Android四大组件(Activity,service,broadcast,Content Provider)跨进程通信相信在android项目中进程用到,此处将一一做以说明以及总结.
1.简括:
首先需要看四大组件都继承了什么,实现了什么,也就知道了它们的用途以及作用.
public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper implements LayoutInflater.Factory2,
Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks2,
Window.OnWindowDismissedCallback, WindowControllerCallback,AutofillManager.AutofillClient
public abstract class Service extends ContextWrapper implements ComponentCallbacks2
*****public class ContextThemeWrapper extends ContextWrapper
从activity和service看出来,它们都继承自context实现不同的接口,实现决定了它们的功能.
2.Activity:界面显示组件,且实现了很多Ui交互接口.
(1)不同app跨进程调用主要通过startActivity. eg:OneMainActivity调用AnotherMainActivity.下面只做简单说明.需要运行验证的可以copy代码进行运行校验.
package com.example.oneactivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.util.Log; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; public class OneMainActivity extends Activity { Button button; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_one_main); button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button); button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction("com.ysfl.otherActivity");//此处设置需要起动app的action. Log.d(this.getClass().getName(),"I'm OneMainActivity onclick to start anotherActivity"); startActivity(intent);//跨进程调用其它应用 } }); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_one_main, menu); return true; } @Override protected void onPause(){ super.onPause(); Log.d(this.getClass().getName(),"I'm OneMainActivity onPause"); } @Override protected void onStop(){ super.onStop(); Log.d(this.getClass().getName(),"I'm OneMainActivity onStop"); } @Override protected void onDestroy(){ super.onDestroy(); Log.d(this.getClass().getName(),"I'm OneMainActivity onDestroy"); } }
OneMainActivity的xml文件不做说明,它只是一个简单的配置.AnotherMainActivity的代码和配置文件如下.
package com.example.anotheractivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.util.Log; import android.view.Menu; import android.widget.Toast; public class AnotherMainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_another_main); Log.d(this.getClass().getName(),"I'm AnotherMainActivity onCreate"); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_another_main, menu); return true; } @Override protected void onPause(){ super.onPause(); Log.d(this.getClass().getName(),"I'm AnotherMainActivity onPause"); } @Override protected void onStop(){ super.onStop(); Log.d(this.getClass().getName(),"I'm AnotherMainActivity onStop"); } @Override protected void onDestroy(){ super.onDestroy(); Log.d(this.getClass().getName(),"I'm AnotherMainActivity onDestroy"); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.anotheractivity" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="17" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name="com.example.anotheractivity.AnotherMainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter>
<!-- 此处的action是其它应用需要起动的action --> <action android:name="com.ysfl.otherActivity" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
运行结果如下图:
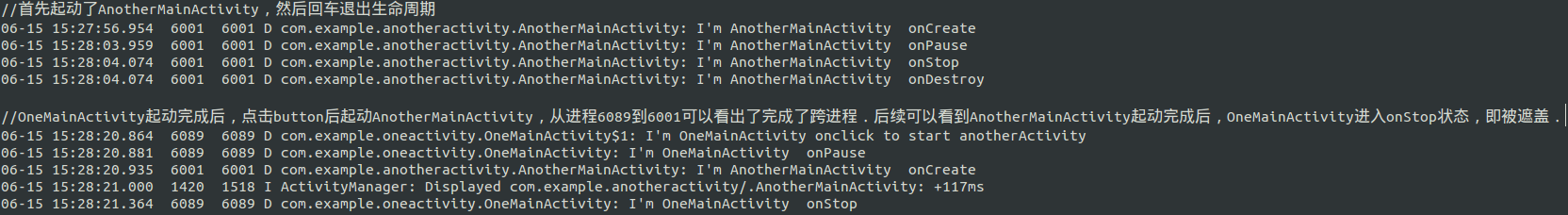
3.Service
(1)activity到service跨进程有两种方式:startService和bindService
a.startService单向传递数据
b.bindService可通过binder实现数据的交互以及监听。
(2)service生命周期如下:
startService:onCreate()->onStartCommand()-----service running -----onDestroy()
bindService:onCreate()->onBind()----------service running -------onUnbind()->onDestroy()
service总结:当service已经被oncreate后,就不会再次oncreate,因为service只有一个,不会被重复创建.当被bind后也不会进行再次bind,此时binder已经存在于缓存区.
(3)关于activity跨进程调用service的例子可以直接参考:Android进程间通信-AIDL-经典的Hello World诠释
后续待续..........