1、模块化
一般来说,编程语言中,库,包,模块是同一个概念,是代码组织方式。
Python中,只有一种模块对象类型,但是为了模块化组织模块的遍历,提供了‘包’的概念。
模块 module,指的是Python的源代码文件。
包package,指的是模块组织在一起的和包同名的目录及其相关文件。
2、导入语句 :
2.1:import
import 模块1[, 模块2 ] ------完全导入,当然EPE8 推荐多个模块分别导入
import... as.... -------模块别名
import语句:
1、找到指定的模块,加载和初始化它,生成模块对象,找不到,抛出importError异常
2、在import所在的作用域的局部命名空间中,增加名称和上一步创建的对象关联。
测试1:

1 print(dir()) 2 ''' 3 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'partial'] 4 5 ''' 6 7 import functools 8 print(dir()) 9 print(functools) 10 print(functools.wraps) 11 12 ''' 13 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'functools', 'partial'] 14 <module 'functools' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\functools.py'> 15 <function wraps at 0x00000000022508C8> 16 ''' 17 18 import os.path 19 print(dir()) 20 print(os) 21 print(os.path) 22 23 ''' 24 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'os', 'partial'] 25 <module 'os' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\os.py'> 26 <module 'ntpath' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\ntpath.py'> 27 ''' 28 29 import os.path as osp 30 print(dir()) 31 print(osp) 32 33 ''' 34 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'osp', 'partial'] 35 <module 'ntpath' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\ntpath.py'>
总结:
- 导入顶级模块,其名称会加入到本地名词空间中,并绑定到其模块对象。这里说的模块对象,就是导入的模块
- 导入非顶级模块,值将其顶级模块名称加入到本地名词空间中,导入的模块必须使用完全限定名称类访问。
print(path)报错,
print(os.path) 正确
- 如果使用了as,as后的名称直接绑定到导入的模块对象,并将该名称加入到本地名词空间中。
2.2、form...import...
from...import... 部分导入
from...import... as... 别名
测试2:

1 from pathlib import Path, PosixPath # 当前名词空间导入该模块指定成员。 2 print(dir()) 3 ''' 4 ['Path', 'PosixPath', '__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'partial'] 5 ''' 6 from pathlib import * # 在当前名词空间导入该模块所有公共成员(非下划线开头成员)或指定成员 7 print(dir()) 8 ''' 9 ['Path', 'PosixPath', 'PurePath', 'PurePosixPath', 'PureWindowsPath', 'WindowsPath', '__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'partial'] 10 ''' 11 12 from functools import wraps as wr, partial 13 print(dir()) 14 ''' 15 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'partial', 'wr'] 16 ''' 17 18 from os.path import exists # 加载,初始化os, os.path模块, exists 加入bending名词空间并绑定 19 20 if exists('f:/'): 21 print('found') 22 else: 23 print('not found') 24 25 print(dir()) 26 print(exists) 27 28 ''' 29 found 30 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'exists', 'partial'] 31 <function exists at 0x0000000001DD1510> 32 33 ''' 34 import os 35 36 print(dir()) 37 print(os.path.exists) 38 # print(exists) # NameError: name 'exists' is not defined 除非 from os.path import exists 39 print(type(os.path)) # <class 'module'> 40 print(os.path.__dict__['exists']) 41 print(getattr(os.path, 'exists')) 42 43 ''' 44 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'os', 'partial'] 45 <function exists at 0x0000000001DE1510> 46 <function exists at 0x0000000001DE1510> 47 <function exists at 0x0000000001DE1510> 48 ''' 49 import sys 50 print(sys.modules) 51 52 ''' 53 {'sys': <module 'sys' (built-in)>, 'builtins': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '_frozen_importlib': <module 'importlib._bootstrap' (frozen)>, '_imp': <module '_imp' (built-in)>, '_thread': <module '_thread' (built-in)>, '_warnings': <module '_warnings' (built-in)>, '_weakref': <module '_weakref' (built-in)>, 'zipimport': <module 'zipimport' (built-in)>, '_frozen_importlib_external': <module 'importlib._bootstrap_external' (frozen)>, '_io': <module 'io' (built-in)>, 'marshal': <module 'marshal' (built-in)>, 'nt': <module 'nt' (built-in)>, 'winreg': <module 'winreg' (built-in)>, 'encodings': <module 'encodings' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\__init__.py'>, 'codecs': <module 'codecs' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\codecs.py'>, '_codecs': <module '_codecs' (built-in)>, 'encodings.aliases': <module 'encodings.aliases' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\aliases.py'>, 'encodings.utf_8': <module 'encodings.utf_8' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\utf_8.py'>, '_signal': <module '_signal' (built-in)>, '__main__': <module '__main__' from 'E:/code_pycharm/code_test_daye/a测试.py'>, 'encodings.latin_1': <module 'encodings.latin_1' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\latin_1.py'>, 'io': <module 'io' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\io.py'>, 'abc': <module 'abc' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\abc.py'>, '_abc': <module '_abc' (built-in)>, 'site': <module 'site' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\site.py'>, 'os': <module 'os' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\os.py'>, 'stat': <module 'stat' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\stat.py'>, '_stat': <module '_stat' (built-in)>, 'ntpath': <module 'ntpath' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\ntpath.py'>, 'genericpath': <module 'genericpath' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\genericpath.py'>, 'os.path': <module 'ntpath' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\ntpath.py'>, '_collections_abc': <module '_collections_abc' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\_collections_abc.py'>, '_sitebuiltins': <module '_sitebuiltins' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\_sitebuiltins.py'>, '_bootlocale': <module '_bootlocale' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\_bootlocale.py'>, '_locale': <module '_locale' (built-in)>, 'encodings.gbk': <module 'encodings.gbk' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\gbk.py'>, '_codecs_cn': <module '_codecs_cn' (built-in)>, '_multibytecodec': <module '_multibytecodec' (built-in)>, 'types': <module 'types' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\types.py'>, 'importlib': <module 'importlib' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\importlib\__init__.py'>, 'importlib._bootstrap': <module 'importlib._bootstrap' (frozen)>, 'importlib._bootstrap_external': <module 'importlib._bootstrap_external' (frozen)>, 'warnings': <module 'warnings' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\warnings.py'>, 'importlib.util': <module 'importlib.util' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\importlib\util.py'>, 'importlib.abc': <module 'importlib.abc' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\importlib\abc.py'>, 'importlib.machinery': <module 'importlib.machinery' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\importlib\machinery.py'>, 'contextlib': <module 'contextlib' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\contextlib.py'>, 'collections': <module 'collections' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\collections\__init__.py'>, 'operator': <module 'operator' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\operator.py'>, '_operator': <module '_operator' (built-in)>, 'keyword': <module 'keyword' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\keyword.py'>, 'heapq': <module 'heapq' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\heapq.py'>, '_heapq': <module '_heapq' (built-in)>, 'itertools': <module 'itertools' (built-in)>, 'reprlib': <module 'reprlib' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\reprlib.py'>, '_collections': <module '_collections' (built-in)>, 'functools': <module 'functools' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\functools.py'>, '_functools': <module '_functools' (built-in)>, 'mpl_toolkits': <module 'mpl_toolkits' (namespace)>} 54 '''
总结:
-
- 找到from子句中指定的模块,加载并初始化它(注意不是导入)
- 对于import子句后的名称
- 先查from子句导入的模块是否具有该名称的属性
- 如果不是,则尝试导入该名称的子模块
- 还没有找到,就抛出ImportError异常
- 这个名称保存到本地名词空间总,如果有as 子句,则使用as子句后的名称。
举例:
from os import path 按照步骤: 首先加载os模块, 先查os下面有没有path属性,如果没有 再找os下面有没有 path的模块,如果没有就报错 找到后,就把这个名词,保存在本地名词空间中
测试 3:因为类似于 类的方法,只需要定义一次,被不同的实例调用。所以模块下函数只需要生成一次
不同的导入方式,只生成一个,被调用。通过某种机制,保证生成一个类,一个方法等。

1 # from pathlib import Path 2 # print(Path, id(Path)) # 可以看到是 同一个对象。 3 # 4 # import pathlib as p 5 # print(dir()) 6 # print(p) 7 # print(p.Path, id(p.Path)) # # 可以看到是 同一个对象。 8 # 9 # ''' 10 # <class 'pathlib.Path'> 42273688 11 # ['Path', '__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'p', 'partial'] 12 # <module 'pathlib' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\pathlib.py'> 13 # <class 'pathlib.Path'> 42273688 14 # '''
globals(), locals(), dir() 的作用范围总结1:

3、自定义类
测试:
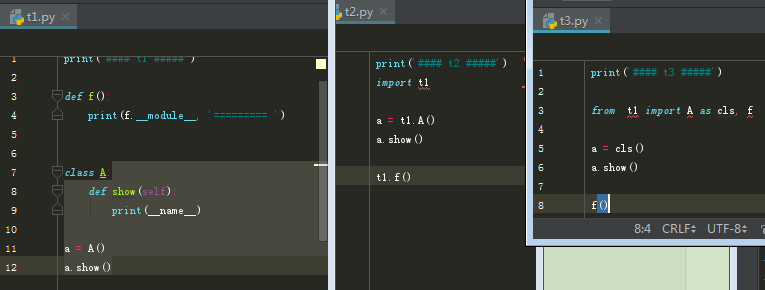
自定义模块命名规范:
- 模块名就是文件名
- 模块名必须符合标识符的要求
- 不要使用系统模块名来避免冲突,除非你明确知道这个模块的用途
- 通常模块名都是小写,下划线分割。
4、模块搜索顺序:
使用 sys.path 查看搜索顺序 :现在自己项目中找,在去系统库,再去第三方库。

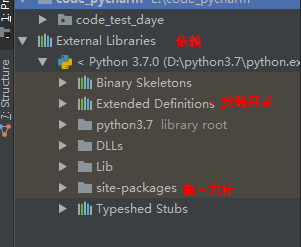
结果为 :Python模块的路径搜索顺序。
上面的是有问题的,因为我之前的代码都在code_pycharm 下的 code_test_daye下.这并不是项目目录
所谓的项目目录是在 code_pycharm下,也就是跟 code_test_daye同一层,
-
- 当加载一个模块的时候,需要从这些搜索路径中从前到后依次查找,并不搜索这些目录的子目录。
- 搜索到模块就加载,搜索不到就抛异常
- 路径也可以为字典,zip文件,egg文件。libzip可以直接访问该文件。
- .egg文件,由setuptools库创建的包,第三方库常用的格式,添加了元数据(版本号,依赖项等)信息的zip文件
- 路径顺序为:
- 程序主目录,程序运行的主程序脚本所在的目录
- PYTHON目录,环境变量PYTHON设置的目录也是搜索模块的路径
-
- 所以打印sys.path 有时候会出现两个项目目录,是因为加入了环境变量。
-
- 标准库目录,Python自带的库模块所在的目录
- sys.path可以被修改,增加新的目录(一般不要修改)
5、模块的重复导入
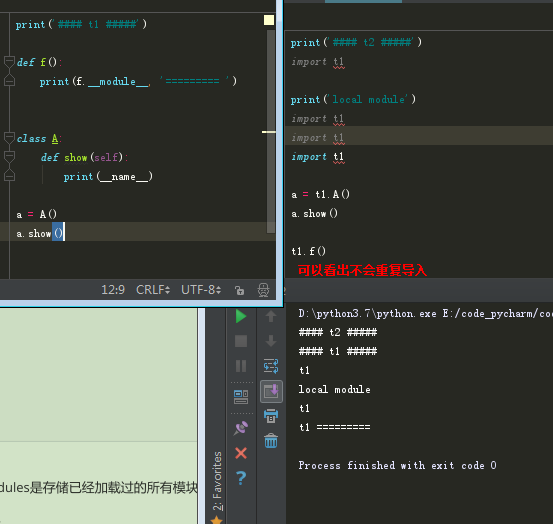
从执行结果来看,不会产生重复导入现象。
也就是说,模块加载一会,产生模块对象,所以模块内定义的属性也只加载一次。
所有加载的模块都会记录在sys.modules中,sys.modules是存储已经加载过的所有模块的字典。
打印sys.modules可以看到os, os.path都已经加载了。就像一个已加载模块的cache

1 import sys 2 3 print(sys.modules) 4 5 {'sys': <module 'sys' (built-in)>, 'builtins': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '_frozen_importlib': <module 'importlib._bootstrap' (frozen)>, '_imp': <module '_imp' (built-in)>, '_thread': <module '_thread' (built-in)>, '_warnings': <module '_warnings' (built-in)>, '_weakref': <module '_weakref' (built-in)>, 'zipimport': <module 'zipimport' (built-in)>, '_frozen_importlib_external': <module 'importlib._bootstrap_external' (frozen)>, '_io': <module 'io' (built-in)>, 'marshal': <module 'marshal' (built-in)>, 'nt': <module 'nt' (built-in)>, 'winreg': <module 'winreg' (built-in)>, 'encodings': <module 'encodings' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\__init__.py'>, 'codecs': <module 'codecs' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\codecs.py'>, '_codecs': <module '_codecs' (built-in)>, 'encodings.aliases': <module 'encodings.aliases' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\aliases.py'>, 'encodings.utf_8': <module 'encodings.utf_8' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\utf_8.py'>, '_signal': <module '_signal' (built-in)>, '__main__': <module '__main__' from 'E:/code_pycharm/code_test_daye/a测试.py'>, 'encodings.latin_1': <module 'encodings.latin_1' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\latin_1.py'>, 'io': <module 'io' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\io.py'>, 'abc': <module 'abc' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\abc.py'>, '_abc': <module '_abc' (built-in)>, 'site': <module 'site' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\site.py'>, 'os': <module 'os' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\os.py'>, 'stat': <module 'stat' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\stat.py'>, '_stat': <module '_stat' (built-in)>, 'ntpath': <module 'ntpath' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\ntpath.py'>, 'genericpath': <module 'genericpath' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\genericpath.py'>, 'os.path': <module 'ntpath' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\ntpath.py'>, '_collections_abc': <module '_collections_abc' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\_collections_abc.py'>, '_sitebuiltins': <module '_sitebuiltins' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\_sitebuiltins.py'>, '_bootlocale': <module '_bootlocale' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\_bootlocale.py'>, '_locale': <module '_locale' (built-in)>, 'encodings.gbk': <module 'encodings.gbk' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\encodings\gbk.py'>, '_codecs_cn': <module '_codecs_cn' (built-in)>, '_multibytecodec': <module '_multibytecodec' (built-in)>, 'types': <module 'types' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\types.py'>, 'importlib': <module 'importlib' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\importlib\__init__.py'>, 'importlib._bootstrap': <module 'importlib._bootstrap' (frozen)>, 'importlib._bootstrap_external': <module 'importlib._bootstrap_external' (frozen)>, 'warnings': <module 'warnings' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\warnings.py'>, 'importlib.util': <module 'importlib.util' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\importlib\util.py'>, 'importlib.abc': <module 'importlib.abc' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\importlib\abc.py'>, 'importlib.machinery': <module 'importlib.machinery' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\importlib\machinery.py'>, 'contextlib': <module 'contextlib' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\contextlib.py'>, 'collections': <module 'collections' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\collections\__init__.py'>, 'operator': <module 'operator' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\operator.py'>, '_operator': <module '_operator' (built-in)>, 'keyword': <module 'keyword' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\keyword.py'>, 'heapq': <module 'heapq' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\heapq.py'>, '_heapq': <module '_heapq' (built-in)>, 'itertools': <module 'itertools' (built-in)>, 'reprlib': <module 'reprlib' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\reprlib.py'>, '_collections': <module '_collections' (built-in)>, 'functools': <module 'functools' from 'D:\python3.7\lib\functools.py'>, '_functools': <module '_functools' (built-in)>, 'mpl_toolkits': <module 'mpl_toolkits' (namespace)>}
6、模块运行
__name__ 每个模块都会定义一个__name__特殊变量来存储当前模块的名称,如果不指定,则默认为源代码文件名,如果是包则有限定名 m.m1.m2
解释器初始化的时候,会初始化sys.modules字典(保存已加载的模块),加载builtion(全局函数,常量)模块,__main__模块,sys模块,以及初始化模块搜索路劲sys.pah
也就是说:如果用sys.path,首先没有被加载,才会去找。
Python 是脚本语言,任何y一个脚本都可以直接执行,也可以作为模块被导入,除了包的__init__.py
当从标准输入(命令行方式敲代码) ,脚本($python test.py)或 交互式读取的时候,会将模块的__name__设置为__main__,模块的顶层代码就在__main__这个作用域中执行,顶层代码:模块中缩进最外层的代码,
如果import导入的,其__name__默认就是模块名,虽然可以修改但是不建议修改。
测试:__name__

1 # t1.py 2 print('#### t1 #####') 3 4 if __name__ == '__main__': 5 print('main') 6 else: 7 print('in import module') 8 9 10 11 # t2.py 12 print('#### t2 #####') 13 import t1
结果:
1 #### t2 ##### 2 #### t1 ##### 3 in import module
if __name__ == '__main__': 用途
- 本模块的功能测试,对于非本主模块,用来测试本模块内的函数,类
- 避免主模块变更的副作用
- 顶层代码,没有封装,当主模块使用时没有问题,
- 但是一旦有了新的主模块,老的主模块成了被导入模块,由于原来代码没有封装,一并执行了。
- 把之前的 旧主模块的代码放到 if __name__ == '__main__' 下,封装起来
判断模块是否以程序的方式运行: $ python test.py
7、模块的属性:
| 属性 | 含义 |
| __file__ | 字符串,源文件路径 |
| __cached__ | 字符串,编译后的字节码文件路径 |
| __spec__ | 显示模块的规模 |
| __name__ | 模块名 |
| __package__ | 当模块是包,同__name__,否则,可以设置为顶级模块的空字符串 |

1 import tt3 2 3 print(tt3.__cached__) 4 print(tt3.__file__) 5 print(__file__) 6 print(tt3.__spec__) 7 print(tt3.__name__) 8 9 print(tt3.__package__) 10 11 12 13 E:code_pycharm__pycache__ t3.cpython-37.pyc 14 E:code_pycharm t3.py 15 E:/code_pycharm/m/m2/m22.py 16 ModuleSpec(name='tt3', loader=<_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x0000000001F0C710>, origin='E:\code_pycharm\tt3.py') 17 tt3
8、包
包,特殊的模块。
Python模块支持目录吗?
pycharm中,创建Directory 和 Python package 不同,前者是创建普通目录,后者是创建一个带有__init__.py文件的目录 即 包
python中,目录可以作为模块,这就是包,不过代码需要写到该目录下的 __init__.py中
9、子模块
关于locals() globals() dir()区别和联系:
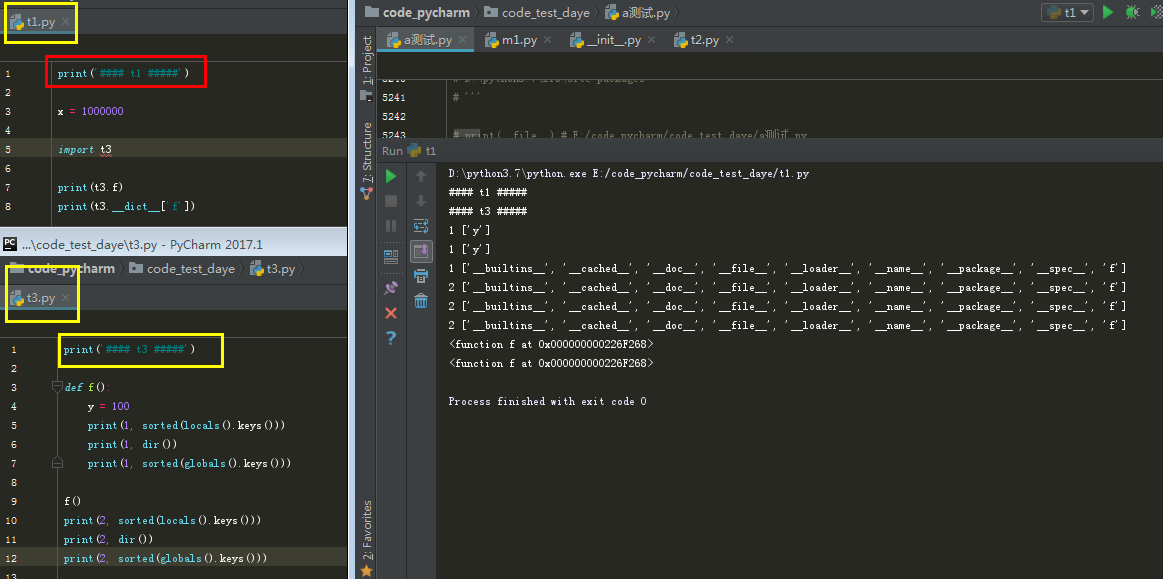
总结:
- 首次,三者都不会突破 所在模块的边界,从上面的大一可以看出。
- 但dir()没传参,和locals() 是一样的,都是收集局部作用域中的变量,loacls() 是字典
- globals() 则永远都是全局的,顶级的。
- 如果dir()给定了参数,就只收集所给参数的变量或属性。
- 主模块打印会有:'__annotations__'
子模块:
包目录下的py文件,子目录都是其子模块
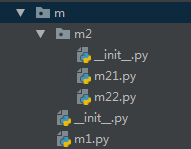
测试:每个模块都 写: print(__name__)

1 print('~===========~', __name__) 2 3 import sys 4 import m.m1 5 import os.path 6 import m.m2.m22 7 8 print(os.path.exists) 9 print(m.m2.m22.show) 10 11 print(dir()) 12 13 print(sorted(filter(lambda x:x.startswith('m'), sys.modules))) 14 15 print(m.m1.show) # 如果不是 import m.m1,就报错 16 # 按照查找顺序,先看有没有m1属性,但是m 模块没m1,所以找m的子模块 17 # 但是从 sys.modules 看,并没有加载,所以报错。 18 # 所以只能先加载 import m.m1 或者m中有m1,如果导入后,m的属性字典中是有m1的 19 20 # 搭配 21 # from m.m2 import m22 22 # print(m22.show)
结果:

1 ~===========~ __main__ 2 m 3 m.m1 4 m.m2 5 m.m2.m22 6 <function exists at 0x0000000002131510> 7 <function show at 0x000000000294F400> 8 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'm', 'os', 'sys'] 9 ['m', 'm.m1', 'm.m2', 'm.m2.m22', 'marshal', 'mpl_toolkits'] 10 <function show at 0x000000000294F268>
注意:import os 直接可以os.path,因为sys就直接导入了,在modules中可以看到,
但是必须导入os,才可以调用,dir()如果没有os,就无法调用
__file__ 只能留给包,__file__ 只能是模块
请保留__init__.py 文件,2版本并不能删,3版本虽然可以删,但不要删。。。。。
10、模块和包的总结:
包能够更好的最值模块,尤其是大的模块,其代码行数很多,可以用把它拆分成很多子模块,便于使用某些功能就加载相应的子模块。
包目录中__init__.py 是在包第一次导入的时候就会执行,内容可以为空,也可以是用于该报初始化工作的代码,最好不要删除它
导入子模块一定会加载福模块,但是导入父模块, 一定 不会导入子模块
包目录之间只能使用点号作为分割符,表示模块及其子模块的底层关系
模块也是封装,如同类,函数,不过他能够封装变量,类,函数。
模块就是命名空间,其内部的顶层标识符,都是它的属性,可以通过dict 或dir(模块名)查看
包也是模块,但是模块不一定是包,包是特殊的模块,是一种组织方式,是目录,它包含__path__, __file__属性等。
1 print(__file__) 2 print(m.__file__) 3 print(m.__path__) 4 5 ''' 6 E:/code_pycharm/code_test_daye/t1.py 7 E:code_pycharmcode_test_dayem\__init__.py 8 ['E:\code_pycharm\code_test_daye\m'] 9 '''

1 print(__file__, type(__file__)) 2 print(m.__file__, type(m.__file__)) 3 print('E:\code_pycharm\code_test_daye\m\__init__.py') 4 5 print(m.__path__, type(m.__path__[0])) 6 7 ''' 8 E:/code_pycharm/code_test_daye/t1.py <class 'str'> 9 E:code_pycharmcode_test_dayem\__init__.py <class 'str'> 10 E:code_pycharmcode_test_dayem\__init__.py 11 ['E:\code_pycharm\code_test_daye\m'] <class 'str'> 12 '''
问题:
from json import encoder之后,json.dump 函数用不了。因为名词空间没有json
import json.encoder之后,json.dump可以,encoder是类,可以导入,其次,名词空间中是json
11、绝对导入,相对导入
在import语句或者from导入模块,模块名称最前面是不是以 . 开头的
绝对导入总是去模块搜索路径中找,当然会查看一下该模块是否已经加载。
相对导入:
只能在包内使用,只能在from语句中使用。
使用 . 点号,表示当前目录内
.. 表示上一级目录
不要在顶层模块中使用相对导入
有相对导入语句的模块不能直接运行,不能当主模块运行!!!!!!!!!!
因为使用了相对导入的模块就是为了内部相互的引用资源的,不是为了直接运行的,对于包来说,正确的使用方式还是在顶级模块使用这些包
在包内使用 相对导入,即便包名改变也不会影响内部资源引用
12、访问控制
下划线开头的模块名?
_ 或 __ 开头的模块,或变量
1 print(__name__) 2 a = 5 3 _b = 6 4 __c = 7 5 __my__ = 8
测试:import访问

1 print(__name__) 2 3 import t2 4 5 import sys 6 7 print(sorted(sys.modules.keys())) 8 print(dir()) 9 print(t2.a, t2._b, t2.__c, t2.__my__) 10 11 12 ''' 13 __main__ 14 t2 15 ['__main__', '_abc', '_bootlocale', '_codecs', '_codecs_cn', '_collections', '_collections_abc', '_frozen_importlib', '_frozen_importlib_external', '_functools', '_heapq', '_imp', '_io', '_locale', '_multibytecodec', '_operator', '_signal', '_sitebuiltins', '_stat', '_thread', '_warnings', '_weakref', 'abc', 'builtins', 'codecs', 'collections', 'contextlib', 'encodings', 'encodings.aliases', 'encodings.gbk', 'encodings.latin_1', 'encodings.utf_8', 'functools', 'genericpath', 'heapq', 'importlib', 'importlib._bootstrap', 'importlib._bootstrap_external', 'importlib.abc', 'importlib.machinery', 'importlib.util', 'io', 'itertools', 'keyword', 'marshal', 'mpl_toolkits', 'nt', 'ntpath', 'operator', 'os', 'os.path', 'reprlib', 'site', 'stat', 'sys', 't2', 'types', 'warnings', 'winreg', 'zipimport'] 16 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'sys', 't2'] 17 5 6 7 8 18 '''
普通变量,保护变量,私有变量,特殊变量,都没有被隐藏,也就是说模块内没有私有的变量,在模块中定义不做特殊处理
测试2:from访问,结果还是可以访问。

1 print(__name__) 2 3 from t2 import a, _b as b, __c as c, __my__ as my 4 5 import sys 6 7 print(sorted(sys.modules.keys())) 8 print(dir()) 9 print(a, b, c, my) 10 11 12 ''' 13 __main__ 14 t2 15 ['__main__', '_abc', '_bootlocale', '_codecs', '_codecs_cn', '_collections', '_collections_abc', '_frozen_importlib', '_frozen_importlib_external', '_functools', '_heapq', '_imp', '_io', '_locale', '_multibytecodec', '_operator', '_signal', '_sitebuiltins', '_stat', '_thread', '_warnings', '_weakref', 'abc', 'builtins', 'codecs', 'collections', 'contextlib', 'encodings', 'encodings.aliases', 'encodings.gbk', 'encodings.latin_1', 'encodings.utf_8', 'functools', 'genericpath', 'heapq', 'importlib', 'importlib._bootstrap', 'importlib._bootstrap_external', 'importlib.abc', 'importlib.machinery', 'importlib.util', 'io', 'itertools', 'keyword', 'marshal', 'mpl_toolkits', 'nt', 'ntpath', 'operator', 'os', 'os.path', 'reprlib', 'site', 'stat', 'sys', 't2', 'types', 'warnings', 'winreg', 'zipimport'] 16 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'my', 'sys'] 17 5 6 7 8 18 '''
from ... import * 和 __all__
使用from ... import * 导入
测试1:结果,t2中的下划线开头的都没有导入

1 print(__name__) 2 3 from t2 import * 4 5 import sys 6 7 print(sorted(sys.modules.keys())) 8 print(dir()) 9 print(locals()['a']) 10 # print(locals()['_b']) # 访问不到 11 12 a = 1888888888888888888 13 print(locals()['a']) 14 15 ''' 16 __main__ 17 t2 18 ['__main__', '_abc', '_bootlocale', '_codecs', '_codecs_cn', '_collections', '_collections_abc', '_frozen_importlib', '_frozen_importlib_external', '_functools', '_heapq', '_imp', '_io', '_locale', '_multibytecodec', '_operator', '_signal', '_sitebuiltins', '_stat', '_thread', '_warnings', '_weakref', 'abc', 'builtins', 'codecs', 'collections', 'contextlib', 'encodings', 'encodings.aliases', 'encodings.gbk', 'encodings.latin_1', 'encodings.utf_8', 'functools', 'genericpath', 'heapq', 'importlib', 'importlib._bootstrap', 'importlib._bootstrap_external', 'importlib.abc', 'importlib.machinery', 'importlib.util', 'io', 'itertools', 'keyword', 'marshal', 'mpl_toolkits', 'nt', 'ntpath', 'operator', 'os', 'os.path', 'reprlib', 'site', 'stat', 'sys', 't2', 'types', 'warnings', 'winreg', 'zipimport'] 19 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'a', 'sys'] 20 5 21 1888888888888888888 22 '''
测试2:t2 使用了__all__
1 print(__name__) 2 3 __all__ = ['x', 'y','a','_b'] 4 a = 5 5 _b = 6 6 __c = 7 7 __my__ = 8 8 9 x = 9 10 y = 10

1 print(__name__) 2 3 from t2 import * 4 5 import sys 6 7 print(sorted(sys.modules.keys())) 8 print(dir()) 9 print(locals()['a']) 10 print(locals()['x']) 11 print(locals()['_b']) 12 13 14 15 ''' 16 __main__ 17 t2 18 ['__main__', '_abc', '_bootlocale', '_codecs', '_codecs_cn', '_collections', '_collections_abc', '_frozen_importlib', '_frozen_importlib_external', '_functools', '_heapq', '_imp', '_io', '_locale', '_multibytecodec', '_operator', '_signal', '_sitebuiltins', '_stat', '_thread', '_warnings', '_weakref', 'abc', 'builtins', 'codecs', 'collections', 'contextlib', 'encodings', 'encodings.aliases', 'encodings.gbk', 'encodings.latin_1', 'encodings.utf_8', 'functools', 'genericpath', 'heapq', 'importlib', 'importlib._bootstrap', 'importlib._bootstrap_external', 'importlib.abc', 'importlib.machinery', 'importlib.util', 'io', 'itertools', 'keyword', 'marshal', 'mpl_toolkits', 'nt', 'ntpath', 'operator', 'os', 'os.path', 'reprlib', 'site', 'stat', 'sys', 't2', 'types', 'warnings', 'winreg', 'zipimport'] 19 ['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', '_b', 'a', 'sys', 'x', 'y'] 20 5 21 9 22 6 23 24 '''
__all__ 的意思是,宣称当前模块有多少属性公布出去
13、包和子模块
测试;
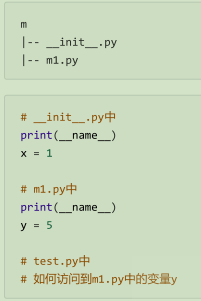

在__init__.py 中有什么变量,则使用ffrom m import * 加载什么变量,这依然符合模块访问控制
总结:

14、模块变量的修改
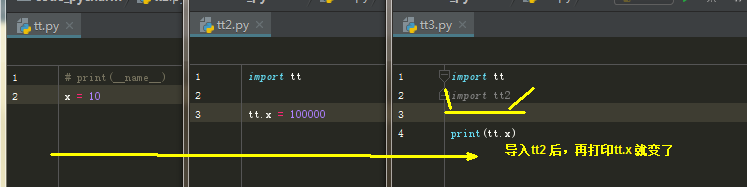
总结:
模块对象是同一个,因此模块的变量也是同一个,对模块变量的修改,会影响所有使用者。
除非万不得已,或明确知道自己在做什么,否则不要修改模块的变量
前面说的猴子补丁,也可以通过打补丁的方式,修改模块的变量,类,函数等内容。
补充:
1、
import os
import os.path
两者明面上一样,通过dir(),都是os,但是后者导入的是, os 和 os.path
2、
import os.path 名词空间只有os 这种只将os 导入
import os.path as osp 名词空间 osp ,也就是说,直接将 os.path 导入
import os.path as osp
print(osp.exists)
print(os.path) # 所以这样是报错的,因为名词空间中没有os 只有osp
3、
import 后面只能导入 module
from ... import ... import 后面可以导入属性,函数等 from后面只能是module
理解:从 。。。 导入。。。 出错一般是说 从。。。 出现问题,是模块吗,问自己
4、
from后面紧跟的,是不会导入到名词空间,只将import后面的加入到名词空间中
import单独使用,只导入顶级模块,除了别名外。
