使用场景
定义一系列的算法,将算法进行封装、隔离、相互独立、又能相互替换。
公司最近在做直播功能,底层原来有一套直播API,现在新增一套网宿直播API。
考虑以后的扩展性,需要将两套API进行统一管理。现在以网上的支付方式演示我对策略模式的理解。
支付方式
我们知道网上有很多支付方式。支付宝、微信、银行卡、花呗...
我们以三种支付方式进行演示。
策略模式的组成有三部分
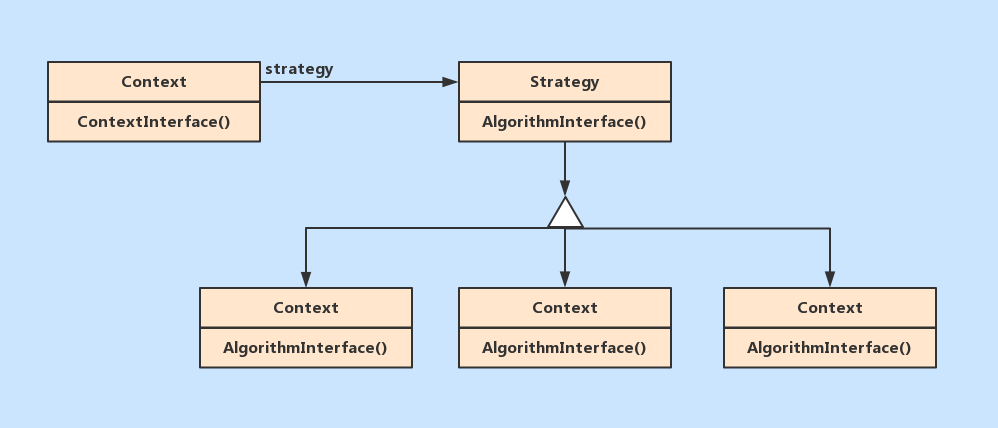
环境类(Context):用一个ConcreteStrategy对象来配置。维护一个对Strategy对象的引用。
可定义一个接口来让Strategy访问它的数据,在上一个例子中相当于Staff。
抽象策略类(Strategy):定义所有支持的算法的公共接口。 Context使用这个接口来调用某ConcreteStrategy定义的算法,
在上一个例子中相当于GrantReward。
具体策略类(ConcreteStrategy):以Strategy接口实现某具体算法,在上一个例子中相当于GrantSuger,GrantMoonCake,GrantNone。
支付方式的组成也有三部分
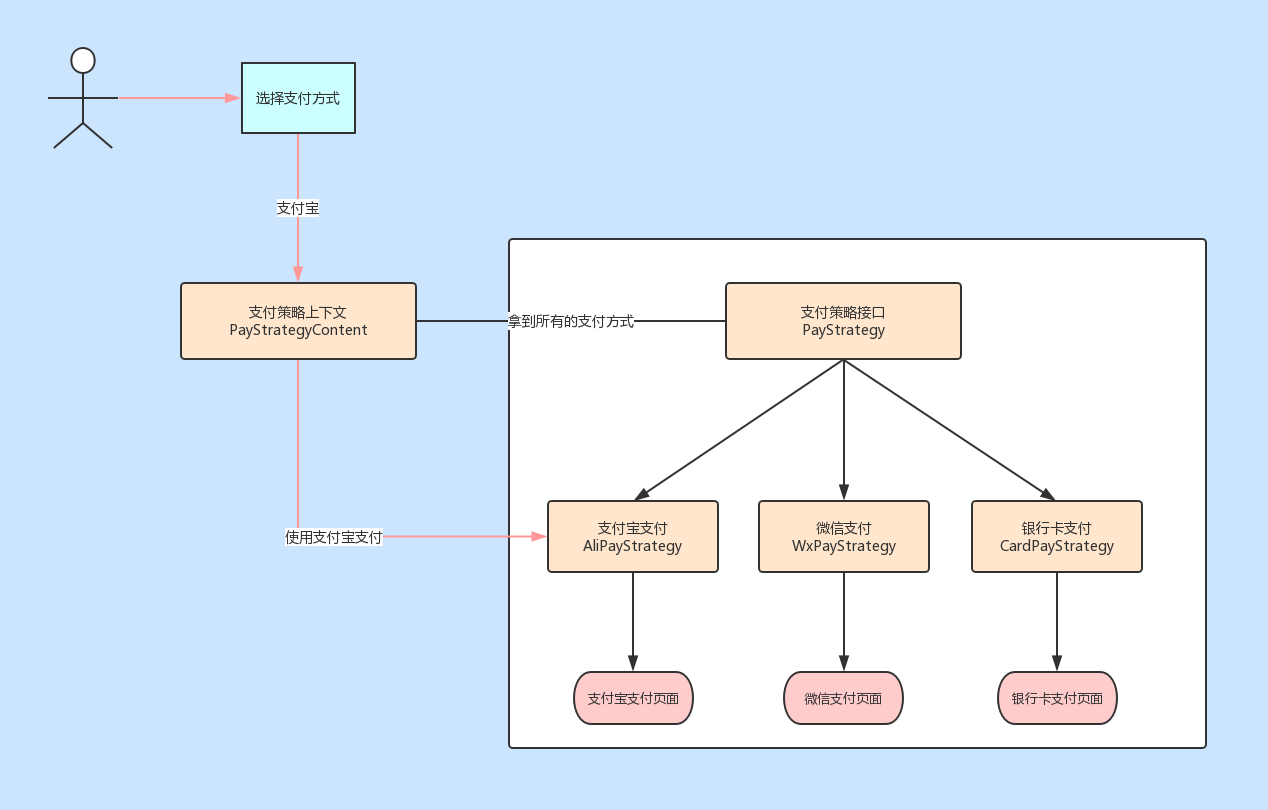
支付策略接口(PayStrategy):定义支付方式
具体支付方式(AliPayStrategy、WxPayStrategy、CardPayStrategy):具体的支付算法
支付策略上下文(PayStrategyContent):管理所有支付方式的引用,并根据用户选择引用对应的支付方式。
代码实现
支付策略接口(PayStrategy)
1 /**
2 * 支付策略接口
3 * @author JinXing
4 * @date 2019/7/12 13:58
5 */
6 public interface PayStrategy {
7
8
9
10 /**
11 *
12 * 选择支付方式
13 * 支付宝
14 * 微信
15 * 银行卡
16 * @return RemoteResult
17 */
18 RemoteResult<String> toPayHtml();
19
20
21 }
具体支付方式(AliPayStrategy)
1 /**
2 * 阿里pay
3 * @author JinXing
4 * @date 2019/7/12 14:36
5 */
6 @Service
7 public class AliPayStrategy implements PayStrategy {
8
9 @Override
10 public RemoteResult<String> toPayHtml() {
11
12 System.out.println("现在采用的支付方式为:支付宝支付......");
13
14 return null;
15 }
16 }
具体支付方式(WxPayStrategy)
1 /**
2 * 微信支付
3 * @author JinXing
4 * @date 2019/7/12 14:36
5 */
6
7 @Service
8 public class WxPayStrategy implements PayStrategy {
9
10 @Override
11 public RemoteResult<String> toPayHtml() {
12
13 System.out.println("现在采用的支付方式为:微信支付......");
14
15 return null;
16 }
17 }
具体支付方式(CardPayStrategy)
1 /**
2 * 银行卡支付
3 * @author JinXing
4 * @date 2019/7/12 14:36
5 */
6
7 @Service
8 public class CardPayStrategy implements PayStrategy {
9
10 @Override
11 public RemoteResult<String> toPayHtml() {
12
13 System.out.println("现在采用的支付方式为:银行卡支付......");
14
15 return null;
16 }
17 }
支付策略上下文(PayStrategyContent)
/**
* 支付策略上下文
* @author JinXing
* @date 2019/7/12 14:39
*/
@Component
public class PayStrategyContent {
/** 策略实例集合 */
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, PayStrategy> strategyMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(20);
/**
* 注入策略实例
* 如果使用的是构造器注入,可能会有多个参数注入进来。
*
* 如果使用的是field反射注入
*
* 如果使用的是setter方法注入,那么你将不能将属性设置为final。
*
* @param strategyMap
* 注意注入类型要是Map基础类型
*/
@Autowired
public PayStrategyContent(Map<String, PayStrategy> strategyMap) {
//清空集合数据
this.strategyMap.clear();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(strategyMap)) {
strategyMap.forEach((beanName, payStrategy) -> {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(beanName) || payStrategy == null) {
return;
}
this.strategyMap.put(beanName.toLowerCase(), payStrategy);
});
}
}
/**
* 选择支付方式
* 支付宝、微信、银行卡
*
* @param paymentEnums
*
* @return RemoteResult
*/
RemoteResult<String> toPayHtml(PaymentEnums paymentEnums) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(strategyMap)) {
return new RemoteResult<String>().error("策略实例集合初始化失败,请检查是否正确注入!");
}
return this.strategyMap.get(paymentEnums.getBeanName()).toPayHtml();
}
}
支付方式枚举(PaymentEnums)
1 /** 2 * 支付方式枚举对象 3 * code -> 支付方式别名 4 * beanName -> 实例的名称 5 * 6 * @author JinXing 7 * @date 2019/7/12 14:40 8 */ 9 public enum PaymentEnums { 10 11 /** 支付方式 */ 12 ALI_PAY("ali_pay", AliPayStrategy.class.getSimpleName()), 13 WX_PAY("WX_PAY", WxPayStrategy.class.getSimpleName()), 14 CARD_PAY("card_pay", CardPayStrategy.class.getSimpleName()), 15 16 ; 17 18 /** 枚举定义+描述 */ 19 private String code; 20 private String beanName; 21 22 PaymentEnums(String code, String beanName) { 23 this.code = code; 24 this.beanName = StringUtils.isNotEmpty(beanName)?beanName.toLowerCase():null; 25 } 26 27 28 /** 根据code获取对应的枚举对象 */ 29 public static PaymentEnums getEnum(String code) { 30 PaymentEnums[] values = PaymentEnums.values(); 31 if (null != code && values.length > 0) { 32 for (PaymentEnums value : values) { 33 if (value.code.equals(code)) { 34 return value; 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 return null; 39 } 40 41 /** 该code在枚举列表code属性是否存在 */ 42 public static boolean containsCode(String code) { 43 PaymentEnums anEnum = getEnum(code); 44 return anEnum != null; 45 } 46 47 /** 判断code与枚举中的code是否相同 */ 48 public static boolean equals(String code, PaymentEnums calendarSourceEnum) { 49 return calendarSourceEnum.code.equals(code); 50 } 51 52 53 public String getCode() { 54 return code; 55 } 56 57 public String getBeanName() { 58 return beanName; 59 } 60 }
结果集包装类(RemoteResult)
1 /**
2 * <pre>
3 * 远程接口值对象,此对象使用说明
4 * 使用时,判断isSuccess返回值,true表示业务成功、false表示接口调用失败
5 * errorCode,用于判断失败原因(非系统错误),系统预设错误码,用负数表示:-1表示参数不合法,用户自定义错误码使用正数表示,0表示无错误
6 * </pre>
7 *
8 * @author jx
9 * @param <T>
10 */
11
12
13 public class RemoteResult<T> implements Serializable {
14
15 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
16 /** 接口调用是否成功(业务),系统错误、业务失败都将返回false */
17 private boolean isSuccess = true;
18 /** 自定义错误信息,发生可处理错误时,返回自定义信息 */
19 private String errorMsg = "ok";
20 /** 接口返回结果(Void表示无返回值) */
21 private T result;
22 /** 异常堆栈信息,需要提供调试功能时,将异常加入此堆栈中,便于协调调用方调试,仅作调试用 */
23 private Exception exceptionStack;
24
25 public RemoteResult() {
26 }
27
28 public RemoteResult<T> error(String errorMsg) {
29 this.errorMsg = errorMsg;
30 this.isSuccess = false;
31 return this;
32 }
33
34 public static long getSerialVersionUID() {
35 return serialVersionUID;
36 }
37
38 public boolean isSuccess() {
39 return isSuccess;
40 }
41
42 public void setSuccess(boolean success) {
43 isSuccess = success;
44 }
45
46 public String getErrorMsg() {
47 return errorMsg;
48 }
49
50 public void setErrorMsg(String errorMsg) {
51 this.errorMsg = errorMsg;
52 }
53
54 public T getResult() {
55 return result;
56 }
57
58 public void setResult(T result) {
59 this.result = result;
60 }
61
62 public Exception getExceptionStack() {
63 return exceptionStack;
64 }
65
66 public void setExceptionStack(Exception exceptionStack) {
67 this.exceptionStack = exceptionStack;
68 }
69
70 }