Kickdown
Description
A research
laboratory of a world-leading automobile company has received an order to create a special transmission mechanism, which allows for incredibly efficient kickdown -- an operation of switching to lower gear. After several months of research engineers found that
the most efficient solution requires special gears with teeth and cavities placed non-uniformly. They calculated the optimal flanks of the gears. Now they want to perform some experiments to prove their findings.
The
first phase of the experiment is done with planar toothed sections, not round-shaped gears. A section of length n consists
of n units. The unit is either a cavity of height h or a tooth of height 2h . Two sections are required for the experiment: one to emulate master gear
(with teeth at the bottom) and one for the driven gear (with teeth at the top).
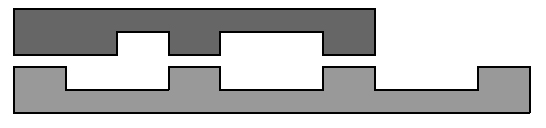
There
is a long stripe of width 3h in the laboratory and its length is enough for cutting two engaged sections
together. The sections are irregular but they may still be put together if shifted along each other.
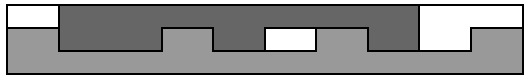
The stripe is made of an expensive alloy, so the engineers want to use as little of it as possible. You need to find the minimal length of the stripe which is enough for cutting both sections simultaneously.
Input
The input file contains several test cases, each of them as described below.There are two lines in the input, each contains a string to describe a section. The first line describes master section (teeth at the bottom) and the second line describes driven section (teeth at the top). Each character in a string represents one section unit -- 1 for a cavity and 2 for a tooth. The sections can not be flipped or rotated.Each string is non-empty and its length does not exceed 100.
Output
For each test case, write to the output a line containing a single integer number -- the minimal length of the stripe required to cut off given sections.
Sample Input
2112112112
2212112
12121212
21212121
2211221122
21212
Sample Output
10
8
15
分别将第二个长条往右移动求容器长度,第一个长条往右移动求容器长度;
最后输出最小值。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char s[105], t[105];
int len1, len2, len;
while(cin>>s>>t)
{
int i, j, x, y;
int len1 = strlen(s), len2 = strlen(t);
for( i=0; i<len1; i++ )
{
bool flag = true;
for( j=0; j<len2 && j+i<len1 ; j++ )
if(s[i+j]=='2'&&t[j]=='2')
{flag = false; break;}
if(flag)
break;
}
x = max(len1, len2+i);
i = j = 0;
for( i=0; i<len2; i++ )
{
bool flag = true;
for( j=0; j<len1 && j+i<len2; j++ )
if(t[i+j]=='2'&&s[j]=='2')
{flag = false; break ;}
if(flag)
break;
}
y = max(len2, len1+i);
cout<<min(x,y)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}