持续集成之道:在你的开源项目中使用Travis CI
自从接触并践行了敏捷的一些实践之后,便深深的喜欢上了敏捷。尤其是测试自动化和持续集成这两个实践,可以显著的提高软件的质量和集成效率,实时检测项目健康度,使团队成员对项目保持充足的信心。
但是对于个人项目而言,虽然测试自动化好实现,但是要实现持续集成还是稍有难度。因为持续集成需要搭建一个集成服务器,并建立某种反馈机制。而大多数人来说并没有自己的独立服务器,并且配置也极为繁琐。
不过不用怕,现在已经进入了云时代。 Travis CI为我们提供了免费的集成服务器,让我们省却了自己搭建集成服务器的烦恼。
Travis CI的官网介绍是: A hosted continuous integration service for the open source community. 表明它主要是给开源社区提供持续集成服务。其与github这个全球最火爆的代码托管网站高度集成,可以很方便的为github中的项目建立持续集成服务。
它不仅支持多种语言,而且支持同时在多个运行环境中运行build,能全方位的测试你的程序。
下面就介绍下如何将Travis CI与自己在github上的某个repository集成。(这里以我自己的repository https://github.com/huangbowen521/SpringMessageSpike 为例。 )
首先,使Travis CI通过github OAuth认证。
点击https://travis-ci.org/右上角的Sign in with GitHub按钮,输入自己的github账号和密码,并允许Travis CI的认证。
然后,激活GitHub Service Hook。
GitHub给用户提供了一个Service Hook接口,只要用户对host在github上的repository作用了一些action(比如push,pull),就会触发相应的Service Hook。而Travis CI正是基于这个原理来trigger你的build。当你发起一个push操作时,就会trigger Travis CI的服务。
设置方法是访问Travis CI的profile,选择相应的repository打开Service Hook开关。
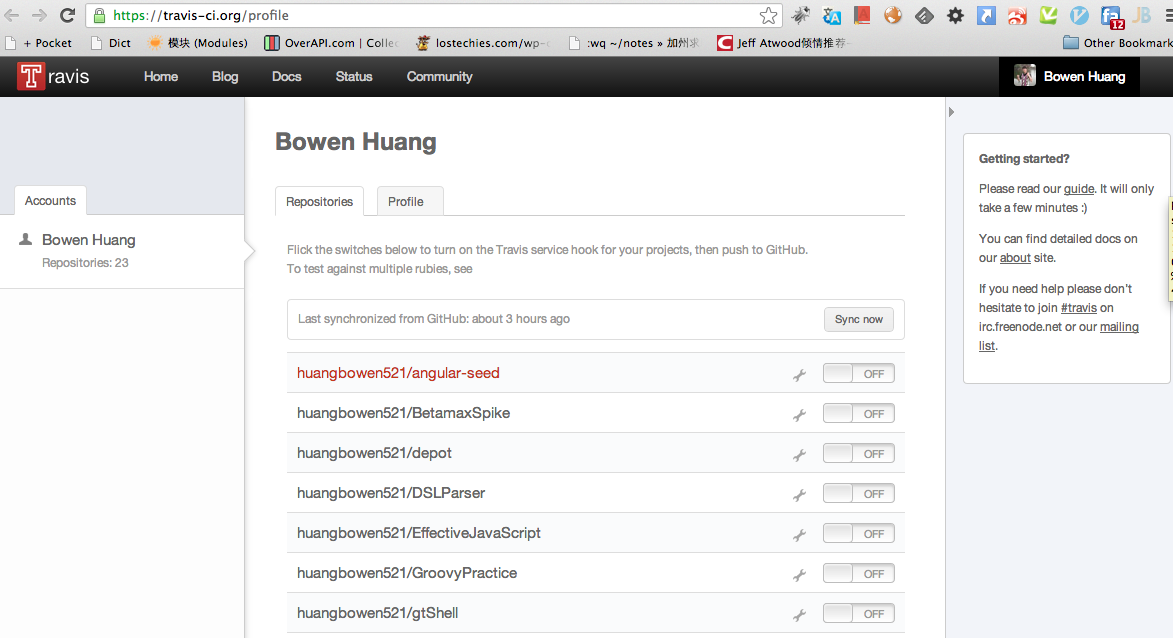
然后登陆你的github,访问具体的repository的Service Hook页面,确保设置了Travis CI Hook的github name和travis token。

最后,给repository配置.travis.yml文件。该文件需要放置在repository的跟目录下。
.travis.yml文件是一个相当重要的文件,里面需要配置你所使用的语言、运行环境、构建工具、构建脚本、通知方式等。最重要的是设置语言,其它的都有相应的默认值。
这是为我的SpringMessageSpike设置的.travis.yml文件。由于我的项目中使用了maven作为构建工具,而Travis CI对java语言设置的默认构建工具就是maven,所以无需在文件中显式指定。
.travis.yml
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
你可以使用一个travis-lint来检查你的yml文件是否是有效的。他是ruby写的一个gem,需要ruby的运行环境。安装方式是在terminal下gem install travis-lint。你只需要在你的repository根目录下运行travis-lint即可进行检查。
想要更进一步的关于.travis.yml的配置请参见:http://about.travis-ci.org/docs/user/build-configuration/
只要这三步就完成了配置。现在发起一个push就可以trigger你在Travis CI的build。 这时候登陆Travis CI可以看到你的Build的状态和日志。

你可以在respository的README.md文件中加入build状态图标。方法是在在该文件中加入 [](https://travis-ci.org/[YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME]/[YOUR_PROJECT_NAME])即可。

总体来说Travis CI是一个轻量级、可高度定制化的免费的持续集成服务。但我觉得还是有几个缺点:
-
运行build需要大量的准备,耗时较长。
-
作为免费的服务,不支持build时间超过20分钟的项目。
-
主站访问速度略慢。
Table中对tr的上下拖拽移动
前天公司门户网站中新闻发布后写好的新闻想实现手动上下换位置。在网上找了一个专门为table写的js,有源码,可以自己改样式,动态效果。
正文开始:
首先需要引用一个js:
 jquery
jqueryjQuery.tableDnD = { /** Keep hold of the current table being dragged */ currentTable : null, /** Keep hold of the current drag object if any */ dragObject: null, /** The current mouse offset */ mouseOffset: null, /** Remember the old value of Y so that we don't do too much processing */ oldY: 0, /** Actually build the structure实际构建结构 */ build: function(options) { // Set up the defaults if any this.each(function() { // This is bound to each matching table, set up the defaults and override with user options这是绑定到每个匹配表,设置默认值,并与用户选项覆盖 this.tableDnDConfig = jQuery.extend({ onDragStyle: null, onDropStyle: null, // Add in the default class for whileDragging onDragClass: "tDnD_whileDrag", onDrop: null, onDragStart: null, scrollAmount: 5, serializeRegexp: /[^\-]*$/, // The regular expression to use to trim row IDs serializeParamName: null, // If you want to specify another parameter name instead of the table ID dragHandle: null // If you give the name of a class here, then only Cells with this class will be draggable }, options || {}); // Now make the rows draggable jQuery.tableDnD.makeDraggable(this); }); // Now we need to capture the mouse up and mouse move event // We can use bind so that we don't interfere with other event handlers jQuery(document) .bind('mousemove', jQuery.tableDnD.mousemove) .bind('mouseup', jQuery.tableDnD.mouseup); // Don't break the chain return this; }, /** This function makes all the rows on the table draggable apart from those marked as "NoDrag" */ makeDraggable: function(table) { var config = table.tableDnDConfig; if (table.tableDnDConfig.dragHandle) { // We only need to add the event to the specified cells var cells = jQuery("td."+table.tableDnDConfig.dragHandle, table); cells.each(function() { // The cell is bound to "this" jQuery(this).mousedown(function(ev) { jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject = this.parentNode; jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable = table; jQuery.tableDnD.mouseOffset = jQuery.tableDnD.getMouseOffset(this, ev); if (config.onDragStart) { // Call the onDrop method if there is one config.onDragStart(table, this); } return false; }); }) } else { // For backwards compatibility, we add the event to the whole row var rows = jQuery("tr", table); // get all the rows as a wrapped set rows.each(function() { // Iterate through each row, the row is bound to "this" var row = jQuery(this); if (! row.hasClass("nodrag")) { row.mousedown(function(ev) { if (ev.target.tagName == "TD") { jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject = this; jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable = table; jQuery.tableDnD.mouseOffset = jQuery.tableDnD.getMouseOffset(this, ev); if (config.onDragStart) { // Call the onDrop method if there is one config.onDragStart(table, this); } return false; } }).css("cursor", "move"); // Store the tableDnD object } }); } }, updateTables: function() { this.each(function() { // this is now bound to each matching table if (this.tableDnDConfig) { jQuery.tableDnD.makeDraggable(this); } }) }, /** Get the mouse coordinates from the event (allowing for browser differences) */ mouseCoords: function(ev){ if(ev.pageX || ev.pageY){ return {x:ev.pageX, y:ev.pageY}; } return { x:ev.clientX + document.body.scrollLeft - document.body.clientLeft, y:ev.clientY + document.body.scrollTop - document.body.clientTop }; }, /** Given a target element and a mouse event, get the mouse offset from that element. To do this we need the element's position and the mouse position */ getMouseOffset: function(target, ev) { ev = ev || window.event; var docPos = this.getPosition(target); var mousePos = this.mouseCoords(ev); return {x:mousePos.x - docPos.x, y:mousePos.y - docPos.y}; }, /** Get the position of an element by going up the DOM tree and adding up all the offsets */ getPosition: function(e){ var left = 0; var top = 0; /** Safari fix -- thanks to Luis Chato for this! */ if (e.offsetHeight == 0) { /** Safari 2 doesn't correctly grab the offsetTop of a table row this is detailed here: http://jacob.peargrove.com/blog/2006/technical/table-row-offsettop-bug-in-safari/ the solution is likewise noted there, grab the offset of a table cell in the row - the firstChild. note that firefox will return a text node as a first child, so designing a more thorough solution may need to take that into account, for now this seems to work in firefox, safari, ie */ e = e.firstChild; // a table cell } while (e.offsetParent){ left += e.offsetLeft; top += e.offsetTop; e = e.offsetParent; } left += e.offsetLeft; top += e.offsetTop; return {x:left, y:top}; }, mousemove: function(ev) { if (jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject == null) { return; } var dragObj = jQuery(jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject); var config = jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable.tableDnDConfig; var mousePos = jQuery.tableDnD.mouseCoords(ev); var y = mousePos.y - jQuery.tableDnD.mouseOffset.y; //auto scroll the window var yOffset = window.pageYOffset; if (document.all) { // Windows version //yOffset=document.body.scrollTop; if (typeof document.compatMode != 'undefined' && document.compatMode != 'BackCompat') { yOffset = document.documentElement.scrollTop; } else if (typeof document.body != 'undefined') { yOffset=document.body.scrollTop; } } if (mousePos.y-yOffset < config.scrollAmount) { window.scrollBy(0, -config.scrollAmount); } else { var windowHeight = window.innerHeight ? window.innerHeight : document.documentElement.clientHeight ? document.documentElement.clientHeight : document.body.clientHeight; if (windowHeight-(mousePos.y-yOffset) < config.scrollAmount) { window.scrollBy(0, config.scrollAmount); } } if (y != jQuery.tableDnD.oldY) { // work out if we're going up or down... var movingDown = y > jQuery.tableDnD.oldY; // update the old value jQuery.tableDnD.oldY = y; // update the style to show we're dragging if (config.onDragClass) { dragObj.addClass(config.onDragClass); } else { dragObj.css(config.onDragStyle); } // If we're over a row then move the dragged row to there so that the user sees the // effect dynamically var currentRow = jQuery.tableDnD.findDropTargetRow(dragObj, y); if (currentRow) { // TODO worry about what happens when there are multiple TBODIES if (movingDown && jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject != currentRow) { jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject.parentNode.insertBefore(jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject, currentRow.nextSibling); } else if (! movingDown && jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject != currentRow) { jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject.parentNode.insertBefore(jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject, currentRow); } } } return false; }, /** We're only worried about the y position really, because we can only move rows up and down */ findDropTargetRow: function(draggedRow, y) { var rows = jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable.rows; for (var i=0; i<rows.length; i++) { var row = rows[i]; var rowY = this.getPosition(row).y; var rowHeight = parseInt(row.offsetHeight)/2; if (row.offsetHeight == 0) { rowY = this.getPosition(row.firstChild).y; rowHeight = parseInt(row.firstChild.offsetHeight)/2; } // Because we always have to insert before, we need to offset the height a bit if ((y > rowY - rowHeight) && (y < (rowY + rowHeight))) { // that's the row we're over // If it's the same as the current row, ignore it if (row == draggedRow) {return null;} var config = jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable.tableDnDConfig; if (config.onAllowDrop) { if (config.onAllowDrop(draggedRow, row)) { return row; } else { return null; } } else { // If a row has nodrop class, then don't allow dropping (inspired by John Tarr and Famic) var nodrop = jQuery(row).hasClass("nodrop"); if (! nodrop) { return row; } else { return null; } } return row; } } return null; }, mouseup: function(e) { if (jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable && jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject) { var droppedRow = jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject; var config = jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable.tableDnDConfig; // If we have a dragObject, then we need to release it, // The row will already have been moved to the right place so we just reset stuff if (config.onDragClass) { jQuery(droppedRow).removeClass(config.onDragClass); } else { jQuery(droppedRow).css(config.onDropStyle); } jQuery.tableDnD.dragObject = null; if (config.onDrop) { // Call the onDrop method if there is one config.onDrop(jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable, droppedRow); } jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable = null; // let go of the table too } }, serialize: function() { if (jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable) { return jQuery.tableDnD.serializeTable(jQuery.tableDnD.currentTable); } else { return "Error: No Table id set, you need to set an id on your table and every row"; } }, serializeTable: function(table) { var result = ""; var tableId = table.id; var rows = table.rows; for (var i=0; i<rows.length; i++) { if (result.length > 0) result += "&"; var rowId = rows[i].id; if (rowId && rowId && table.tableDnDConfig && table.tableDnDConfig.serializeRegexp) { rowId = rowId.match(table.tableDnDConfig.serializeRegexp)[0]; } result += tableId + '[]=' + rowId; } return result; }, serializeTables: function() { var result = ""; this.each(function() { // this is now bound to each matching table result += jQuery.tableDnD.serializeTable(this); }); return result; } } jQuery.fn.extend( { tableDnD : jQuery.tableDnD.build, tableDnDUpdate : jQuery.tableDnD.updateTables, tableDnDSerialize: jQuery.tableDnD.serializeTables } );
里面的
 View Code
View Codethis.each(function() { // This is bound to each matching table, set up the defaults and override with user options这是绑定到每个匹配表,设置默认值,并与用户选项覆盖 this.tableDnDConfig = jQuery.extend({ onDragStyle: null, onDropStyle: null, // Add in the default class for whileDragging onDragClass: "tDnD_whileDrag", onDrop: null, onDragStart: null, scrollAmount: 5, serializeRegexp: /[^\-]*$/, // The regular expression to use to trim row IDs serializeParamName: null, // If you want to specify another parameter name instead of the table ID dragHandle: null // If you give the name of a class here, then only Cells with this class will be draggable }, options || {}); // Now make the rows draggable jQuery.tableDnD.makeDraggable(this); });
是为控制拖拽样式,拖拽的元素的控制,里面还有好多自定义模式的自己可以看看发觉下。
源码下载:Table拖拽
