前言:
使用springMvc已经三年了,但是内部原来一直不太了解,看到ServletConetxt和ApplicationContext头就大,趁着这几天学习,正好学习下相关的知识。
1.ServletContext
首先我们说到ServletContext,ServletContext是一个Web应用的全局上下文,可以理解为整个Web应用的全局变量,项目中的所有方法皆可以获取ServletContext。
说到ServletContext,就到说到所有web项目的web.xml,下面我们先贴出web.xml的一部分配置:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>log4jConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:log4j.properties</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.util.IntrospectorCleanupListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>listener.SessionListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<filter>
<filter-name>sessionFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>web.filter.SessionFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>sessionFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
上面贴出的就是web.xml的部分配置,在这里我们首先讲解下web项目启动的加载顺序:
以Tomcat举例,启动Tomcat之后,首先会加载web.xml文件:
a)容器首先读取web.xml中的<context-param>的配置内容和<listener>标签中配置项;
b)紧接着实例化ServletContext对象,并将<context-param>配置的内容转化为键值传递给ServletContext;
c)创建<listener>配置的监听器的类实例,并且启动监听;
d)随后调用listener的contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent args)方法,ServletContext = ServletContextEvent.getServletContext();
此时你可以通过ServletContext获取context-param配置的内容并可以加以修改,此时Tomcat还没完全启动完成。
e)后续加载配置的各类filter;
f)最后加载servlet;
最后的结论是:web.xml中配置项的加载顺序是context-param=>listener=>filter=>servlet,配置项的顺序并不会改变加载顺序,但是同类型的配置项会应该加载顺序,servlet中也可以通过load-on-startup来指定加载顺序。
ServletContext中的属性所有的servlet皆可以使用ServletContext.
2.ApplicationContext
首先介绍下applicationContext,applicationContext是spring的BeanFactory的实现类:
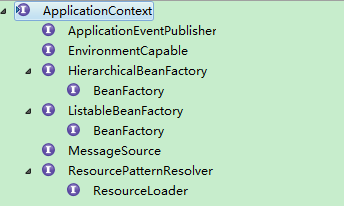
ApplicationContext接口的继承关系如上面的截图,ApplicationContext是如何产生的呢,这里我们看之前的web.xml中的
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
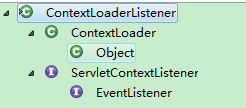 继承关系如左图
继承关系如左图
我们看看是如何初始化的
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(c, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
代码中加粗的部分就是讲WebApplicationContext以WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE为key保存到ServletContext中,所以我们在需要获取时,可以根据request.getSession().
getAttribute("WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE")来获取WebApplicationContext.
所以WebApplicationContext依赖于ServletContext,ApplicationContext存储了Spring中所有的Bean,
但是我们常规的Springmvc项目一般除了applicationContext.xml之外还有springmvc.xml,两个配置文件会对应两个ApplicationContext,springmvc的ApplicationContext中可以调用applicationContext.xml的ApplciationContext。
3.获取WebApplication的几种方式
a)request.getSession().getServletContext().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext.ROOT")
b)实现ApplicationContextAware接口
public interface ApplicationContextAware {
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}

