1、语法介绍:与java很相近,可以认为就是java。
2、运行命令(linux):
processing-java --output=/tmp/processing-xx --run --force --sketch={问存在路径}
3、sketch:
每个sketch(草稿)就是保存在电脑相应文件夹中的,存放有相关processing代码的文件,后缀为:pde以及影音文件(另外存放在data文件夹中)。
4、变量:
1)、区分大小写。
2)、类型包括:整形(int),浮点型(float),字符串(String),布尔型(boolean)
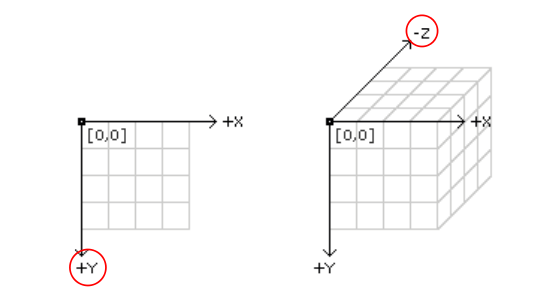
5、坐标(Coordinates):
x轴向右渐增,y轴向右渐增,z轴向外渐增。

// Sets the screen to be 640 pixels wide and 360 pixels high 窗口大小 size(640, 360); // Set the background to black and turn off the fill color背景颜色 background(0); noFill(); // The two parameters of the point() method each specify coordinates. // The first parameter is the x-coordinate and the second is the Y stroke(255);//画笔颜色 point(width * 0.5, height * 0.5); point(width * 0.5, height * 0.25); // Coordinates are used for drawing all shapes, not just points. // Parameters for different functions are used for different purposes. // For example, the first two parameters to line() specify // the coordinates of the first endpoint and the second two parameters // specify the second endpoint stroke(0, 153, 255); line(0, height*0.33, width, height*0.33); // By default, the first two parameters to rect() are the // coordinates of the upper-left corner and the second pair // is the width and height stroke(255, 153, 0); rect(width*0.25, height*0.1, width * 0.5, height * 0.8);//矩形
6、判断:
< == > != >= <= && || !
7、类:
Object 和 class
8、3D:
pushMatrix();
translate(width/2,height/2);
rotateX(1);
box(150);
popMatrix();
lights();//在draw里面调用即可。
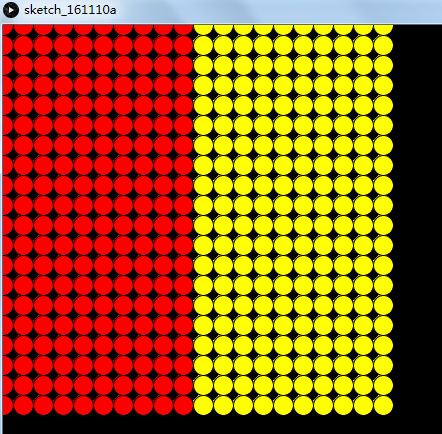
9、循环:
void setup(){ size(600,600); background(0); } void draw(){ for (int i=0;i<20;i++){ for (int j=0;j<20;j++){ if(i<10){ fill(255,0,0); }else{ fill(255,255,0); } ellipse(i*20,j*20,20,20); } } }
10、函数
函数可以写在函数里面:
Ball myBall; void setup(){ size(600,600); background(0); myBall = new Ball(500,100); } void draw(){ myBall.display(); } class Ball{ int x= 500; int y= 500; //construct Ball(int x, int y){ this.x = x; this.y = y; } void display(){ ellipse(x,y,20,20); } }

11、Ball bounce and graity 跳跃和重力
//When the shape hits the edge of the window, it reverses its direction. int rad = 60; // Width of the shape float xpos, ypos; // Starting position of shape float xspeed = 2.8; // Speed of the shape float yspeed = 2.2; // Speed of the shape int xdirection = 1; // Left or Right int ydirection = 1; // Top to Bottom void setup() { size(640, 360); noStroke(); frameRate(30); ellipseMode(RADIUS); // Set the starting position of the shape xpos = width/2; ypos = height/2; } void draw() { background(102); // Update the position of the shape xpos = xpos + ( xspeed * xdirection ); ypos = ypos + ( yspeed * ydirection ); // Test to see if the shape exceeds the boundaries of the screen // If it does, reverse its direction by multiplying by -1 if (xpos > width-rad || xpos < rad) { xdirection *= -1; } if (ypos > height-rad || ypos < rad) { ydirection *= -1; } // Draw the shape ellipse(xpos, ypos, rad, rad); }

12、数组
myBalls = new Ball[100];
for(int i=0;i<myBalls.length;i++){
myBalls[i] = new Ball(xpos,ypos);
}
13、ArrayList
ArrayList myList;
mylist.add(new Ball(200,200));
mylist.size();
mylist.get(1);
14、声明和注解

// The size function is a statement that tells the computer // how large to make the window. // Each function statement has zero or more parameters. // Parameters are data passed into the function // and are used as values for telling the computer what to do. size(640, 360); // The background function is a statement that tells the computer // which color (or gray value) to make the background of the display window background(204, 153, 0);
15、setup & draw

int y = 100; // The statements in the setup() function // execute once when the program begins //只执行一次 void setup() { size(640, 360); // Size must be the first statement stroke(255); // Set line drawing color to white frameRate(30); //帧率 } // The statements in draw() are executed until the // program is stopped. Each statement is executed in // sequence and after the last line is read, the first // line is executed again.//一直执行直到程序停止,每一个变量以队列的方式被读取来执行,直到最后一个,然后又去执行第一个。 void draw() { background(0); // Clear the screen with a black background y = y - 1; if (y < 0) { y = height; } line(0, y, width, y); }
16、No Loop:让draw()方法只执行一次。

float y; // The statements in the setup() function // execute once when the program begins void setup() { size(640, 360); // Size should be the first statement stroke(255); // Set line drawing color to white noLoop(); y = height * 0.5; } // The statements in draw() are executed until the // program is stopped. Each statement is executed in // sequence and after the last line is read, the first // line is executed again. void draw() { background(0); // Set the background to black y = y - 1; if (y < 0) { y = height; } line(0, y, width, y); }
17、Loop:让draw()方法持续执行。下面列子:在鼠标点击是让draw()持续执行:
float y = 100; // The statements in the setup() function // run once when the program begins void setup() { size(640, 360); // Size should be the first statement stroke(255); // Set stroke color to white noLoop(); y = height * 0.5; } // The statements in draw() are run until the // program is stopped. Each statement is run in // sequence and after the last line is read, the first // line is run again. void draw() { background(0); // Set the background to black line(0, y, width, y); y = y - 1; if (y < 0) { y = height; } } void mousePressed() { loop(); }
18、Redraw:让draw()执行一次。下面列子:当鼠标点击时,执行draw():
float y; // The statements in the setup() function // execute once when the program begins void setup() { size(640, 360); // Size should be the first statement stroke(255); // Set line drawing color to white noLoop(); y = height * 0.5; } // The statements in draw() are executed until the // program is stopped. Each statement is executed in // sequence and after the last line is read, the first // line is executed again. void draw() { background(0); // Set the background to black y = y - 4; if (y < 0) { y = height; } line(0, y, width, y); } void mousePressed() { redraw(); }
19、方法调用:

void setup() { size(640, 360); background(51); noStroke(); noLoop(); } void draw() { drawTarget(width*0.25, height*0.4, 200, 4); drawTarget(width*0.5, height*0.5, 300, 10); drawTarget(width*0.75, height*0.3, 120, 6); } void drawTarget(float xloc, float yloc, int size, int num) { float grayvalues = 255/num; float steps = size/num; for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { fill(i*grayvalues); ellipse(xloc, yloc, size - i*steps, size - i*steps); } }
20、Recursion (递归):

void setup() { size(640, 360); noStroke(); noLoop(); } void draw() { drawCircle(width/2, 280, 6); } void drawCircle(int x, int radius, int level) { float tt = 126 * level/4.0; fill(tt); ellipse(x, height/2, radius*2, radius*2); if(level > 1) { level = level - 1; drawCircle(x - radius/2, radius/2, level); drawCircle(x + radius/2, radius/2, level); } }
21、Create Graphics.(画图):

PGraphics pg; void setup() { size(640, 360); pg = createGraphics(400, 200); } void draw() { fill(0, 12); rect(0, 0, width, height); fill(255); noStroke(); ellipse(mouseX, mouseY, 60, 60); pg.beginDraw(); pg.background(51); pg.noFill(); pg.stroke(255); pg.ellipse(mouseX-120, mouseY-60, 60, 60); pg.endDraw(); // Draw the offscreen buffer to the screen with image() image(pg, 120, 60); }
