面试题海量数据处理经常出现BitMap,所以记一下笔记
1. BitMap
BitMap也称为位图,其原理和布隆过滤器类似,其基本原理都是使用位数组及其下标来表示某些元素是否存在,其在处理大量数据的排序、查询、去重,以及在用户群做交集和并集运算的时候也有极大的便利
假如我们要将 {5,6,1,10} 进行排序,利用位图思想的话:(这里并不是真实原理,是个假设)
- 遍历找出或预计最大元素值
- 然后创建最大元素值大小的位数组(比如上例就创建大小为10的位数组)
- 最后遍历数据,每遇到一个元素则在对应的位数组置1
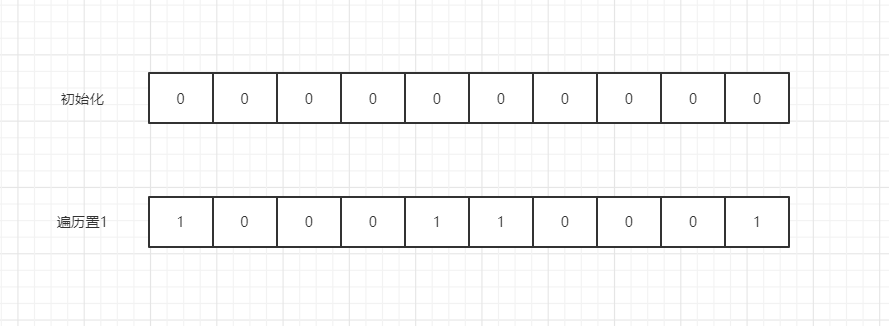
其时间复杂度为O(N),比一般的排序算法都快
且空间利用率高,在普通情况下10亿个整数占用空间3.8G,而位图占用120MB左右
2. 实际操作
我们使用 byte[] arr = new byte[max]数组来模拟位数组:
- 一个 byte占用8bit,那么可以表示 0~7 的数
- byte[10] 占用80bit,那么可以表示 0~79的数
- 根据上两条,那么 8这个数是在 byte[1] 里面存放的
那么我们可以总结出:若最大数为N,那么需要创建数组大小为 byte[ N / 8+ 1]
找出某数 n对应的整型数组下标:n / 8 == n >> 3
在具体整型下标中,找出的位下标:n % 8 == n & 0x07
综合起来的Java实现就是
public class BitMap {
private byte[] data;
private int capacity;
public BitMap(int cacapacity){ // 还可以做个扩容机制?
this.capacity = cacapacity;
data = new byte[ (cacapacity >> 3) + 1];
}
public void add(int num){
int arrayIndex = num >> 3; // /8
int position = num & 0x07; // %8
// 左移表示将1向左移动几位,加上小端存储,即可占用对应位了
data[arrayIndex] |= 1 << position;
}
public boolean contain(int num){
int arrayIndex = num >> 3;
int position = num & 0x07;
return ( data[arrayIndex] & (1 << position) ) != 0;
}
public void clear(int num){
int arrayIndex = num >> 3;
int position = num & 0x07;
data[arrayIndex] &= ~(1 << position);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BitMap bitmap = new BitMap(100);
bitmap.add(10);
System.out.println("是否存在10:"+ bitmap.contain(10));
bitmap.clear(10);
System.out.println("是否存在10:" + bitmap.contain(10));
}
}