实验报告
实验目的
理解抽象类与接口的使用;
了解包的作用,掌握包的设计方法。
实验要求
掌握使用抽象类的方法。
掌握使用系统接口的技术和创建自定义接口的方法。
了解 Java 系统包的结构。
掌握创建自定义包的方法。
实验内容
(一)抽象类的使用
设计一个类层次,定义一个抽象类--形状,其中包括有求形状的面积的抽象方法。 继承该抽象类定义三角型、矩形、圆。 分别创建一个三角形、矩形、圆存对象,将各类图形的面积输出。
注:三角形面积s=sqrt(p(p-a)(p-b)*(p-c)) 其中,a,b,c为三条边,p=(a+b+c)/2
2.编程技巧
(1) 抽象类定义的方法在具体类要实现;
(2) 使用抽象类的引用变量可引用子类的对象;
(3) 通过父类引用子类对象,通过该引用访问对象方法时实际用的是子类的方法。可将所有对象存入到父类定义的数组中。
(二)使用接口技术
1定义接口Shape,其中包括一个方法size(),设计“直线”、“圆”、类实现Shape接口。分别创建一个“直线”、“圆”对象,将各类图形的大小输出。
编程技巧
(1) 接口中定义的方法在实现接口的具体类中要重写实现;
(2) 利用接口类型的变量可引用实现该接口的类创建的对象。
抽象类的使用
代码
抽象类
package abstractclass;
public abstract class Shape {
private String shapename;
public String getShapename() {
return shapename;
}
public void setShapename(String shapename) {
this.shapename = shapename;
}
public Shape() {
}
public Shape(String shapename) {
this.shapename = shapename;
}
public void printArea() {
System.out.println(this.getshapeArea());
}
public abstract String getshapeArea();
}
三角形
package abstractclass;
public class Triangle extends Shape {
private float lengtha;
private float lengthb;
private float lengthc;
private float p;
private double area;
public float getLengtha() {
return lengtha;
}
public void setLengtha(float lengtha) {
this.lengtha = lengtha;
}
public float getLengthb() {
return lengthb;
}
public void setLengthb(float lengthb) {
this.lengthb = lengthb;
}
public float getLengthc() {
return lengthc;
}
public void setLengthc(float lengthc) {
this.lengthc = lengthc;
}
public float getP() {
return p;
}
public void setP(float p) {
this.p = p;
}
public double getArea() {
return area;
}
public void setArea(double area) {
this.area = area;
}
public Triangle(String shapename,float lengtha,float lengthb,float lengthc) {
super(shapename);
this.lengtha = lengtha;
this.lengthb = lengthb;
this.lengthc = lengthc;
}
public String getshapeArea() {
if(this.lengtha !=0 && this.lengthb != 0 && lengthc !=0)
{
this.p = (this.lengtha + this.lengthb + this.lengthc)/2;
this.area = Math.sqrt(p*(p-lengtha)*(p-lengthb)*(p-lengthc));
if(this.area == 0)
{
return "边长值不合法";
}
else
return super.getShapename()+"的面积是:"+this.area;
}
return super.getShapename()+"的面积是:"+ 0;
}
}
矩形
package abstractclass;
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
private float width;
private float heigth;
private double area;
public float getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(float width) {
this.width = width;
}
public float getHeigth() {
return heigth;
}
public void setHeigth(float heigth) {
this.heigth = heigth;
}
public double getArea() {
return area;
}
public void setArea(double area) {
this.area = area;
}
public Rectangle(String shapename,float heigth,float width) {
super(shapename);
this.heigth = heigth;
this.width = width;
}
@Override
public String getshapeArea() {
if(this.width < 0 || this.heigth < 0)
return "边长值不能为负";
this.area = this.width * this.heigth;
return super.getShapename()+"的面积是:"+this.area;
}
}
圆形
package abstractclass;
public class Circle extends Shape {
private float radius;
private double area;
public float getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(float radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getArea() {
return area;
}
public void setArea(double area) {
this.area = area;
}
public Circle(String shapename,float radius) {
super(shapename);
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public String getshapeArea() {
if(this.radius < 0)
return "半径值不能为负";
this.area = Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2);
return super.getShapename()+"的面积是:"+this.area;
}
}
测试
package abstractclass;
public class test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
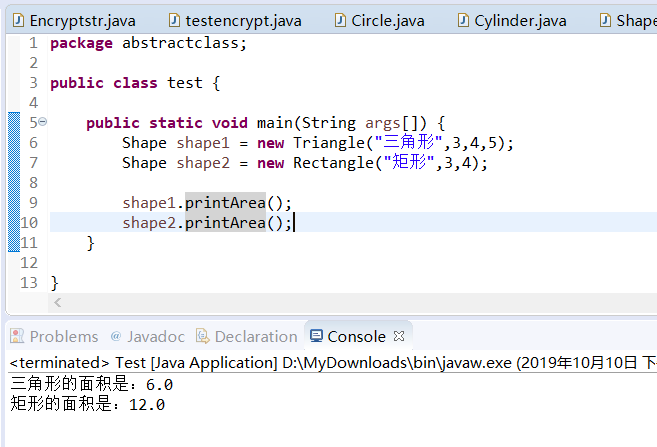
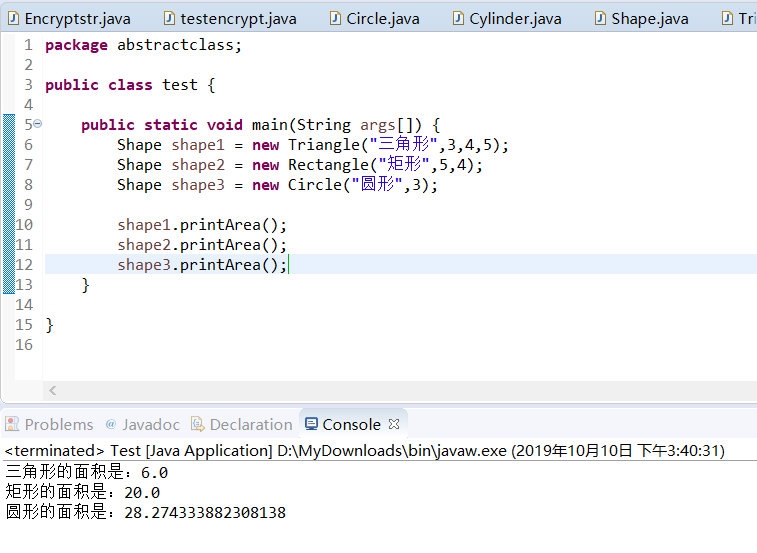
Shape shape1 = new Triangle("三角形",3,4,5);
Shape shape2 = new Rectangle("矩形",5,4);
Shape shape3 = new Circle("圆形",3);
shape1.printArea();
shape2.printArea();
shape3.printArea();
}
}
遇到的问题
1.输出三角形面积的值不正确;
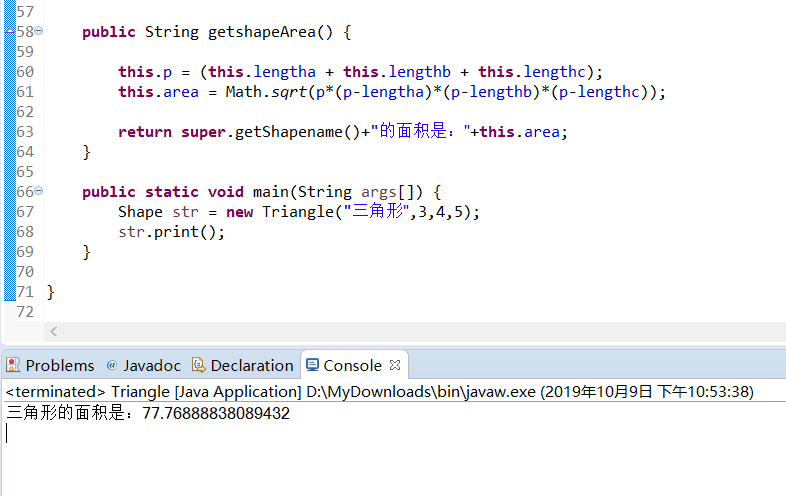
解决办法:在计算p的值时没有除以2。
运行结果

使用接口技术
代码
接口
package interfaceclass;
public interface Shape {
public void size();
}
方法
package interfaceclass;
public class Methods {
public static void figure(Shape shape) {
shape.size();
}
}
直线
package interfaceclass;
public class Beeline implements Shape {
private float x1;
private float x2;
private float y1;
private float y2;
public float getX1() {
return x1;
}
public void setX1(float x1) {
this.x1 = x1;
}
public float getX2() {
return x2;
}
public void setX2(float x2) {
this.x2 = x2;
}
public float getY1() {
return y1;
}
public void setY1(float y1) {
this.y1 = y1;
}
public float getY2() {
return y2;
}
public void setY2(float y2) {
this.y2 = y2;
}
public Beeline(float x1,float y1,float x2,float y2) {
this.x1 = x1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y1 = y1;
this.y2 = y2;
}
@Override
public void size() {
System.out.println("直线长为:"+ Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.x1-this.x2,2)+Math.pow(this.y1-this.y2, 2)));
}
}
圆类
package interfaceclass;
public class Circle implements Shape {
private float radius;
public float getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(float radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public Circle(float radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void size() {
System.out.println("圆形面积是:"+ Math.PI * Math.pow(this.radius,2));
}
}
测试
package interfaceclass;
public class test {
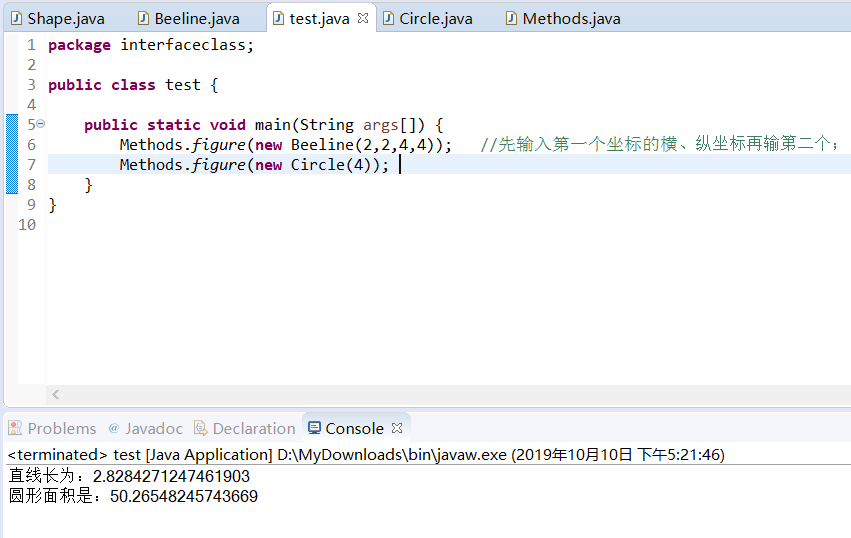
public static void main(String args[]) {
Methods.figure(new Beeline(2,2,4,4)); //先输入第一个坐标的横、纵坐标再输第二个;
Methods.figure(new Circle(4));
}
}
遇到的问题
一开始不理解编程技巧中的第2条是什么意思,用的方法和上面抽象类一样;
解决办法:看了书上的例题才知道是什么意思,然后改成了现在的版本。
运行结果
学习总结
抽象类与接口的应用
1.抽象类是在对象们有共同特性,也有不同时使用;共同属性在抽象类中赋值,不同点则创建抽象方法,在子类继承之后具体实现。
接口更多用于制定标准;接口中只有抽象方法,由子类实现接口之后具体实现,还要创建一个作用类似于“中转站”的类,在其中用前面创建的接口的类型的变量来应用具体的方法。
2.抽象类和接口都可以使用的话,优先使用接口,接口没有单继承的局限;
Object类
Object类主要讲了两个方法
toString():输出对象时调用该方法打印内容。
equals():Object类中的equals()方法默认是比较地址,返回值时boolean型,要比较内容的话,要在子类覆写。
一开始我其实很疑惑,此前我们学过的String类的equals()方法不是比较内容的吗?去网上查了后知道在Object类的equals方法的本质其实是和“==”一样的,都是比较两个对象引用是否指向同一个对象(即两个对象是否为同一对象)。String类继承Object类后,也继承了equals方法,但String类对equals方法进行了重写,改变了equals方法的比较形式。