简单的权限(拦截)管理
-
给特定的用户以不同的权限来访问不同的资源
-
很多人把权限模型理解为 用户—权限,这样不是不可以,是不够好。因为如果有100个用户,20个权限呢?给每个用户单独一个个设置不太现实,所以这时候就要加入另一个模块(角色),结构模型如下:
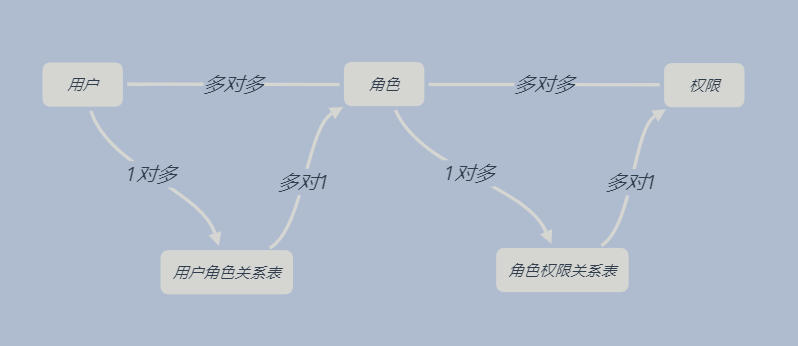
1. 建5张表
用户
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`username` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
角色
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`description` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
权限
CREATE TABLE `privilege` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`description` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
用户角色关系表
CREATE TABLE `user_role` (
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`role_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`,`role_id`),
CONSTRAINT `role_id_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`role_id`) REFERENCES `role` (`id`),
CONSTRAINT `user_id_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `user` (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
角色权限关系表(外键不能重名)
CREATE TABLE `role_privilege` (
`role_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`privilege_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`role_id`,`privilege_id`),
CONSTRAINT `privilege_id_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`privilege_id`) REFERENCES `privilege` (`id`),
CONSTRAINT `role_id_fk1` FOREIGN KEY (`role_id`) REFERENCES `role` (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
查询用户的所有角色
SELECT * FROM role WHERE id IN (SELECT role_id FROM user_role WHERE user_id=1);
查询角色的所有权限
SELECT * FROM privilege WHERE id IN (SELECT privilege_id FROM role_privilege WHERE role_id=1);
查询用户的所有权限
SELECT * FROM privilege WHERE id IN (SELECT DISTINCT privilege_id FROM role_privilege WHERE role_id IN (SELECT role_id FROM user_role WHERE user_id=1));
2. Bean对象
Privilege
public class Privilege {
int id;
String name;
String description;
public Privilege(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//getters和setters
}
3. Dao层(这里只写获取全部权限)
public class PrivilegeDao {
public HashSet<Privilege> getAllPrivilege(String user_id) {
//各种逻辑操作
return Privileges;
}
}
4. 拦截功能
- 使用contains()方法需要在权限类上重写hashCode()和equals()方法的。因为我们比较的是字符串。
public class PermissionInterception implements Filter {
//存放需要权限的资源地址
private Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
map.put("/addServlet", new Privilege("增加"));
map.put("/deleteServlet", new Privilege("删除"));
map.put("/updateServlet", new Privilege("修改"));
map.put("/findServlet", new Privilege("查账单"));
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;
//获取请求地址
String uri = httpServletRequest.getRequestURI();
//公开地址,直接放行
if (map.get(uri) == null) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return ;
}
//需要权限的地址,即要先登录
if (httpServletRequest.getSession().getAttribute("user") == null) {
httpServletResponse.sendRedirect("/login.html");
return;
}
//查询用户的所有权限,返回一个权限集合
PrivilegeService privilegeService = new PrivilegeService();
int user_id = (int) httpServletRequest.getSession().getAttribute("user_id");
HashSet privileges = privilegeService.getAllPrivilege(user_id);
//是否拥有访问该地址的权限
if (!privileges.contains(map.get(uri))) {
httpServletResponse.sendRedirect("/404.html");
return ;
}
//通过权限认证,放行
chain.doFilter(httpServletRequest, httpServletResponse);
}
public void destroy() {
}
}
参考Java3y