很久没有写文章了,之前有个功能是批量向ios设备推送通知的,网上的文章比较少,所以还是记录一下。分享一下,水平有限,欢迎指正。
APNs(英文全称:Apple Push Notification service)苹果推送通知服务。ios不像安卓,苹果管控发送通知比较严格,都要经过苹果的服务。
如果想要向ios设备发送服务的话,首先要通过apns,然后再由apns发送到指定的ios设备当中。
大致流程如下图:
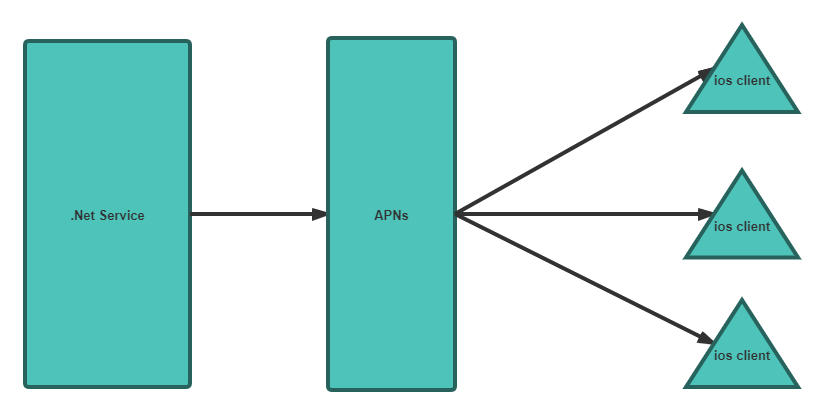
也就是说我们想要发送通知到Ios设备的话,只需要发送通知到Apns上就可以了。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
首先要准备相应的数据(这里的例子全是错误的,是我模仿可以用的数据格式随机乱写的,请不用使用):
证书(.p8 格式的文件:例子AuthKey_E13BAE3RS3.p8)、keyId(证书.p8文件名中authkey后面的一连串的字母加数字:E13BAE3RS3)、bagId(例子:com.test.apnsTest)、teamId(格式:242D5UZ432),以及比较关键的device_token。
这些数据都可以找你们公司中ios开发部门提供。
这里的device_token是指用来标识一台ios设备的,也就是说apns通过device_token识别发送到那一台ios设备,一般用ios开发人员提供。
下一步来到代码环节:
apns提供两个地址:
一个是用来开发的地址:https://api.development.push.apple.com
一个是正式发送的地址:https://api.push.apple.com
区别就是开发的地址是需要ios应用是debug模式,否则会发送不成功。
下一步是代码环节:
首先将keyid,teamid和app_id传入,这里默认使用ES256加密的,
这里有个细节,一个是linux环境下和window环境创建秘钥的方式是有所区别的,(以下所有的代码都是部分关键的伪代码)
public IOSPushAPNs(string key_id, string team_id, string app_id, byte[] auth_key_path, string algorithm = "ES256", bool production = false, int port = 443) //auth_key_path 是证书p8文件转换的byte数组 { Algorithm = algorithm; if (production == false) HostServerUrl = "api.development.push.apple.com"; else HostServerUrl = "api.push.apple.com"; HostPort = port; APNsKeyId = key_id; TeamId = team_id; BundleAppId = app_id; var _private_key_content = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(auth_key_path); var _private_key = _private_key_content.Replace(" ", "").Replace(" ", "") .Replace("-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----", "").Replace("-----END PRIVATE KEY-----", ""); #region windows环境下 创建秘钥 //var _secret_key_blob = Convert.FromBase64String(_private_key); //PrivateKey = CngKey.Import(_secret_key_blob, CngKeyBlobFormat.Pkcs8PrivateBlob); #endregion #region linux 环境下 创建秘钥 _private_key = $"-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- {_private_key} -----END PRIVATE KEY-----"; var ecPrivateKeyParameters = (ECPrivateKeyParameters)new PemReader(new StringReader(_private_key)).ReadObject(); // See https://github.com/dotnet/core/issues/2037#issuecomment-436340605 as to why we calculate q ourselves // TL;DR: we don't have Q coords in ecPrivateKeyParameters, only G ones. They won't work. var q = ecPrivateKeyParameters.Parameters.G.Multiply(ecPrivateKeyParameters.D).Normalize(); var d = ecPrivateKeyParameters.D.ToByteArrayUnsigned(); var msEcp = new ECParameters { Curve = ECCurve.NamedCurves.nistP256, Q = { X = q.AffineXCoord.GetEncoded(), Y = q.AffineYCoord.GetEncoded() }, D = d }; PrivateKey = ECDsa.Create(msEcp); #endregion _httpClient = new HttpClient(); var payload = new Dictionary<string, object>() { { "iss", TeamId }, { "iat", ToUnixEpochDate(DateTime.Now) } }; var header = new Dictionary<string, object>() { { "alg", Algorithm }, { "kid", APNsKeyId } }; AccessToken = Jose.JWT.Encode(payload, PrivateKey, JwsAlgorithm.ES256, header); }
这里将发送需要的数据导入后,就可以准备发送了:
private async Task<(bool success, string message)> JwtAPNsPush(Uri host_uri, string access_token, byte[] payload_bytes) { var _result = (success: false, message: "ok"); try { //using (var _handler = new Http2CustomHandler()) //{ // using (var _http_client = new HttpClient(_handler)) // { var _request_message = new HttpRequestMessage(); { _request_message.Version = new Version(2, 0); _request_message.RequestUri = host_uri; _request_message.Headers.Add("authorization", String.Format("bearer {0}", access_token)); _request_message.Headers.Add("apns-id", Guid.NewGuid().ToString()); _request_message.Headers.Add("apns-expiration", "0"); _request_message.Headers.Add("apns-priority", "10"); _request_message.Headers.Add("apns-topic", BundleAppId); _request_message.Method = HttpMethod.Post; _request_message.Content = new ByteArrayContent(payload_bytes); } _httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Connection.Add("Keep-Alive"); var _response_message = await _httpClient.SendAsync(_request_message); if (_response_message.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK) { var _response_uuid = ""; IEnumerable<string> values; if (_response_message.Headers.TryGetValues("apns-id", out values)) { _response_uuid = values.First(); _result.message = $"success: '{_response_uuid}'"; _result.success = true; } else _result.message = "failure"; } else { var _response_body = await _response_message.Content.ReadAsStringAsync(); var _response_json = JObject.Parse(_response_body); var _reason_str = _response_json.Value<string>("reason"); _result.message = $"failure: '{_reason_str}'"; } // } //} } catch (Exception ex) { _result.message = $"exception: '{ex.Message}'"; } Console.WriteLine("result:" + JsonConvert.SerializeObject(_result)); return _result; }
这里的要注意的点就是:
如果是大批量发送设备用户的话,需要建议长连接去发送,苹果官方建议也是批量发送使用长连接。
以及这里使用的http版本是http2.0
如果苹果发送成功,会在response 的头里面携带一个uuid,然后就可以确定发送成功了。
基本上.net core 发送ios推送就是这样,踩了好多坑,值得记录一下。
未经作者同意禁止转载。