委托的作用:太多了,没学会如何使用委托,就永远是一个菜鸡
委托
委托太常见了,能灵活运用可以使你在编程中游刃有余。
简单说它就是一个能把方法当参数传递的对象,而且还知道怎么调用这个方法,同时也是粒度更小的“接口”(约束了指向方法的签名)。
委托的简单使用
一个委托类型定义了该类型的实例能调用的一类方法,这些方法含有同样的返回类型和同样参数(类型和个数相同)。
委托和接口一样,可以定义在类的外部。
如下定义了一个委托类型 - Calculator: delegate int Calculator (int x);
此委托适用于任何有着int返回类型和一个int类型参数的方法,如:
static int Double (int x) { return x * 2; }
创建一个委托实例,将该此方法赋值给该委托实例:
Calculator c = new Calculator(Double); 也可以简写成: Calculator c = Double; 这个方法可以通过委托调用: int result = c(2); 下面是完整代码: delegate int Calculator(int x);class Program { static int Double(int x) { return x * 2; } static void Main(string[] args) { Calculator c = Double; int result = c(2); Console.Write(result); Console.ReadKey(); }}
用委托实现插件式编程
我们可以利用“委托是一个能把方法作为参数传递的对象”这一特点,来实现一种插件式编程。
例如,我们有一个Utility类,这个类实现一个通用方法(Calculate),用来执行任何有一个整型参数和整型返回值的方法。这样说有点抽象,下面来看一个例子:
delegate int Calculator(int x); class Program { static int Double(int x) { return x * 2; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[] values = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; Utility.Calculate(values, Double); foreach (int i in values) Console.Write(i + " "); // 2 4 6 8 Console.ReadKey(); } } class Utility { public static void Calculate(int[] values, Calculator c) { for (int i = 0; i < values.Length; i++) values[i] = c(values[i]); } }
这个例子中的Utility是固定不变的,程序实现了整数的Double功能。我们可以把这个Double方法看作是一个插件,如果将来还要实现诸如求平方、求立方的计算,我们只需向程序中不断添加插件就可以了。
如果Double方法是临时的,只调用一次,若在整个程序中不会有第二次调用,那么我们可以在Main方法中更简洁更灵活的使用这种插件式编程,无需先定义方法,使用λ表达式即可,如:
...Utility.Calculate(values, x => x * 2);...
以后我们会经常写这样的代码。
多播委托
所有的委托实例都有多播的功能。所谓多播,就像一群程序员在瞬聘网填好了求职意向后,某天有个公司发布了一个和这些程序员求职意向刚好相匹配的工作,然后这些求职者都被通知了 - “有一份好工作招人啦,你们可以直接申请去上班了!”。
也就是说,一个委托实例不仅可以指向一个方法,还可以指向多个方法。例如:
MyDelegate d = MyMethod1;// “+=” 用来添加,同理“-=”用来移除。d += MyMethod2;// d -= MyMethod2
调用时,按照方法被添加的顺序依次执行。注意,对于委托,+= 和 -= 对null是不会报错的,如:
MyDelegate d;d += MyMethod1;// 相当于MyDelegate d = MyMethod1;
为了更好的理解多播在实际开发中的应用,我用模拟瞬聘网的职位匹配小工具来做示例。在职位匹配过程中会有一段处理时间,所以在执行匹配的时候要能看到执行的进度,而且还要把执行的进度和执行情况写到日志文件中。在处理完一个步骤时,将分别执行两个方法来显示和记录执行进度。
我们先定义一个委托(ProgressReporter),然后定义一个匹配方法(Match)来执行该委托中的所有方法。如下:
public delegate void ProgressReporter(int percentComplete); public class Utility { public static void Match(ProgressReporter p) { if (p != null) { for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) { p(i * 10); System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(100); } } } }
然后我们需要两个监视进度的方法,一个把进度写到Console,另一个把进度写到文件。如下:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ProgressReporter p = WriteProgressToConsole; p += WriteProgressToFile; Utility.Match(p); Console.WriteLine("Done."); Console.ReadKey(); } static void WriteProgressToConsole(int percentComplete) { Console.WriteLine(percentComplete + "%"); } static void WriteProgressToFile(int percentComplete) { System.IO.File.AppendAllText("progress.txt", percentComplete + "%"); } }
运行结果:
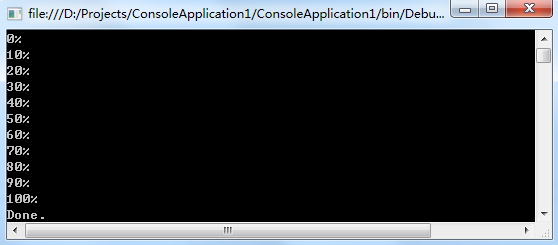
看到这里,是不是发现你已然更加爱上C#了。
静态方法和实例方法对于委托的区别
当一个类的实例的方法被赋给一个委托对象时,在上下文中不仅要维护这个方法,还要维护这个方法所在的实例。System.Delegate 类的Target属性指向的就是这个实例。举个例子:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { X x = new X(); ProgressReporter p = x.InstanceProgress; p(1); Console.WriteLine(p.Target == x); // True Console.WriteLine(p.Method); // Void InstanceProgress(Int32) } static void WriteProgressToConsole(int percentComplete) { Console.WriteLine(percentComplete + "%"); } static void WriteProgressToFile(int percentComplete) { System.IO.File.AppendAllText("progress.txt", percentComplete + "%"); } class X { public void InstanceProgress(int percentComplete) { } } }
但对于静态方法,System.Delegate 类的Target属性是Null,所以将静态方法赋值给委托时性能更优。
泛型委托
如果你知道泛型,那么就很容易理解泛型委托,说白了就是含有泛型参数的委托,例如:
public delegate T Calculator<T> (T arg);
我们可以把前面的例子改成泛型的例子,如下:
public delegate T Calculator<T>(T arg); class Program { static int Double(int x) { return x * 2; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[] values = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; Utility.Calculate(values, Double); foreach (int i in values) Console.Write(i + " "); // 2 4 6 8 Console.ReadKey(); } } class Utility { public static void Calculate<T>(T[] values, Calculator<T> c) { for (int i = 0; i < values.Length; i++) values[i] = c(values[i]); } }
Func 和 Action 委托
有了泛型委托,就有了一能适用于任何返回类型和任意参数(类型和合理的个数)的通用委托,Func 和 Action。如下所示(下面的in表示参数,out表示返回结果):
delegate TResult Func <out TResult> ();
delegate TResult Func <in T, out TResult> (T arg);delegate TResult Func <in T1, in T2, out TResult> (T1 arg1, T2 arg2);
有了这样的通用委托,我们上面的Calculator泛型委托就可以删掉了,示例就可以更简洁了:
public static void Calculate<T>(T[] values, Func<T,T> c) {
for (int i = 0; i < values.Length; i++)
values[i] = c(values[i]);
}
Func 和 Action 委托,除了ref参数和out参数,基本上能适用于任何泛型委托的场景,非常好用。
委托的兼容
1. 委托的类型兼容
delegate void D1();delegate void D2();...D1 d1 = Method1;D2 d2 = d1;
下面是被允许的:
D2 d2 = newD2 (d1);
对于具体相同的目标方法的委托是被视为相等的:
delegate void D();...D d1 = Method1;D d2 = Method1;Console.WriteLine (d1 == d2); // True
同理,对于多播委托,如果含有相同的方法和相同的顺序,也被视为相等。
2. 参数类型兼容
在OOP中,任何使用父类的地方均可以用子类代替,这个OOP思想对委托的参数同样有效。如:
delegate void StringAction(string s); class Program { static void Main() { StringAction sa = new StringAction(ActOnObject); sa("hello"); } static void ActOnObject(object o) { Console.WriteLine(o); // hello } }
3. 返回值类型兼容
道理和参数类型兼容一样:
delegate object ObjectRetriever();
class Program { static void Main() { ObjectRetriever o = new ObjectRetriever(RetriveString); object result = o(); Console.WriteLine(result); // hello } static string RetriveString() { return "hello"; } } }
事件
当我们使用委托场景时,我们很希望有这样两个角色出现:广播者和订阅者。我们需要这两个角色来实现订阅和广播这种很常见的场景。
广播者这个角色应该有这样的功能:包括一个委托字段,通过调用委托来发出广播。而订阅者应该有这样的功能:可以通过调用 += 和 -= 来决定何时开始或停止订阅。
事件就是描述这种场景模式的一个词。事件是委托的一个子集,为了满足“广播/订阅”模式的需求而生。
事件的基本使用
声明一个事件很简单,只需在声明一个委托对象时加上event关键字就行。如下:
public delegate void PriceChangedHandler(decimal oldPrice, decimal newPrice); public class IPhone6 { public event PriceChangedHandler PriceChanged; }
事件的使用和委托完全一样,只是多了些约束。下面是一个简单的事件使用例子:
public delegate void PriceChangedHandler(decimal oldPrice, decimal newPrice); public class IPhone6 { public event PriceChangedHandler PriceChanged; } 事件的使用和委托完全一样,只是多了些约束。下面是一个简单的事件使用例子: public delegate void PriceChangedHandler(decimal oldPrice, decimal newPrice); public class IPhone6 { decimal price; public event PriceChangedHandler PriceChanged; public decimal Price { get { return price; } set { if (price == value) return; decimal oldPrice = price; price = value; // 如果调用列表不为空,则触发。 if (PriceChanged != null) PriceChanged(oldPrice, price); } } } class Program { static void Main() { IPhone6 iphone6 = new IPhone6() { Price = 5288 }; // 订阅事件 iphone6.PriceChanged += iphone6_PriceChanged; // 调整价格(事件发生) iphone6.Price = 3999; Console.ReadKey(); } static void iphone6_PriceChanged(decimal oldPrice, decimal price) { Console.WriteLine("年终大促销,iPhone 6 只卖 " + price + " 元, 原价 " + oldPrice + " 元,快来抢!"); } }
运行结果:
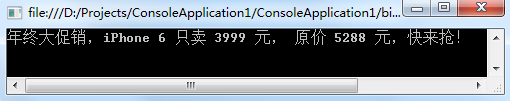
有人可能会问,如果把上面的event关键字拿掉,结果不是一样的吗,到底有何不同?
没错可以用事件的地方就一定可以用委托代替。
但事件有一系列规则和约束用以保证程序的安全可控,事件只有 += 和 -= 操作,这样订阅者只能有订阅或取消订阅操作,没有权限执行其它操作。如果是委托,那么订阅者就可以使用 = 来对委托对象重新赋值(其它订阅者全部被取消订阅),甚至将其设置为null,甚至订阅者还可以直接调用委托,这些都是很危险的操作,广播者就失去了独享控制权。
事件保证了程序的安全性和健壮性。
事件的标准模式
.NET 框架为事件编程定义了一个标准模式。设定这个标准是为了让.NET框架和用户代码保持一致。System.EventArgs是标准模式的核心,它是一个没有任何成员,用于传递事件参数的基类。
按照标准模式,我们对于上面的iPhone6示例进行重写。首先定义EventArgs:
public class PriceChangedEventArgs : EventArgs { public readonly decimal OldPrice; public readonly decimal NewPrice; public PriceChangedEventArgs(decimal oldPrice, decimal newPrice) { OldPrice = oldPrice; NewPrice = newPrice; } }
然后为事件定义委托,必须满足以下条件:
必须是 void 返回类型;
必须有两个参数,且第一个是object类型,第二个是EventArgs类型(的子类);
它的名称必须以EventHandler结尾。
由于考虑到每个事件都要定义自己的委托很麻烦,
.NET 框架为我们预定义好一个通用委托System.EventHandler<TEventArgs>:
public delegate void EventHandler<TEventArgs> (object source, TEventArgs e) where TEventArgs : EventArgs;
如果不使用框架的EventHandler<TEventArgs>,我们需要自己定义一个:
public delegate void PriceChangedEventHandler (object sender, PriceChangedEventArgs e);
如果不需要参数,可以直接使用EventHandler(不需要<TEventArgs>)。有了EventHandler<TEventArgs>,我们就可以这样定义示例中的事件:
public class IPhone6 { ... public event EventHandler<PriceChangedEventArgs> PriceChanged; ...}
最后,事件标准模式还需要写一个受保护的虚方法来触发事件,这个方法必须以On为前缀,加上事件名(PriceChanged),还要接受一个EventArgs参数,如下:
public class IPhone6 { ... public event EventHandler<PriceChangedEventArgs> PriceChanged; protected virtual void OnPriceChanged(PriceChangedEventArgs e) { if (PriceChanged != null) PriceChanged(this, e); } ... }
下面给出完整示例:
public class PriceChangedEventArgs : System.EventArgs { public readonly decimal OldPrice; public readonly decimal NewPrice; public PriceChangedEventArgs(decimal oldPrice, decimal newPrice) { OldPrice = oldPrice; NewPrice = newPrice; } } public class IPhone6 { decimal price; public event EventHandler<PriceChangedEventArgs> PriceChanged; protected virtual void OnPriceChanged(PriceChangedEventArgs e) { if (PriceChanged != null) PriceChanged(this, e); } public decimal Price { get { return price; } set { if (price == value) return; decimal oldPrice = price; price = value; // 如果调用列表不为空,则触发。 if (PriceChanged != null) OnPriceChanged(new PriceChangedEventArgs(oldPrice, price)); } } } class Program { static void Main() { IPhone6 iphone6 = new IPhone6() { Price = 5288M }; // 订阅事件 iphone6.PriceChanged +=iphone6_PriceChanged; // 调整价格(事件发生) iphone6.Price = 3999; Console.ReadKey(); } static void iphone6_PriceChanged(object sender, PriceChangedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("年终大促销,iPhone 6 只卖 " + e.NewPrice + " 元, 原价 " + e.OldPrice + " 元,快来抢!"); } }
public class PriceChangedEventArgs : System.EventArgs { public readonly decimal OldPrice; public readonly decimal NewPrice; public PriceChangedEventArgs(decimal oldPrice, decimal newPrice) { OldPrice = oldPrice; NewPrice = newPrice; } } public class IPhone6 { decimal price; public event EventHandler<PriceChangedEventArgs> PriceChanged; protected virtual void OnPriceChanged(PriceChangedEventArgs e) { if (PriceChanged != null) PriceChanged(this, e); } public decimal Price { get { return price; } set { if (price == value) return; decimal oldPrice = price; price = value; // 如果调用列表不为空,则触发。 if (PriceChanged != null) OnPriceChanged(new PriceChangedEventArgs(oldPrice, price)); } } } class Program { static void Main() { IPhone6 iphone6 = new IPhone6() { Price = 5288M }; // 订阅事件 iphone6.PriceChanged +=iphone6_PriceChanged; // 调整价格(事件发生) iphone6.Price = 3999; Console.ReadKey(); } static void iphone6_PriceChanged(object sender, PriceChangedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("年终大促销,iPhone 6 只卖 " + e.NewPrice + " 元, 原价 " + e.OldPrice + " 元,快来抢!"); } }
运行结果:
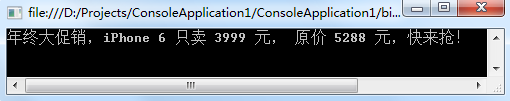
一般现在常见的 带参数func的和不带参数Action的事件定义
public event Func<string> updateEvent;
using ObserverPattern.Observer; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ObserverPattern.Subject { public class pushSystem { public event Func<string> updateEvent; //调用委托事件 public void update(string name) { if (updateEvent != null) { foreach (Func<string> item in updateEvent.GetInvocationList()) { AsyncCallback asyncCallback = a => { Console.WriteLine("BeginInfoceke,每次都会开启一个线程来执行"); Console.WriteLine("接收 值:A" + a.IsCompleted); }; item.BeginInvoke(asyncCallback, "传值 A"); IAsyncResult asyncResult = null;//获取 //得到返回值 var returnvale = item.EndInvoke(asyncResult); } updateEvent.Invoke(); //BeginInvoke } } public void aaaa() { pushSystem push = new pushSystem(); push.updateEvent += () => new KA().returnstring("ID"); push.update("name"); } public class KA { public string updatePush(string id) { Console.WriteLine($"KA的线程{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); var times = DateTime.Now.ToString($"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff"); try { //if (id == "ID3") //{ // string a = null; // a.ToString(); //} Console.WriteLine($"开始KA{id}:{times}"); return $"返回调用KA{id}:{times}"; } catch { return $"抛出异常程序"; Console.WriteLine("抛出异常程序继续"); } } public void deltePush(int aa) { Console.WriteLine("推送数据给KA"); } public string returnstring(string id) { return "111111111"; } } } }
public event Action updateEvent;

using ObserverPattern.Observer; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ObserverPattern.Subject { public class pushSystem { #region 定义 #endregion public event Action updateEvent; //调用委托事件 public void update(string name) { if (updateEvent != null) { foreach (Action item in updateEvent.GetInvocationList()) { item.BeginInvoke(null,null); } updateEvent.Invoke(); //BeginInvoke } } //如何调用 public void aaaa() { pushSystem push = new pushSystem(); push.updateEvent += () => new KA().updatePush("带参数的"); push.update("name"); } public class KA { public string updatePush(string id) { Console.WriteLine($"KA的线程{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); var times = DateTime.Now.ToString($"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.fff"); try { Console.WriteLine($"开始KA{id}:{times}"); return $"返回调用KA{id}:{times}"; } catch { return $"抛出异常程序"; Console.WriteLine("抛出异常程序继续"); } } } } }
