又是两个黑科技一般的存在。
首先我们来介绍一下这两个函数:
ForwardIter lower_bound(ForwardIter first, ForwardIter last,const _Tp& val)
返回一个非递减序列[first, last)中的第一个大于等于值val的位置。
ForwardIter upper_bound(ForwardIter first, ForwardIter last, const _Tp& val)
返回一个非递减序列[first, last)中第一个大于val的位置。
如图:
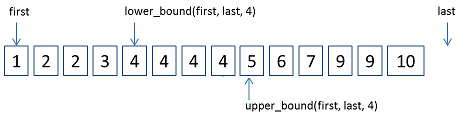
两种函数均采用了二分的方法。
注意:
函数调用序列必须有序。
upper_bound()和lower_bound()的返回值都是迭代器的位置,不能直接与int等类型进行赋值。
std::lower_bound:
| default (1) |
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
const T& val);
|
|---|
| custom (2) |
template <class ForwardIterator, class T, class Compare>
ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
const T& val, Compare comp);
|
|---|
作用:
返回一个非递减序列[first, last)中的第一个大于等于值val的位置。
源代码为:
1 template <class ForwardIterator, class T> 2 ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val) 3 { 4 ForwardIterator it; 5 iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::difference_type count, step; 6 count = distance(first,last); 7 while (count>0) 8 { 9 it = first; step=count/2; advance (it,step); 10 if (*it<val) { // or: if (comp(*it,val)), for version (2) 11 first=++it; 12 count-=step+1; 13 } 14 else count=step; 15 } 16 return first; 17 }
Example:
1 // lower_bound/upper_bound example 2 #include <iostream> // std::cout 3 #include <algorithm> // std::lower_bound, std::upper_bound, std::sort 4 #include <vector> // std::vector 5 6 int main () { 7 int myints[] = {10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20}; 8 std::vector<int> v(myints,myints+8); // 10 20 30 30 20 10 10 20 9 10 std::sort (v.begin(), v.end()); // 10 10 10 20 20 20 30 30 11 12 std::vector<int>::iterator low,up; 13 low=std::lower_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^ 14 up= std::upper_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^ 15 16 std::cout << "lower_bound at position " << (low- v.begin()) << ' '; 17 std::cout << "upper_bound at position " << (up - v.begin()) << ' '; 18 19 return 0; 20 }
Output:
lower_bound at position 3 upper_bound at position 6
资料参考:
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/lower_bound/
std::upper_bound:
| default (1) |
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
const T& val);
|
|---|---|
| custom (2) |
template <class ForwardIterator, class T, class Compare>
ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,
const T& val, Compare comp);
|
作用:
返回一个非递减序列[first, last)中第一个大于val的位置。
源代码为:
1 template <class ForwardIterator, class T> 2 ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val) 3 { 4 ForwardIterator it; 5 iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::difference_type count, step; 6 count = std::distance(first,last); 7 while (count>0) 8 { 9 it = first; step=count/2; std::advance (it,step); 10 if (!(val<*it)) // or: if (!comp(val,*it)), for version (2) 11 { first=++it; count-=step+1; } 12 else count=step; 13 } 14 return first; 15 }
Example:
1 // lower_bound/upper_bound example 2 #include <iostream> // std::cout 3 #include <algorithm> // std::lower_bound, std::upper_bound, std::sort 4 #include <vector> // std::vector 5 6 int main () { 7 int myints[] = {10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20}; 8 std::vector<int> v(myints,myints+8); // 10 20 30 30 20 10 10 20 9 10 std::sort (v.begin(), v.end()); // 10 10 10 20 20 20 30 30 11 12 std::vector<int>::iterator low,up; 13 low=std::lower_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^ 14 up= std::upper_bound (v.begin(), v.end(), 20); // ^ 15 16 std::cout << "lower_bound at position " << (low- v.begin()) << ' '; 17 std::cout << "upper_bound at position " << (up - v.begin()) << ' '; 18 19 return 0; 20 }
Output:
lower_bound at position 3 upper_bound at position 6
资料参考:
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/upper_bound/
附一道简单例题: