



---恢复内容结束---





package workhome; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; public class MapDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Integer, String> map=new HashMap<Integer,String>(); map.put(100,"tom100"); map.put(200,"tom200"); map.put(300,"tom300"); System.out.println(map.size()); map.remove(300); //迭代 Set<Entry<Integer,String>> entires=map.entrySet(); for(Entry<Integer,String> entry :entires) { Integer key=entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"-"+value); } // System.out.println(map.get(100)); //2.通过key迭代 Set<Integer> keys = map.keySet(); for(Integer key:keys) { System.out.println(key+"=="+map.get(key)); } } }
重写equals和hashcode方法

package workhome; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class MapDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<MyKey,Cat> map=new HashMap<MyKey, Cat>(); map.put(new MyKey("tom-1"), new Cat("tom-1",12)); map.put(new MyKey("tom-2"), new Cat("tom-1",13)); map.put(new MyKey("tom-3"), new Cat("tom-1",14)); Cat c=map.get(new MyKey("tom-1")); System.out.println(c); System.out.println(map.size()); } } class Cat{ private String name; private int height; public Cat(String name, int height) { super(); this.name = name; this.height = height; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(int height) { this.height = height; } } class MyKey{ private String name; private Integer age; MyKey(String name){ super(); this.name=name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public int hashCode() { int namehash= name==null ? 0 :name.hashCode(); int agehash=age==null? 0 : age.intValue(); return namehash+agehash; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { MyKey key0=(MyKey)obj; return name.equals(key0.name) && age==key0.age; } }

package workhome; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class setDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Dog2> dogs=new HashSet<Dog2>(); dogs.add((new Dog2("white"))); dogs.add(new Dog2("white")); System.out.println(dogs.size()); //System.out.println(dogs.contains(new Dog("white"))); } } class Dog2{ private String name; Dog2(String name){ super(); this.name=name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public int hashCode() { return 1; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { return true; } }





package base; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; public class CollectionToolDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] src= {1,2,3,4}; int[] desc=new int[6]; System.arraycopy(src, 1, desc, 2,3); System.out.println(desc); Person[] src0= {new Person(100),new Person(200),new Person(300),new Person(400)}; Person[] dest=new Person[6]; System.arraycopy(src0, 1, dest, 2, 3); src[2]=1000; System.out.println(dest[3]); src0[2].setHeight(1000); System.out.println(dest[3].getHeight()); // List<String> names=Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<String>()); names.add("tom"); names.add("tom"); names.add("tom"); System.out.println(names.size()); //最大值,最小值 //Collections.max() min() //排序 //Collections.sort(list, c); //asList将参数转换成Array$ArrayList集合对象 List list=Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4); //排序 //Arrays.sort(list); //Arrays.binarySearch(a, key) System.out.println(list.size()); } }

package base; import java.util.Hashtable; public class HashTableDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Hashtable<String,Person> ht=new Hashtable<String,Person>(); ht.put("tom1", new Person(100)); ht.put("tom1", new Person(100)); ht.put("tom2", new Person(100)); ht.put("tom3", new Person(100)); System.out.println(ht.size()); } }

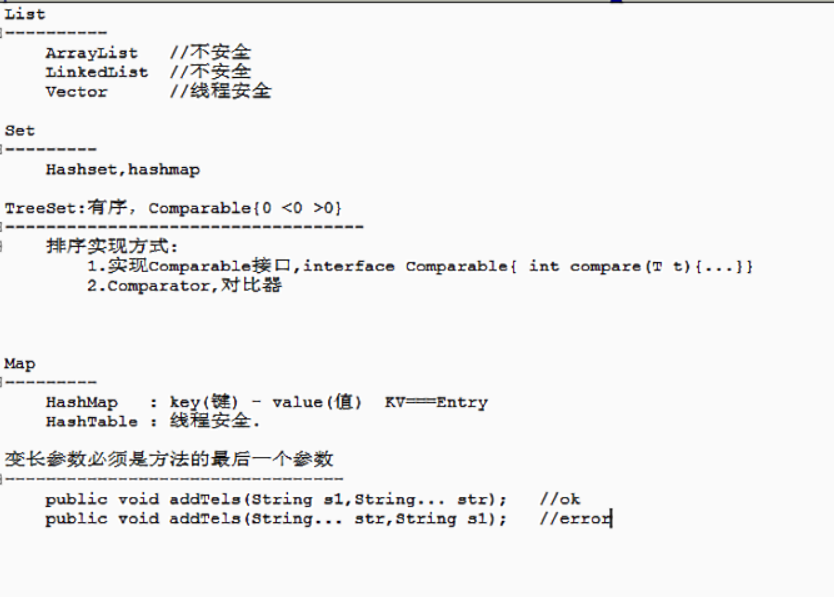
package base; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * * @author ASUS * */ public class Person { private int height; private List<String> tels=new ArrayList<String>(); public Person(int height) { super(); this.height = height; } public List<String> getTels() { return tels; } public void setTels(List<String> tels) { this.tels = tels; } public int getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(int height) { this.height = height; } //变长参数,可变参数,相当于数组 public void addTel(String... str) { for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++) { tels.add(str[i]); } // for(String s:str) { // // tels.add(s); // } } }

package base; import java.util.Comparator; /** * 自定义对比器 * @author ASUS * */ public class PersonComparator implements Comparator<Person>{ @Override public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) { if(o1==null) { if(o2==null) { return 0; } else { return -1; } }else { if(o2==null) { return 1; }else { return o1.getHeight()-o2.getHeight(); } } } }

package base; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; public class ProForDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr= {1,2,3,4}; //对数组进行for循环 for(int i:arr) { System.out.println(i); } //List Set Map.entrySet|Map.keySet List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("tom"); list.add("tom"); list.add("tom"); list.add("tom"); //对集合 for(String s:list) { System.out.println(s); } Person p = new Person(1000); p.addTel("132","31111","5353"); } }

package base; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; import java.util.TreeMap; import workhome.Student; public class TreeMapDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { TreeMap<String,Student> tm1=new TreeMap<String,Student>(); tm1.put("tom1",new Student(1,2,3)); tm1.put("tom1",new Student(1,2,3)); tm1.put("tom2",new Student(1,2,3)); tm1.put("tom3",new Student(1,2,3)); System.out.println(tm1.size()); //迭代 for(Entry<String,Student> entry : tm1.entrySet()) { String k=entry.getKey(); Student v=entry.getValue(); System.out.println(k+"-"+v); } // TreeMap<Person,String> tm2=new TreeMap<Person,String>(new PersonComparator()); tm2.put(new Person(100), "tom1"); tm2.put(new Person(100), "tom2"); tm2.put(new Person(200), "tom3"); tm2.put(new Person(300), "tom4"); System.out.println(tm2.size()); //得到所有key元素 Set<Person> keys = tm2.keySet(); Iterator<Person> it=keys.iterator(); for(;it.hasNext();) { Person p = it.next(); String v=tm2.get(p); System.out.println(p+"-"+v); } } }

package base; import java.util.TreeSet; public class TreeSetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { TreeSet<Person> ts2=new TreeSet<Person>(new PersonComparator()); ts2.add(new Person(1)); ts2.add(new Person(1)); ts2.add(new Person(2)); ts2.add(new Person(3)); System.out.println(ts2.size()); } }

package workhome; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; public class MapDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Integer, String> map=new HashMap<Integer,String>(); map.put(100,"tom100"); map.put(200,"tom200"); map.put(300,"tom300"); System.out.println(map.size()); map.remove(300); //迭代 Set<Entry<Integer,String>> entires=map.entrySet(); for(Entry<Integer,String> entry :entires) { Integer key=entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key+"-"+value); } // System.out.println(map.get(100)); //2.通过key迭代 Set<Integer> keys = map.keySet(); for(Integer key:keys) { System.out.println(key+"=="+map.get(key)); } } }

package workhome; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class MapDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<MyKey,Cat> map=new HashMap<MyKey, Cat>(); map.put(new MyKey("tom-1"), new Cat("tom-1",12)); map.put(new MyKey("tom-2"), new Cat("tom-1",13)); map.put(new MyKey("tom-3"), new Cat("tom-1",14)); Cat c=map.get(new MyKey("tom-1")); System.out.println(c); System.out.println(map.size()); } } class Cat{ private String name; private int height; public Cat(String name, int height) { super(); this.name = name; this.height = height; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(int height) { this.height = height; } } class MyKey{ private String name; private Integer age; MyKey(String name){ super(); this.name=name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public int hashCode() { int namehash= name==null ? 0 :name.hashCode(); int agehash=age==null? 0 : age.intValue(); return namehash+agehash; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { MyKey key0=(MyKey)obj; return name.equals(key0.name) && age==key0.age; } }

package workhome; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; /** * Map嵌套 * * @author ASUS * */ public class MapNestedDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 名单集合() Map<String, String> names = null; // 班级集合 Map<String, Map<String, String>> classes = null; // 年级集合 Map<String, Map<String, Map<String, String>>> grades = new HashMap<String, Map<String, Map<String, String>>>(); int no = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { // 创建班级集合 classes = new HashMap<String, Map<String, String>>(); grades.put(i + "年级", classes); for (int j = 1; j <= 2; j++) { // 创建名单集合 names = new HashMap<String, String>(); classes.put(i + "年级" + j + "班", names); for (int k = 1; k <= 5; k++) { names.put("NO" + i + "-" + j + "-" + k, "tom" + (no++)); } } } //迭代输出 for(Entry<String,Map<String,Map<String,String>>> entry : grades.entrySet()) { //年级 String key=entry.getKey(); //班级集合 Map<String,Map<String,String>> classes1=entry.getValue(); //先输出年级名称 System.out.println(key); //年级内的每个班 for(Entry<String,Map<String,String>> e : classes1.entrySet()) { //班级名称 String className=e.getKey(); //名单集合 Map<String,String> v=e.getValue(); System.out.println(" "+className); for(Entry<String,String> e2 : v.entrySet()) { String stuNo=e2.getKey(); String strName=e2.getValue(); System.out.println(" "+stuNo+"-"+strName); } } } // //迭代器 // Iterator<Entry<String,Map<String,Map<String,String>>>> it1=grades.entrySet().iterator(); // while(it1.hasNext()) { // Entry<String,Map<String,Map<String,String>>> e1 =it1.next(); // String k1=e1.getKey(); // Map<String,Map<String,String>> v1=e1.getValue(); // System.out.println(k1); // // Iterator<Entry<String,Map<String,String>>> it2=v1.entrySet().iterator(); // while(it2.hasNext()) { // Entry<String,Map<String,String>> e2=it2.next(); // String k2=e2.getKey(); // Map<String,String> v2= e2.getValue(); // // System.out.println(" "+k2); // // Iterator<Entry<String,String>> it3=v2.entrySet().iterator(); // while(it3.hasNext()) { // Entry<String,String> e3=it3.next(); // String k3 = e3.getKey(); // String v3=e3.getValue(); // System.out.println(" "+k3+"-"+v3); // } // } // } } }

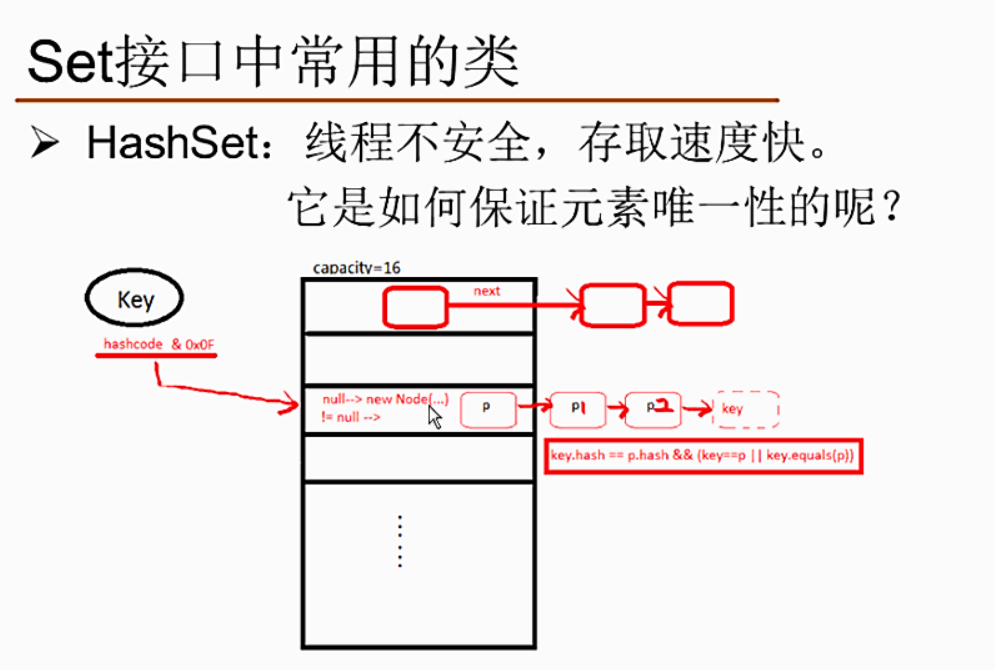
package workhome; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class SetDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //hash:散列,去重 Set<String> set=new HashSet<String>(); set.add("tom"); set.add("tom"); } }

package workhome; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class setDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Dog2> dogs=new HashSet<Dog2>(); dogs.add((new Dog2("white"))); dogs.add(new Dog2("white")); System.out.println(dogs.size()); //System.out.println(dogs.contains(new Dog("white"))); } } class Dog2{ private String name; Dog2(String name){ super(); this.name=name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public int hashCode() { return 1; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { return true; } }
