异常:就是Java代码在运行时期发生的问题
异常的继承体系
Throwable类是所有错误和异常的祖宗类
在Throwable类下有两大子类:Error类和Exception类
Error类:指在程序运行期间发生了某种错误,没有具体的处理办法,程序就结束了。
Error错误的发生一般都是系统级别的,只能修改代码
Exception类:编译时期异常,一般是编译Java程序时出现的问题
在Exception下的RuntimeException子类,是运行时期异常,是Java程序在运行时期发生的问题
异常产生的过程分析
public static int getArray(int[] arr) {
int i = arr[3];
return i;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int[] arr = {1,3};
int i = getArray(arr);
System.out.println(i);
}
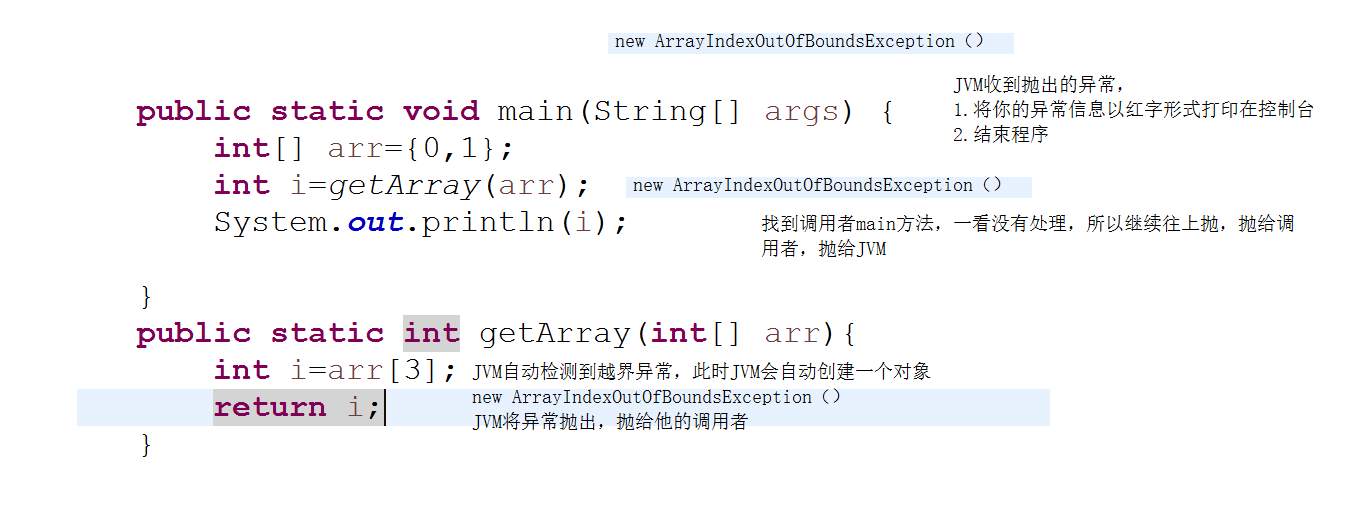
过程:1、JVM自动检测到数组越界异常,此时JVM会自动创建一个对象new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(),JVM将异常抛给它的调用者
2、在main方法中找到调用者,一看没有得到处理,就继续往上抛,抛给JVM
3、JVM收到抛出的异常
a:将异常信息以红字的形式打印在控制台上
b:结束程序
所以代码修改为:
public static int getArray(int[] arr) throws Exception {
if (arr == null) {
throw new Exception("你传进来的数组是null");
}
if (arr.length < 3) {
throw new Exception("你传得数组长度太小了,请传三个以上");
}
int i = arr[3];
return i;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int[] arr = {1,3,5,7};
int i = getArray(arr);
System.out.println(i);
}
异常的处理方式
1、throws
2、try.....catch 或 try...catch...finally
在Java中,用throw关键字抛出一个异常对象 throw new 异常类名(参数) 如:throw new Exception();
声明异常throws:异常已经抛出,但是需要需要声明给调用者 在方法后面加上 throws 异常类名1,异常类名2.....
try{
被检测得代码
可能出现异常得代码
}catch(异常类名 变量名){
异常得处理方式
}finally{
必须要执行得代码
}
作用:try检测到有异常得发生,接收到一个异常对象,将异常对象抛给catch代码块处理,catch捕获到这个异常对象,那么就执行处理方式代码
finally代码块里面的内容是一定要执行的,一般是释放资源的,如关闭数据库,关闭文件
多个catch处理的注意事项
多个catch时:1、看抛出的异常是否是平级关系(是否有继承)
如:NullPointerException extends RuntimeException
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException
如果没有继承就可以随便写
2、如果有上下级关系,就必须把下级放前面,上级放后面
如:Exception 上级
NullPointerException 下级
如果把Exception放到了NullPointerException的前面,若方法中首先抛出的NullPointerException 异常,它会转到catch处,Exception首先接收,就会形 成多态关系(父类引用指向子类对象),那么后面catch中的NullPointerException就会没有作用,编译报错
public static int getArray(int[] arr) throws NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {
if (arr == null) {
// 抛出一个异常对象,谁调用就抛给谁
// 然后声明异常 throws NullPointerException
throw new NullPointerException("你传的数组为空");
}
if (arr.length < 3) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("你传得数组长度不够");
}
return arr[arr.length - 1];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = null;
try {
int i = getArray(arr); // 异常抛到here
System.out.println(i);
} catch (NullPointerException ex) {
//NullPointerException extends RuntimeException
//getMessage()方法打印的是传入的字符串
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
//printStackTrace()打印的是完整的异常信息,包括类名+字符串+报错位置
ex.printStackTrace();
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException extends IndexOutOfBoundsException
//IndexOutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException
//toString方法打印的是完整的异常类名+传入的字符串
System.out.println(ex.toString());
}finally{
//finally用于存放释放资源得代码,如:关闭数据库,关闭文件等
System.out.println("必须要执行得代码");
}
System.out.println("Game Over");
}
运行时期异常和编译时期异常
运行时期异常: 方法中抛出运行时期异常,方法定义中无需throws声明,调用者也无需处理此异常
运行时期异常一旦发生,需要程序人员修改源代码.
RuntimeException和他的所有子类异常,都属于运行时期异常。NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException等都属于运行时期异常
编译时期异常:只要调用了抛出异常的方法,但是没有处理,就会编译失败 处理方式(try throws) 必须用throws声明
异常在方法重写中的细节问题
class Fu{
public void fumethod(){
}
}
class Zi extends Fu{
public void fumethod(){
try {
method();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void method() throws Exception{
}
}
当父类中有异常方法时
子类继承父类重写这个异常方法的时候,注意:
1、子类可以选择不抛出,但是如果子类选择抛出异常 那么你抛出的异常类不得超过你父类的异常,可以是你父类的异常也可以是你父类异常的子类
当父类方法中没有抛异常时
1、你子类重写这个方法也不可以抛异常
2、父类方法中没有抛异常,但是子类重写这个方法时,在方法中调用了带有抛出异常的方法
由于父类没有抛异常,那么只能try catch处理这个异常,不能throws
异常中常用的方法

getMessage方法:返回该异常的详细信息字符串,即异常提示信息
toString方法:返回该异常的名称+详细信息字符串
printStackTrace:在控制台输出该异常的名称+详细信息字符串+异常出现的代码位置
自定义异常类
NullPointerException异常类源代码:
public class NullPointerException extends RuntimeException {
public NullPointerException() {
super();//调用父类构造方法
}
public NullPointerException(String s) {
super(s);//调用父类具有异常信息的构造方法
}
}
格式:
Class 异常名 extends Exception{ //或继承RuntimeException
public 异常名(){
}
public 异常名(String s){
super(s);
}
}
package com.oracle.demo1;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个方法 计算平均数的方法
System.out.println(avgnum(2, -4, 5, 6));
}
public static double avgnum(double... b) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
if (b[i] < 0) {
throw new FuShuException("你传入的是负数");
}
sum = sum + b[i];
}
return sum / b.length;
}
}
package com.oracle.demo1;
public class FuShuException extends RuntimeException {
public FuShuException(String s) {
super(s);
}
public FuShuException() {
super();
}
}