2618: [Cqoi2006]凸多边形
Description
逆时针给出n个凸多边形的顶点坐标,求它们交的面积。例如n=2时,两个凸多边形如下图:则相交部分的面积为5.233。
Input
第一行有一个整数n,表示凸多边形的个数,以下依次描述各个多边形。第i个多边形的第一行包含一个整数mi,表示多边形的边数,以下mi行每行两个整数,逆时针给出各个顶点的坐标。
Output
输出文件仅包含一个实数,表示相交部分的面积,保留三位小数。
Sample Input
2
6
-2 0
-1 -2
1 -2
2 0
1 2
-1 2
4
0 -3
1 -1
2 2
-1 0Sample Output
5.233HINT
100%的数据满足:2<=n<=10,3<=mi<=50,每维坐标为[-1000,1000]内的整数
半平面交模板:(终于缩到100行以内了。。。之前没删调试恶心的180+)

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstdlib> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<cmath> 7 using namespace std; 8 #define Maxn 1100 9 10 struct P 11 { 12 double x,y; 13 P() {x=y=0;} 14 P(double x,double y):x(x),y(y){} 15 friend P operator - (P x,P y) {return P(x.x-y.x,x.y-y.y);} 16 friend P operator + (P x,P y) {return P(x.x+y.x,x.y+y.y);} 17 friend P operator * (P x,double y) {return P(x.x*y,x.y*y);} 18 friend double operator * (P x,P y) {return x.x*y.y-x.y*y.x;} 19 friend double operator / (P x,P y) {return x.x*y.x+x.y*y.y;} 20 }a[Maxn]; 21 struct L 22 { 23 P a,b,v;double slop; 24 friend bool operator < (L a,L b) {return (a.slop!=b.slop)?(a.slop<b.slop):a.v*(b.b-a.a)>0;} 25 friend P inter(L a,L b) 26 { 27 P nw=b.a-a.a; 28 double tt=(nw*a.v)/(a.v*b.v); 29 return b.a+b.v*tt; 30 } 31 friend bool jud(P x,L c) {return c.v*(x-c.a)<0;} 32 }l[Maxn],q[Maxn];int cnt,tot; 33 34 void ffind() 35 { 36 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) l[i].v=l[i].b-l[i].a,l[i].slop=atan2(l[i].v.y,l[i].v.x); 37 sort(l+1,l+1+cnt); 38 int L=1,R=0; 39 tot=0; 40 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 41 { 42 if(l[i].slop!=l[i-1].slop) tot++; 43 l[tot]=l[i]; 44 } 45 cnt=tot;tot=0; 46 q[++R]=l[1];q[++R]=l[2]; 47 for(int i=3;i<=cnt;i++) 48 { 49 while(L<R&&jud(inter(q[R-1],q[R]),l[i])) R--; 50 while(L<R&&jud(inter(q[L+1],q[L]),l[i])) L++; 51 q[++R]=l[i]; 52 } 53 while(L<R&&jud(inter(q[R-1],q[R]),q[L])) R--; 54 while(L<R&&jud(inter(q[L+1],q[L]),q[R])) L++; 55 q[R+1]=q[L]; 56 for(int i=L;i<=R;i++) a[++tot]=inter(q[i],q[i+1]); 57 } 58 59 void init() 60 { 61 int n; 62 scanf("%d",&n); 63 cnt=0; 64 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 65 { 66 int m; 67 scanf("%d",&m); 68 P ft,now,nw; 69 scanf("%lf%lf",&ft.x,&ft.y); 70 now=ft; 71 for(int j=2;j<=m;j++) 72 { 73 scanf("%lf%lf",&nw.x,&nw.y); 74 l[++cnt].b=nw,l[cnt].a=now; 75 now=nw; 76 } 77 l[++cnt].a=now;l[cnt].b=ft; 78 } 79 } 80 81 void get_area() 82 { 83 double ans=0; 84 for(int i=1;i<tot;i++) ans+=a[i]*a[i+1]; 85 ans+=a[tot]*a[1]; 86 if(tot<3) ans=0; 87 printf("%.3lf ",ans/2); 88 } 89 90 int main() 91 { 92 init(); 93 ffind(); 94 get_area(); 95 return 0; 96 }
【分析】
然而只是想做一道半平面交的模版题,就从星期二打到了现在。。。【下午还要考试呢真是无爱。。
这题是求凸包的交,我们可以把每一条线段转化半平面,求半平面交。
对于半平面交,最朴素的想法应该是两两线段求交点,然后判断是否在每一个平面内,然后求凸包吧(感觉奇慢无比啊)
而事实上,如果有n的半平面的话,半平面交的答案那个凸包不会超过n条边,因为每个半平面最多只贡献一条边,说明我们事实上做了很多很多无用功。
根据凸包的思想,我们觉得半平面交也是有单调性的。
那个nlogn的算法可以看zzy的论文《半平面交的新算法及其实用价值》。
半平面共用向量表示,向量的左边为有效半平面。
定义半平面的极角为表示半平面的向量的极角。
根据半平面的极角进行排序,若两个半平面极角相同,明显只需要保存最靠左的半平面,根据这个去重。
然后这样做:
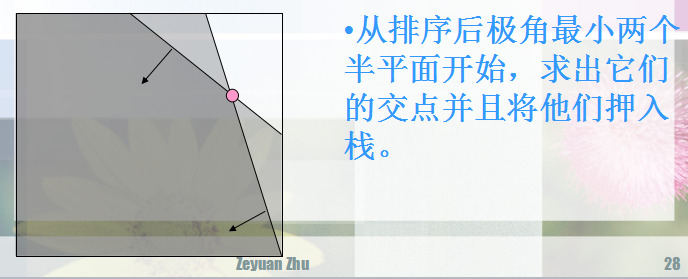
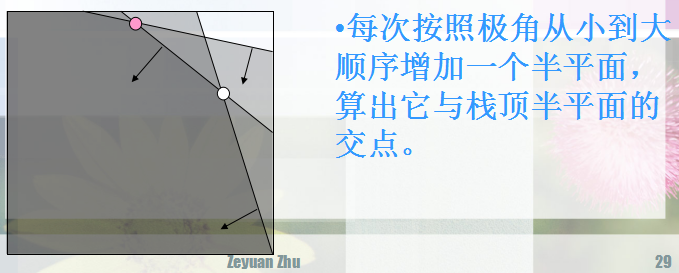

跟单调队列差不多,两边判断,删减。
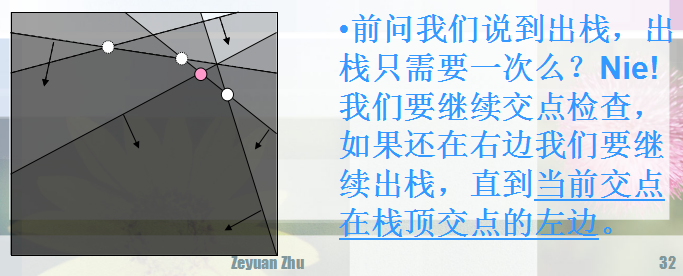
注意最后还要判断一下,去尾。像这样:
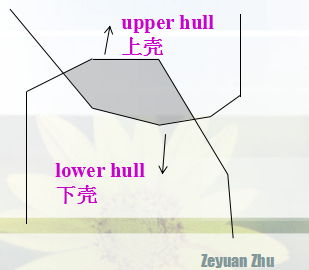


这题就是这样了。
放代码(调试很多,不删了)

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstdlib> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<cmath> 7 using namespace std; 8 #define Maxn 1100 9 10 struct P {double x,y;}; 11 struct L {P a,b;double slop;}l[Maxn]; 12 //半平面只方向向量a->b的左部分 13 //slop 极角 14 int cnt; 15 16 P operator - (P x,P y) 17 { 18 P tt; 19 tt.x=x.x-y.x; 20 tt.y=x.y-y.y; 21 return tt; 22 } 23 24 P operator + (P x,P y) 25 { 26 P tt; 27 tt.x=x.x+y.x; 28 tt.y=x.y+y.y; 29 return tt; 30 } 31 32 double Dot(P x,P y) {return x.x*y.x+x.y*y.y;} 33 double Cross(P x,P y) {return x.x*y.y-x.y*y.x;} 34 // bool operator < (L x,L y) {return x.slop<y.slop;} 35 36 bool operator < (L a,L b) 37 { 38 if(a.slop!=b.slop)return a.slop<b.slop; 39 return Cross(a.b-a.a,b.b-a.a)>0; 40 } 41 42 P operator * (P X,double y) 43 { 44 P tt; 45 tt.x=X.x*y; 46 tt.y=X.y*y; 47 return tt; 48 } 49 50 P a[Maxn]; 51 L q[Maxn]; 52 int tot; 53 54 P inter(L a,L b) 55 { 56 P X=a.a-a.b,Y=b.a-b.b,nw; 57 double tt; 58 nw=b.a-a.a; 59 tt=Cross(nw,X)/Cross(X,Y); 60 P ans=b.a+Y*tt; 61 return ans; 62 } 63 64 bool jud(L a,L b,L c) 65 { 66 P p=inter(a,b); 67 return Cross(c.b-c.a,p-c.a)<0; 68 } 69 70 void opp() 71 { 72 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 73 { 74 printf("%.2lf %.2lf %.2lf %.2lf = %.2lf ",l[i].a.x,l[i].a.y,l[i].b.x,l[i].b.y,l[i].slop); 75 } 76 printf(" "); 77 } 78 79 void output() 80 { 81 for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++) printf("%2lf %.2lf ",a[i].x,a[i].y); 82 printf(" "); 83 } 84 85 void op(int L,int R) 86 { 87 for(int i=L;i<=R;i++) 88 printf("%lf %lf %lf %lf ",l[i].a.x,l[i].a.y,l[i].b.x,l[i].b.y); 89 printf(" "); 90 } 91 92 void ffind() 93 { 94 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 95 l[i].slop=atan2(l[i].b.y-l[i].a.y,l[i].b.x-l[i].a.x); 96 sort(l+1,l+1+cnt); 97 98 // opp(); 99 100 int L=1,R=0; 101 //去重? 102 tot=0; 103 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 104 { 105 if(l[i].slop!=l[i-1].slop) tot++; 106 l[tot]=l[i]; 107 } 108 cnt=tot;tot=0; 109 // opp(); 110 q[++R]=l[1];q[++R]=l[2]; 111 for(int i=3;i<=cnt;i++) 112 { 113 while(L<R&&jud(q[R-1],q[R],l[i])) R--; 114 while(L<R&&jud(q[L+1],q[L],l[i])) L++; 115 q[++R]=l[i]; 116 // op(L,R); 117 } 118 while(L<R&&jud(q[R-1],q[R],q[L])) R--; 119 while(L<R&&jud(q[L+1],q[L],q[R])) L++; 120 q[R+1]=q[L]; 121 for(int i=L;i<=R;i++) 122 a[++tot]=inter(q[i],q[i+1]); 123 // output(); 124 125 // output(); 126 } 127 128 void init() 129 { 130 int n; 131 /*scanf("%d",&n); 132 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 133 { 134 scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf ",&l[i].a.x,&l[i].a.y,&l[i].b.x,&l[i].b.y); 135 } 136 cnt=n;*/ 137 scanf("%d",&n); 138 cnt=0; 139 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 140 { 141 int m; 142 scanf("%d",&m); 143 P ft,now; 144 scanf("%lf%lf",&ft.x,&ft.y); 145 now=ft; 146 for(int j=2;j<=m;j++) 147 { 148 P nw; 149 scanf("%lf%lf",&nw.x,&nw.y); 150 l[++cnt].b=nw; 151 l[cnt].a=now; 152 now=nw; 153 } 154 l[++cnt].a=now;l[cnt].b=ft; 155 // opp(); 156 } 157 158 159 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 160 l[i].slop=atan2(l[i].b.y-l[i].a.y,l[i].b.x-l[i].a.x); 161 // opp(); 162 163 } 164 165 void get_area() 166 { 167 double ans=0; 168 for(int i=1;i<tot;i++) 169 { 170 ans+=Cross(a[i],a[i+1]); 171 } 172 ans+=Cross(a[tot],a[1]); 173 if(tot<3) ans=0; 174 printf("%.3lf ",ans/2); 175 } 176 177 int main() 178 { 179 init(); 180 ffind(); 181 // output(); 182 get_area(); 183 return 0; 184 }
用向量法求两直线的交点:

本质就是用面积比表示线段比。
P inter(L a,L b)
{
P X=a.a-a.b,Y=b.a-b.b,nw;
double tt;
nw=b.a-a.a;
tt=Cross(nw,X)/Cross(X,Y);
P ans=b.a+Y*tt;
return ans;
}
半平面交核心过程:
q[++R]=l[1];q[++R]=l[2];
for(int i=3;i<=cnt;i++)
{
while(L<R&&jud(q[R-1],q[R],l[i])) R--;
while(L<R&&jud(q[L+1],q[L],l[i])) L++;
q[++R]=l[i];
}
if(L<R&&jud(q[R-1],q[R],q[L])) R--;
代码的具体实现其实没有分上壳和下壳,是一起做的,每次保存有用的半平面,最后相邻的求交点形成凸包。
最后也不用处理上面去尾的情况了,但是注意加一句if,判断最后加的那个半平面是有效的。
:if(L<R&&jud(q[R-1],q[R],q[L])) R--;
【倒是对几何画板越来越熟练了,捂脸= =
2016-12-24 09:48:20
