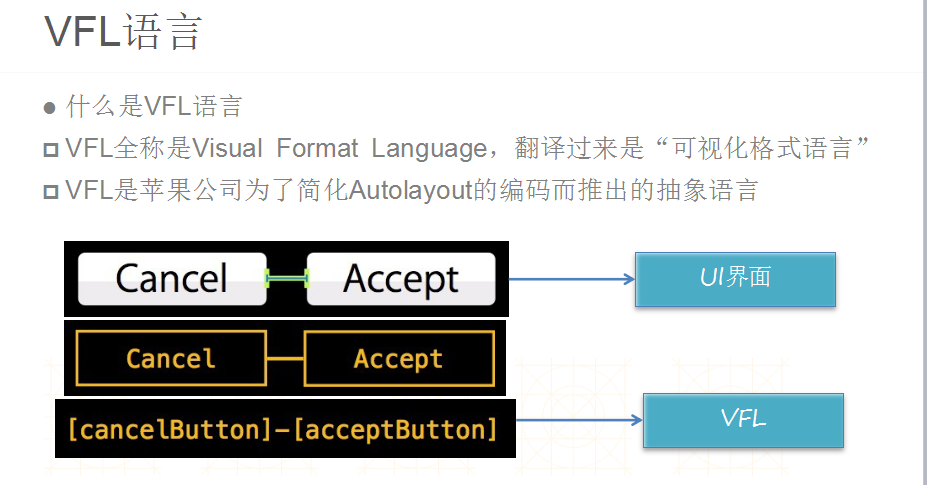

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
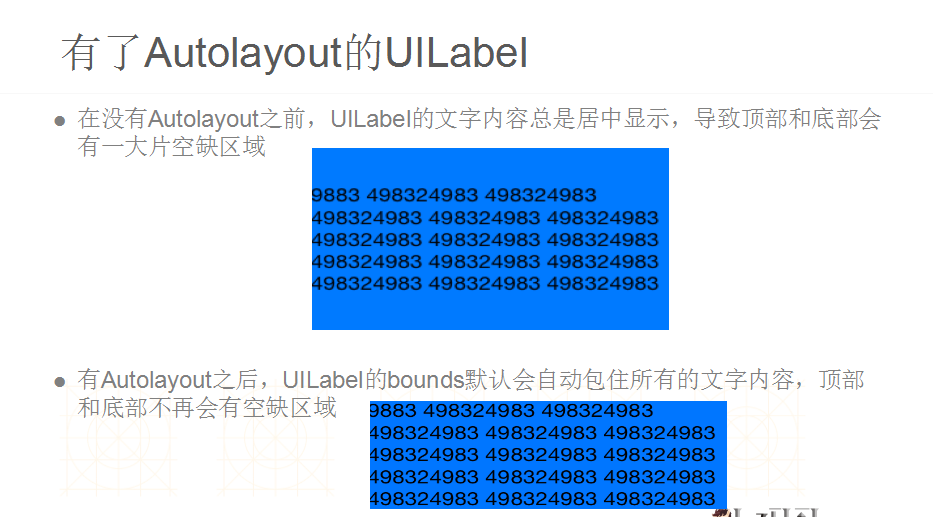
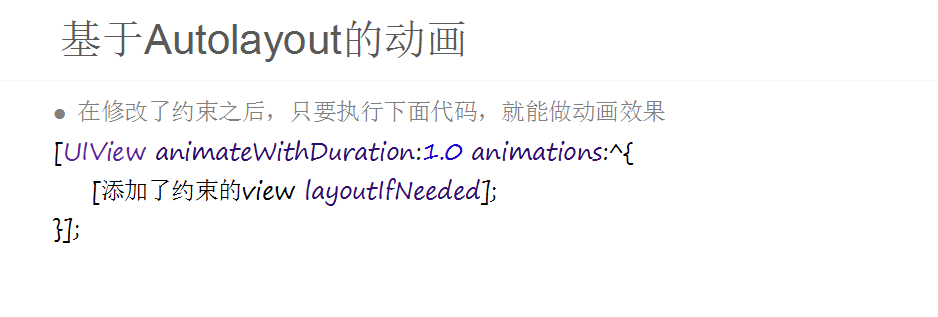



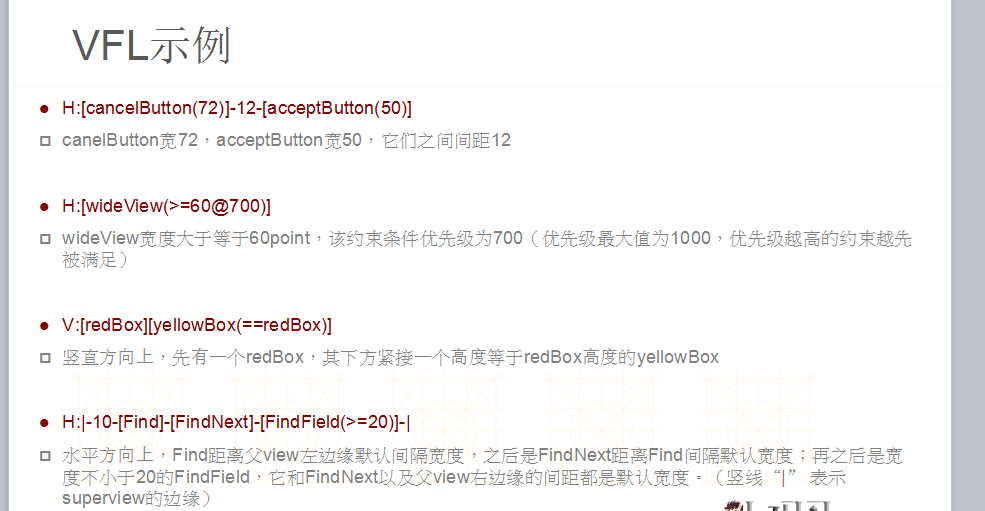
二.AutoLayout
1.前言
•在iOS程序中,大部分视图控制器都包含了大量的代码用于设置UI布局,设置控件的水平或垂直位置,以确保组件在不同版本的iOS中都能得到合理的布局
•甚至有些程序员希望在不同的设备使用相同的视图控制器,这就给代码添加了更多的复杂性!
•自动布局AutoLayout的引入很好地解决了这一问题!

2.什么是AutoLayout
•AutoLayout是一种基于约束的,描述性的布局系统
–基于约束:和以往定义frame的位置和尺寸不同,AutoLayout的位置确定是以所谓相对位置的约束来定义的,比如x坐标为superView的中心,y坐标为屏幕底部上方10像素等
–描述性:约束的定义和各个view的关系使用接近自然语言或者可视化语言的方法来进行描述
–布局系统:用来负责界面的各个元素的位置
•AutoLayout为开发者提供了一种不同于传统对于UI元素位置指定的布局方法。以前,不论是在IB里拖放,还是在代码中写,每个UIView都会有自己的frame属性,来定义其在当前视图中的位置和尺寸。而使用AutoLayout,就变为了使用约束条件来定义view的位置和尺寸
3.AutoLayout的优势
•解决不同分辨率和屏幕尺寸下view的适配问题,同时也简化了旋转时view的位置的定义。原来在底部之上10像素居中的view,不论在旋转屏幕或是更换设备(iPad、iPad mini、iPhone 4或者是iPhone5/iPhone6/iPhone6plus)的时候,始终还在底部之上10像素居中的位置,不会发生变化
•使用约束条件来描述布局,view的frame会依据这些约束来进行计算
4.AutoLayout和Autoresizing Mask的区别
•在iOS6之前,关于屏幕旋转的适配和iPhone,iPad屏幕的自动适配,基本都是由Autoresizing Mask来完成的。但是随着大家对iOS App的要求越来越高,以及今后可能出现的多种屏幕和分辨率的设备,Autoresizing Mask显得有些落伍和迟钝了。AutoLayout可以完成所有原来Autoresizing Mask能完成的工作,同时还能胜任一些原来无法完成的任务,其中包括:
•AutoLayout可以指定任意两个view的相对位置,而不需要像Autoresizing Mask那样需要两个view在直系的view hierarchy中
•AutoLayout不必须指定相等关系的约束,它可以指定非相等约束(大于或者小于等);而Autoresizing Mask所能做的布局只能是相等条件的
•AutoLayout可以指定约束的优先级,计算frame时将优先按照满足优先级高的条件进行计算
5.AutoLayout的基本使用
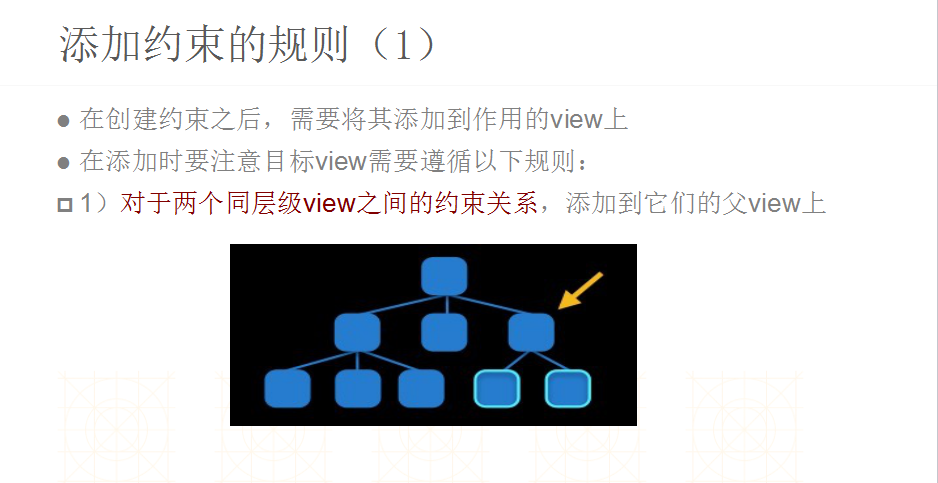
•在创建约束之后,需要将其添加到作用的view上。在添加时要注意目标view需要遵循以下规则:
•1) 对于两个同层级view之间的约束关系,添加到他们的父view上
•2) 对于两个不同层级view之间的约束关系,添加到他们最近的共同父view上
•3) 对于有层次关系的两个view之间的约束关系,添加到层次较高的父view上
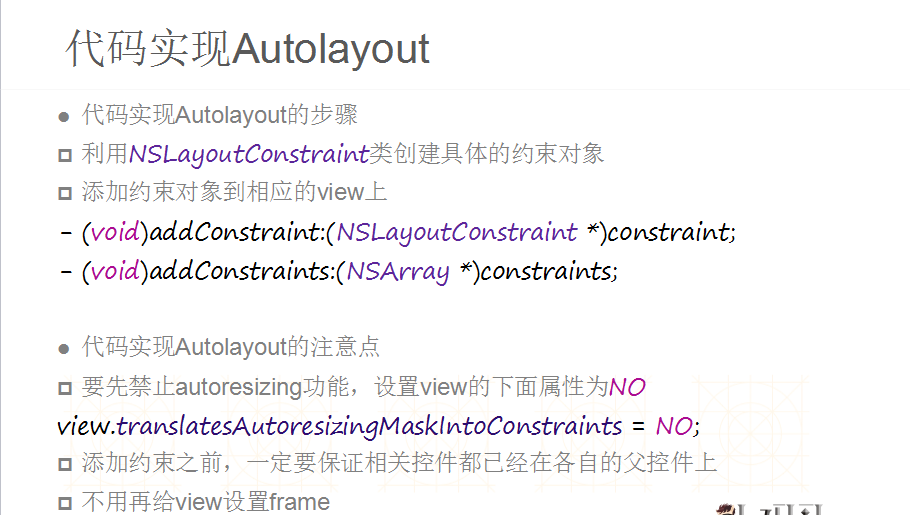
6.添加和刷新约束(代码)
-(void)addConstraint:(NSLayoutConstraint *)constraint
•刷新约束的改变
-setNeedsUpdateConstraints
-layoutIfNeeded
[button setTranslatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints:NO];
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
// 2.1 水平方向的约束NSLayoutConstraint *constraintX = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:button attribute:NSLayoutAttributeCenterX relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual toItem:self.view attribute:NSLayoutAttributeCenterX multiplier:1.0f constant:0.0f];[self.view addConstraint:constraintX];// 2.2 垂直方向的约束NSLayoutConstraint *constraintY = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:button attribute:NSLayoutAttributeCenterY relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual toItem:self.view attribute:NSLayoutAttributeCenterY multiplier:1.0f constant:0.0f];[self.view addConstraint:constraintY]; |
6.使用AutoLayout容易出现的错误
•Ambiguous Layout 布局不能确定,即给出的约束条件无法唯一确定一种布局,也就是约束条件不足,无法得到唯一的布局结果。这种情况一般添加一些必要的约束或者调整优先级可以解决
•Unsatisfiable Constraints 无法满足约束,问题来源是有约束条件互相冲突,因此无法同时满足,需要删掉一些约束
•现在使用IB可以比较容易地完成复杂约束,在实际开发中很少再会遇到遗漏或者多余约束情况的出现,有问题的约束条件将直接在IB中得到错误或者警告。
三.快速领会VFL语言Demo代码:
demo代码如下:
/* Initial views setup */
- (void)setupViews
{
self.redView = [UIView new];
self.redView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
self.redView.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:0.95 green:0.47 blue:0.48 alpha:1.0];
self.yellowView = [UIView new];
self.yellowView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
self.yellowView.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:1.00 green:0.83 blue:0.58 alpha:1.0];
[self.view addSubview:self.redView];
[self.view addSubview:self.yellowView];
}
/*
Hey Devs... the code in the next functions has to be intended for tutorial purposes only.
I have created work-alone examples that contain a lot of code duplication... not a good practice but way easier to explain :P
*/
/* EXAMPLE 1 */
- (void)example_1
{
// 1. Create a dictionary of views
NSDictionary *viewsDictionary = @{@"redView":self.redView};
// 2. Define the redView Size
NSArray *constraint_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:[redView(100)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *constraint_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:[redView(100)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.redView addConstraints:constraint_H];
[self.redView addConstraints:constraint_V];
// 3. Define the redView Position
NSArray *constraint_POS_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:|-30-[redView]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *constraint_POS_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:|-20-[redView]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
// 3.B ...and try to change the visual format string
//NSArray *constraint_POS_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:[redView]-30-|" options:0 metrics:nil views:viewsDictionary];
//NSArray *constraint_POS_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:|-[redView]" options:0 metrics:nil views:viewsDictionary];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_H];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_V];
}
/* EXAMPLE 2 */
- (void)example_2
{
// 1. Create a dictionary of views
NSDictionary *viewsDictionary = @{@"redView":self.redView, @"yellowView":self.yellowView};
// 2. Define the views Sizes
NSArray *red_constraint_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:[redView(100)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *red_constraint_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:[redView(100)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.redView addConstraints:red_constraint_H];
[self.redView addConstraints:red_constraint_V];
NSArray *yellow_constraint_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:[yellowView(200)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *yellow_constraint_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:[yellowView(100)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.yellowView addConstraints:yellow_constraint_H];
[self.yellowView addConstraints:yellow_constraint_V];
// 3. Define the views Positions
NSArray *constraint_POS_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:|-30-[redView]-40-[yellowView]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *constraint_POS_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:|-20-[redView]-10-[yellowView]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_V];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_H];
}
/* EXAMPLE 3 */
- (void)example_3
{
// 1. Create a dictionary of views
NSDictionary *viewsDictionary = @{@"redView":self.redView, @"yellowView":self.yellowView};
// 2. Define the views Sizes
NSArray *red_constraint_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:[redView(100)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *red_constraint_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:[redView(100)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.redView addConstraints:red_constraint_H];
[self.redView addConstraints:red_constraint_V];
NSArray *yellow_constraint_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:[yellowView(150)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *yellow_constraint_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:[yellowView(100)]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.yellowView addConstraints:yellow_constraint_H];
[self.yellowView addConstraints:yellow_constraint_V];
// 3. Define the views Positions using options
NSArray *constraint_POS_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:|-120-[redView]"
options:0
metrics:nil
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *constraint_POS = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:|-20-[redView]-10-[yellowView]"
options:NSLayoutFormatAlignAllTop
metrics:nil views:viewsDictionary];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_V];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS];
}
/* EXAMPLE 4 */
- (void)example_4
{
// 1. Create a dictionary of views and metrics
NSDictionary *viewsDictionary = @{@"redView":self.redView, @"yellowView":self.yellowView};
NSDictionary *metrics = @{@"redWidth": @100,
@"redHeight": @100,
@"yellowWidth": @100,
@"yellowHeight": @150,
@"topMargin": @120,
@"leftMargin": @20,
@"viewSpacing":@10
};
// 2. Define the views Sizes
NSArray *red_constraint_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:[redView(redHeight)]"
options:0
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *red_constraint_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:[redView(redWidth)]"
options:0
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.redView addConstraints:red_constraint_H];
[self.redView addConstraints:red_constraint_V];
NSArray *yellow_constraint_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:[yellowView(yellowHeight)]"
options:0
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *yellow_constraint_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:[yellowView(yellowWidth)]"
options:0
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.yellowView addConstraints:yellow_constraint_H];
[self.yellowView addConstraints:yellow_constraint_V];
// 3. Define the views Positions
NSArray *constraint_POS_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:|-topMargin-[redView]"
options:0
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *constraint_POS = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:|-leftMargin-[redView]-viewSpacing-[yellowView]"
options:NSLayoutFormatAlignAllTop
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_V];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS];
}
/* EXAMPLE 5 */
- (void)example_5
{
// 1. Create a dictionary of views and metrics
NSDictionary *viewsDictionary = @{@"redView":self.redView};
NSDictionary *metrics = @{@"vSpacing":@30, @"hSpacing":@10};
// 2. Define the view Position and automatically the Size
NSArray *constraint_POS_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:|-vSpacing-[redView]-vSpacing-|"
options:0
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *constraint_POS_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:|-hSpacing-[redView]-hSpacing-|"
options:0
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_V];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_H];
}
/* EXAMPLE 6 */
- (void)example_6
{
// 1. Create a dictionary of views
NSDictionary *viewsDictionary = @{@"redView": self.redView, @"yellowView": self.yellowView};
NSDictionary *metrics = @{@"vSpacing":@30, @"hSpacing":@10};
// 2. Define the view Position and automatically the Size (for the redView)
NSArray *constraint_POS_V = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"V:|-vSpacing-[redView]-vSpacing-|"
options:0
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
NSArray *constraint_POS_H = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintsWithVisualFormat:@"H:|-hSpacing-[redView]-hSpacing-|"
options:0
metrics:metrics
views:viewsDictionary];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_V];
[self.view addConstraints:constraint_POS_H];
// 3. Define sizes thanks to relations with another view (yellowView in relation with redView)
[self.view addConstraint:[NSLayoutConstraint
constraintWithItem:self.yellowView
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeWidth
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:self.redView
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeWidth
multiplier:0.5
constant:0.0]];
[self.view addConstraint:[NSLayoutConstraint
constraintWithItem:self.yellowView
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeHeight
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:self.redView
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeHeight
multiplier:0.5
constant:0.0]];
// 4. Define position thanks to relations with another view (yellowView in relation with redView)
[self.view addConstraint:[NSLayoutConstraint
constraintWithItem:self.yellowView
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeCenterX
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:self.redView
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeCenterX
multiplier:1.0
constant:0.0]];
[self.view addConstraint:[NSLayoutConstraint
constraintWithItem:self.yellowView
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeCenterY
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:self.redView
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeCenterY
multiplier:1.0
constant:0.0]];
}
