T1:

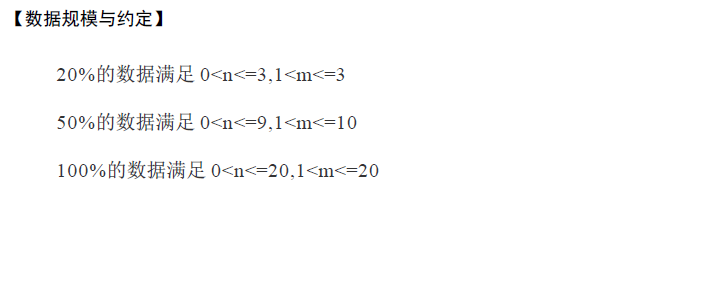
很随便的就能想出来,设 f(i) 为各个位数和为i的数的个数,g(i) 为 。。。。和为i的数的和,然后可以发现递推的系数都是常数,矩阵转移即可。
但是 m^n 可能要高精度表示?? 别忘了可以在算出 d(m^i) 的答案矩阵的基础上 直接m次幂直接算出 d(m^(i+1)) 的答案矩阵。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
#define M(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
const int ha=1e9,maxn=23;
inline void ADD(int &x,int y){ x+=y; if(x>=ha) x-=ha;}
void W(int x,int L){ if(L) W(x/10,L-1); putchar(x%10+'0');}
int n,m,ans;
struct node{
int a[maxn][maxn];
inline void clear(){ M(a);}
inline void Base(){ clear(); for(int i=1;i<=18;i++) a[i][i]=1;}
node operator *(const node &u)const{
node r; r.clear();
for(int k=1;k<=18;k++)
for(int i=1;i<=18;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=18;j++) ADD(r.a[i][j],a[i][k]*(ll)u.a[k][j]%ha);
return r;
}
}b,ANS;
inline void build(){
b.clear();
for(int i=1;i<9;i++) ADD(b.a[i][i+1],1);
for(int i=10;i<18;i++) ADD(b.a[i][i+1],1);
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++) ADD(b.a[i][1],1),ADD(b.a[i][10],i);
for(int i=10;i<=18;i++) ADD(b.a[i][10],10);
}
inline void calc(){
ANS.Base();
node x=b; int y=m;
for(;y;y>>=1,x=x*x) if(y&1) ANS=ANS*x;
ADD(ans,ANS.a[1][10]);
b=ANS;
}
inline void solve(){
build();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) calc();
}
int main(){
// freopen("num.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("num.out","w",stdout);
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
solve();
if(n<=3&&m<=2) printf("%d
",ans);
else W(ans,8),puts("");
return 0;
}
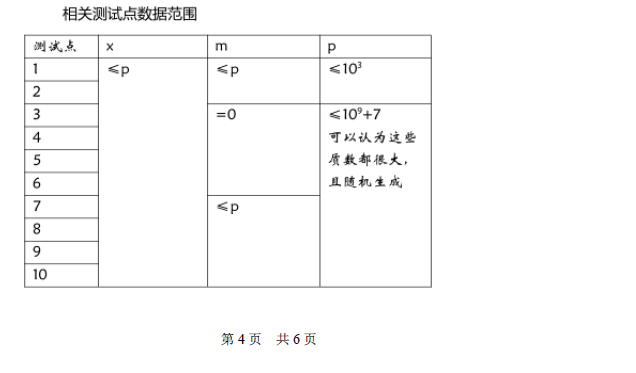
T2:

真是深黑数论题啊23333
可以发现底数是 n%p ,指数是 2n % (p-1)。
所以我们可以先设 now = n % p,然后求出满足 now^y + now^m = x (mod p) 的y,并且要保证y是偶数(因为p-1肯定是偶数,2在这个同余系下是没有逆元的) (一个离散对数就行了)
所以我们现在就得到了 : n % p = now ; n % (p-1) = y/2。
这个玩意手玩中国剩余定理就行了,都不用上模板23333(但注意模数是long long的时候要用快速乘)
好像忘了说now咋找了。。。怕出题人卡我我是随机的now,效果还不错2333
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<ctime>
#include<map>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
map<int,int> mmp;
int b,m,p,now,sz;
ll ans;
inline int add(int x,int y,const int ha){ x+=y; return x>=ha?x-ha:x;}
inline int ksm(int x,int y,const int ha){
int an=1;
for(;y;y>>=1,x=x*(ll)x%ha) if(y&1) an=an*(ll)x%ha;
return an;
}
inline ll ADD(ll x,ll y,const ll ha){ x+=y; return x>=ha?x-ha:x;}
inline ll ksc(ll x,ll y,const ll ha){
ll an=0;
for(;y;y>>=1,x=ADD(x,x,ha)) if(y&1) an=ADD(an,x,ha);
return an;
}
inline ll fpow(ll x,ll y,const ll ha){
ll an=1;
for(;y;y>>=1,x=ksc(x,x,ha)) if(y&1) an=ksc(an,x,ha);
return an;
}
inline bool can(){
mmp.clear();
bool flag=0;
int u=add(b,p-ksm(now,m,p),p),v=1,inv=ksm(ksm(now,sz,p),p-2,p);
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++,v=v*(ll)now%p) if(!mmp.count(v)) mmp[v]=i;
v=u; int z;
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++,v=v*(ll)inv%p) if(mmp.count(v)&&!((i*sz+mmp[v])&1)){
z=i*sz+mmp[v],flag=1;
break;
}
if(!flag) return 0;
z>>=1;
ll to=p*(ll)(p-1);
ans=ADD(ksc(z,ksc(p,p,to),to),ksc(now,ksc(p-1,p-1,to),to),to);
return 1;
}
inline void solve(){
while(1){
now=rand()%p;
if(now) if(can()) break;
}
}
int main(){
// freopen("theory.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("check.out","w",stdout);
srand(time(0));
scanf("%d%d%d",&b,&m,&p),sz=sqrt(p)+3;
solve();
printf("%lld
",ans);
// if(add(ksm(ans%p,ans%(p-1)+ans%(p-1),p),ksm(ans%p,m,p),p)==b%p) puts("yes");
// else puts("no");
return 0;
}
T3:
题目已经传到我校OJ上了: http://lifecraft-mc.com:81/problem/1232
显然这是一个套路题,我们可以很轻松的通过dfs序把子树询问放到线段树的一个区间里,那么现在的问题是access的时候该怎么维护呢?
当我们要把一个点和它爸爸之间的边从轻边变成重边的时候,显然这个点的子树到根的轻边数都会-1,线段树区间加法就行了(可能标记永久化会快一点,反正我写的这个)。
但如果父亲原来就有重儿子的话,那条边是会变成轻边的,所以那颗子树对应的区间会区间+1。
当然不能直接修改splay的根对应的节点,因为重链的顶端对应的节点是splay中序遍历最小的节点,所以还需要写一个找重链顶端的函数。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<ctime>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
#define D double
#define mid (l+r>>1)
#define lc (o<<1)
#define rc ((o<<1)|1)
const int maxn=150005;
int hd[maxn],ne[maxn*2],to[maxn*2],num;
int f[maxn],ch[maxn][2],n,m,dc,dfn[maxn];
int le,ri,tag[maxn*4],siz[maxn],w,Q,pos;
ll sum[maxn*4],ans;
char C;
inline void add(int x,int y){ to[++num]=y,ne[num]=hd[x],hd[x]=num;}
inline int read(){
int x=0; char ch=getchar();
for(;!isdigit(ch);ch=getchar());
for(;isdigit(ch);ch=getchar()) x=x*10+ch-'0';
return x+1;
}
void dfs(int x,int fa){
f[x]=fa,dfn[x]=++dc,siz[x]=1;
for(int i=hd[x];i;i=ne[i]) if(to[i]!=fa){
dfs(to[i],x);
siz[x]+=siz[to[i]];
}
}
inline bool isroot(int x){ return ch[f[x]][0]!=x&&ch[f[x]][1]!=x;}
inline int Get(int x){ return ch[f[x]][1]==x;}
inline void maintain(int x){ }
inline void rotate(int x){
int fa=f[x],ffa=f[fa],tp=Get(x);
ch[fa][tp]=ch[x][tp^1],f[ch[fa][tp]]=fa;
ch[x][tp^1]=fa,f[fa]=x;
f[x]=ffa;
if(ch[ffa][0]==fa||ch[ffa][1]==fa) ch[ffa][ch[ffa][1]==fa]=x;
maintain(fa),maintain(x);
}
inline void splay(int x){
for(;!isroot(x);rotate(x))
if(!isroot(f[x])) rotate(Get(f[x])==Get(x)?f[x]:x);
}
inline int getroot(int x){
while(ch[x][0]) x=ch[x][0];
return x;
}
void update(int o,int l,int r){
if(l>=le&&r<=ri){ sum[o]+=w*(ll)(r-l+1),tag[o]+=w; return;}
if(le<=mid) update(lc,l,mid);
if(ri>mid) update(rc,mid+1,r);
sum[o]=sum[lc]+sum[rc]+tag[o]*(ll)(r-l+1);
}
void query(int o,int l,int r,int Tag){
if(l>=le&&r<=ri){ ans+=sum[o]+Tag*(ll)(r-l+1); return;}
if(le<=mid) query(lc,l,mid,Tag+tag[o]);
if(ri>mid) query(rc,mid+1,r,Tag+tag[o]);
}
inline void access(int x){
for(int pre=0,now;x;pre=x,x=f[x]){
splay(x);
now=ch[x][1],ch[x][1]=0;
if(now){
splay(now),now=getroot(now);
le=dfn[now],ri=le+siz[now]-1;
w=1,update(1,1,n);
}
if(pre){
now=getroot(pre);
le=dfn[now],ri=le+siz[now]-1;
w=-1,update(1,1,n);
}
ch[x][1]=pre;
// maintain(x);
}
}
inline void solve(){
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) le=dfn[i],ri=le+siz[i]-1,w=1,update(1,1,n);
scanf("%d",&Q);
while(Q--){
C=getchar();
while(C!='O'&&C!='q') C=getchar();
pos=read();
if(C=='q'){
ans=0,le=dfn[pos],ri=le+siz[pos]-1;
query(1,1,n,0),printf("%.0lf
",ans/(D)siz[pos]+1e-9);
}
else access(pos);
}
}
int main(){
// freopen("tong.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("ans.out","w",stdout);
scanf("%d",&n);
int uu,vv;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++) uu=read(),vv=read(),add(uu,vv),add(vv,uu);
dfs(1,0);
solve();
return 0;
}